
Statistical Summary of
Commercial Jet
Airplane Accidents
Worldwide Operations | 1959‑2023
August 2024

The Boeing Company
2023 Statistical
Summary
2
Contents
Leadership Message
2023 Statistical Summary
2023 Airplane Accidents
Accident Summaries
and Rates
CAST/ICAO Common
Taxonomy Team Aviation
Occurence Categories
Fatalities
Regional Statistics
About This Document
Definitions and Terms
Leadership Message 3
2023 Statistical Summary 4
2023 Airplane Accidents 5
Accident Rate and Departure Trends by Decade 6
Accident Summary by Injury and Damage 7
Departures, Flight-Hours and Jet Airplanes in Service 8
Accident Summary by Type of Operation 9
Accident Rates and Onboard Fatalities by Year 10
Accident Rates by Airplane Type 11
CAST/ICAO Common Taxonomy Team Aviation Occurrence Categories 12
Fatalities by CICTT Aviation Occurrence Categories 13
Fatal Accidents and Fatalities by Phase of Flight 14
Regional Statistics 15
Asia and Pacific (APAC) 16
Eastern and Southern Africa (ESAF) 17
Europe and North Atlantic (EUR/NAT) 18
Middle East (MID) 19
North America, Central America and Caribbean (NACC) 20
South America (SAM) 21
Western and Central Africa (WACAF) 22
About This Document 24
Definitions 25
Boeing Terms 29
Referenced ICAO and NTSB Definitions 30
Table of Contents
For any inquiries, contact STAT[email protected].

The Boeing Company
2023 Statistical
Summary
3
In 2023, there were no recorded fatalities among the airplane operations that Boeing tracks for this Statistical
Summary of Commercial Jet Airplane Accidents – a first since we started collecting data in 1959.
This report – our 55th annual – shows that accident rates continue to decline to historic lows, despite air trac
nearly returning to pre-pandemic levels. Total accident numbers are also declining, in addition to accident rates.
For example, over the last two decades, we’ve seen total accidents drop by about 30%; hull losses drop by nearly
50%; and fatal accidents drop by 60%.
2023 was one of the safest years on record. But when it comes to the safety of air travel, we know – as an
industry and as a company – that we can never be complacent.
That stark reminder happened in January 2024, when a door plug departed the left side of a 737-9. Thankfully,
the skilled pilots and cabin crew brought the airplane and everyone on board safely back to the ground.
Boeing took immediate containment actions to ensure the safety and quality of our 737-9s. We then developed
and have been implementing a comprehensive plan to strengthen our safety management, quality assurance and
safety culture, based on extensive feedback from our regulator, employees, customers and independent experts.
By listening and learning, we’ve made improvements, including better training for our employees, broader use
of our Safety Management System, and stronger encouragement for employee reporting of product safety and
quality hazards.
While we remain focused on these eorts and more, we are also continuing our engagement with customers,
regulators and other stakeholders around the globe. The demand for air travel continues to grow, as do our
industry eorts to ensure it remains the safest form of transportation.
Boeing teams have engaged more than 200 airline operators in supporting, developing and implementing
solutions that further strengthen the safety of the global air transportation system. We’re also taking in
operational data from the fleet to evaluate the assumptions made during initial aircraft design, address any
risks associated with outdated assumptions and inform future designs.
It takes transparency, collaboration and humility in our never-ending drive to prevent aviation accidents.
At Boeing, we remain committed to doing our part along this journey.
Elisabeth Martin
Vice President, Enterprise Safety and Mission Assurance
Product and Services Safety
Leadership Message
Contents
Leadership Message
2023 Statistical Summary
2023 Airplane Accidents
Accident Summaries
and Rates
CAST/ICAO Common
Taxonomy Team Aviation
Occurence Categories
Fatalities
Regional Statistics
About This Document
Definitions and Terms

The Boeing Company
2023 Statistical
Summary
4
This is the 55th edition of the Boeing Statistical
Summary of Commercial Jet Airplane Accidents,
which has been published by the company every
year since 1969. The annual report provides data
and statistical analysis to yield key insights into the
safety of commercial air travel worldwide.
The information contained in this report can be
used by the aviation industry to identify global
trends and opportunities to advance safety.
The findings underscore the importance of the
industry’s continuous pursuit of new levels of safety
in order to prevent accidents, injury or loss of life.
2023 Statistical Summary
Contents
Leadership Message
2023 Statistical Summary
2023 Airplane Accidents
Accident Summaries
and Rates
CAST/ICAO Common
Taxonomy Team Aviation
Occurence Categories
Fatalities
Regional Statistics
About This Document
Definitions and Terms

The Boeing Company
2023 Statistical
Summary
5
Event
Date
Airline
Model
(Age in
Years)
Type of
Operation
Accident
Location
Phase
of Flight
Event Description
Damage
Category
Hull
Loss
Injury
Category
Onboard Fatalities/
Occupants
(External Fatalities)
Major
Accident
1/25/23
All Nippon
Airways
767-300F
(21)
Sched Cargo Tokyo, Japan Taxi
During taxi, the airplane contacted a cargo loading vehicle while turning. The fuselage was damaged. There
were no injuries.
Substantial None
1/29/23 FlyCAA
A320
(14)
Sched Pax
Mbuji-Mayi,
Democratic Republic
of Congo
Initial Climb A portion of the left-hand elevator departed the airplane after takeo. There were no injuries. Substantial None
3/22/23 United Airlines
A320
(17)
Sched Pax
Houston,
United States
Landing
The airplane sustained a tail strike during landing and received substantial damage. The airplane rolled out
without any further incident and taxied to the apron. There were no injuries.
Substantial None
3/24/23
USA Jet
Airlines
MD-88
(32)
Sched Cargo
Saltillo,
Mexico
Landing The airplane sustained substantial damage after a hard landing. There were no injuries. Substantial None
6/28/23 Delta Air Lines
717
(23)
Sched Pax
Charlotte,
United States
Landing
The airplane sustained substantial damage when the nose landing gear did not extend before landing.
There were no injuries.
Substantial None
7/29/23 United Airlines
767-300
(32)
Sched Pax
Houston,
United States
Landing The airplane sustained substantial damage to the upper fuselage skin while landing. There were no injuries. Substantial None
8/3/23 United Airlines
767-300
(22)
Sched Pax
Washington, D.C.,
United States
Landing
After takeo, a landing gear disagree indication occurred. The airplane landed safely after performing an air
turnback. Postflight inspection discovered substantial damage. There were no injuries.
Substantial None
8/20/23 Alaska Airlines
737-800
(15)
Sched Pax
Santa Ana,
United States
Landing
The airplane sustained damage when the left main landing gear collapsed after landing on the runway.
There were no injuries.
Substantial None
9/18/23
DHL
International
Aviation ME
767-300
(24)
Sched Cargo Beirut, Lebanon Landing
The airplane suered substantial damage during a hard landing that caused the fuselage skin to wrinkle.
There were no injuries.
Substantial None
10/4/23 Ryanair
737-800
(13)
Sched Pax
Stansted,
United Kingdom
Taxi
The airplane received substantial damage to the leading edge of the wing after impacting a catering truck
while taxiing. There were no injuries.
Substantial None
10/4/23 FedEx
757-200
(36)
Sched Cargo
Chattanooga,
United States
Landing
The airplane returned to land after the failure of its left hydraulic system. The landing gear failed to extend
and airplane sustained substantial damage during the emergency landing. There were no injuries.
Substantial None
11
Total
Accidents
0 0
Contents
Leadership Message
2023 Statistical Summary
2023 Airplane Accidents
Accident Summaries
and Rates
CAST/ICAO Common
Taxonomy Team Aviation
Occurence Categories
Fatalities
Regional Statistics
About This Document
Definitions and Terms
2023 Airplane Accidents
Worldwide Commercial Jet Fleet

The Boeing Company
2023 Statistical
Summary
6
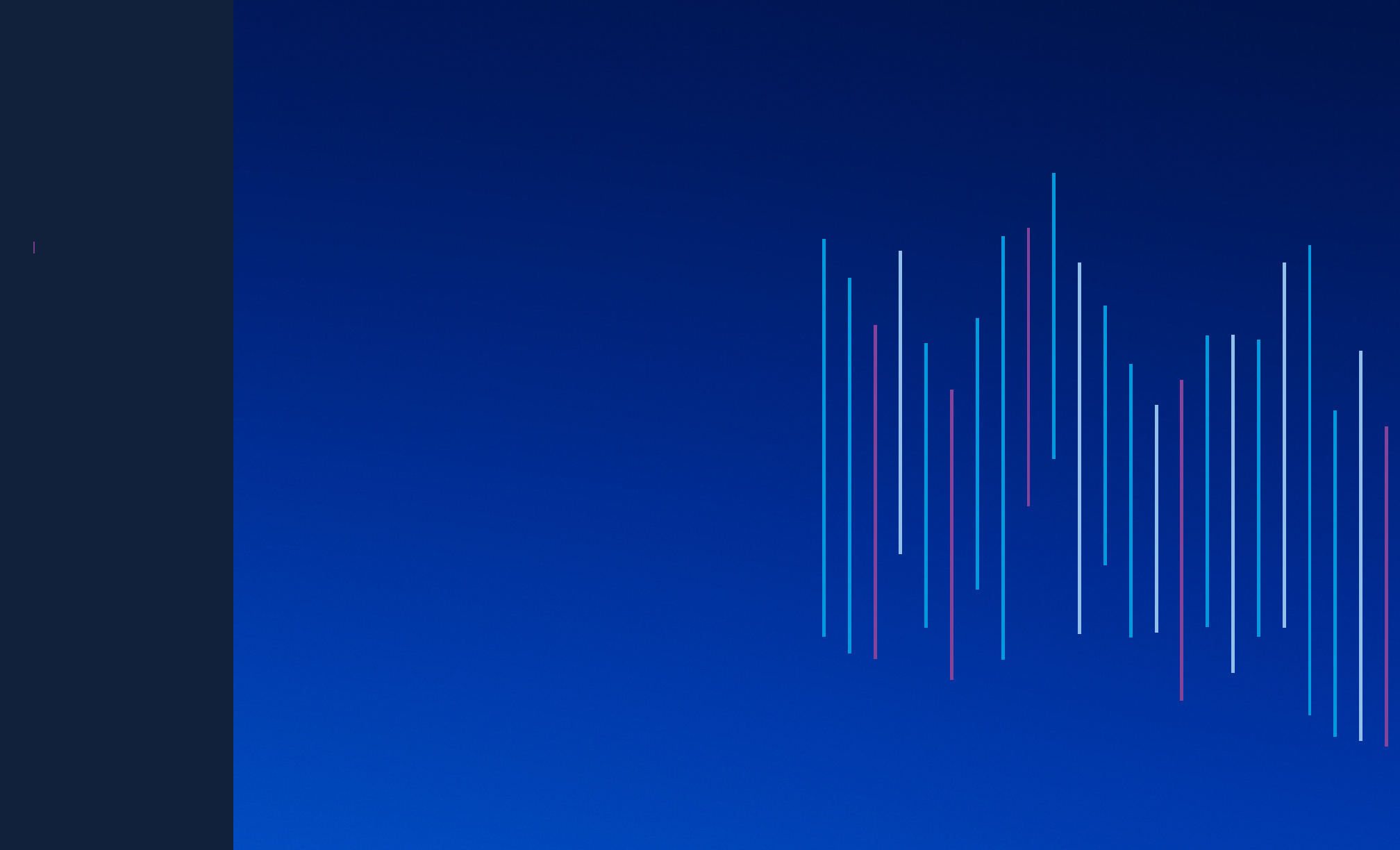
Accident Rate
and Departure
Trends by
Decade
Worldwide Commercial Jet Fleet
1974‑2023
Accident Rates per One Million Departures and Total Departures, Decade View
Over the past five decades, statistics show
that accident rates continue to decline
even though air travel continues to grow
worldwide. Between the last two decades,
data shows the following trends:
• Accident rate: 45% decline
• Hull loss rate: 58% decline
• Fatal accident rate: 68% decline
• Departures: 25% increase
Total accident numbers are also declining,
in addition to accident rates. For example,
between the last two decades, total
accidents dropped by about 30%; hull
losses dropped by nearly 50%; and fatal
accidents dropped by 60%.
Contents
Leadership Message
2023 Statistical Summary
2023 Airplane Accidents
Accident Summaries
and Rates
CAST/ICAO Common
Taxonomy Team Aviation
Occurence Categories
Fatalities
Regional Statistics
About This Document
Definitions and Terms
0
80
160
240
320
400
0
1
2
3
4
5
Departures
All accident rate
Hull loss rate
Fatal accident rate
Departures by Decade (Millions)
Rate per Million Departures
1974-1983 1984-1993 1994-2003 2004-2013 2014-2023

The Boeing Company
2023 Statistical
Summary
7
Accident
Summary by
Injury and
Damage
Worldwide Commercial Jet Fleet
1959‑2023
1,499 Nonfatal accidents
515 with hull loss
897 with substantial damage
87 without substantial damage
635 Fatal accidents
513 with hull loss
28 with substantial damage
94 without substantial damage
251 Nonfatal accidents
67 with hull loss
161 with substantial damage
23 without substantial damage
28 Fatal accidents
20 with hull loss
1 with substantial damage
7 without substantial damage
1959‑2023
2014‑2023
Note: “Hull loss” and the terms here refer to the severity of damage
an airplane incurs from an accident.
Contents
Leadership Message
2023 Statistical Summary
2023 Airplane Accidents
Accident Summaries
and Rates
CAST/ICAO Common
Taxonomy Team Aviation
Occurence Categories
Fatalities
Regional Statistics
About This Document
Definitions and Terms
279
total
accidents
10%
30%
70%
90%
2,134
total
accidents

The Boeing Company
2023 Statistical
Summary
8
Departures,
Flight-Hours
and Jet Airplanes
in Service*
Worldwide Commercial Jet Fleet
2004‑2023
Sources: 2003-2019, Jet Information Services Inc.
2020-2023, Cirium.
*Certified jet airplanes greater than 60,000 pounds (27,216 kilograms) maximum
gross weight, including those in temporary nonflying status and those in use by
non-airline operators. Excluded are commercial airplanes operated in military
service and CIS/USSR/PRC-manufactured airplanes.
71.5 million flight‑hours
1,814 million flight-hours
logged since 1959. 65%
of total hours logged were
on Boeing flights. (1,179
million on Boeing airplanes)
29,061
total airplanes
13,587
Boeing airplanes
31.3 million departures
932 million departures
since 1959. 64% of those
departures were on Boeing
airplanes. (597 million on
Boeing airplanes)
Commercial Airplanes in Service (thousands)
Worldwide fleet Boeing fleet
Departure and Flight-Hours (millions)
Flight-hours
Departures
10
5
0
15
20
25
30
2019
2020
2021
2018
2017
2016
2015
2014
2013
2012
2011
2010
2009
2008
2007
2006
2005
2004
2022
2023
Over the past 20 years, the statistics show
a growing trend in the gap between total
number of departures and total flight-hours.
In 2023, passenger trac continued to
rebound worldwide and nearly returned
to pre-pandemic numbers. The worldwide
airplane fleet and commercial air trac are
expected to continue to grow over the next
two decades.
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
2020
2021
2022
2019
2018
2017
2016
2015
2014
2013
2012
2011
2010
2009
2008
2007
2006
2005
2004
2023
Contents
Leadership Message
2023 Statistical Summary
2023 Airplane Accidents
Accident Summaries
and Rates
CAST/ICAO Common
Taxonomy Team Aviation
Occurence Categories
Fatalities
Regional Statistics
About This Document
Definitions and Terms

The Boeing Company
2023 Statistical
Summary
9
Accident
Summary by
Type of
Operation
Worldwide Commercial Jet Fleet
1959‑2023
*External fatalities include on-ground fatalities as well as fatalities on other aircraft involved.
Type of Operation All Accidents Fatal Accidents Onboard Fatalities
(External Fatalities)*
Hull Loss Accidents
1959-2023 2014-2023 1959-2023 2014-2023 1959-2023 2014-2023 1959-2023 2014-2023
Passenger 1,704 230 510 24 29,643
(810)
1,066
(19)
757 63
– Scheduled 1,580 226 463 23 25,446
(806)
995
(19)
686 62
– Charter 124 4 47 1 4,197
(4)
71
(0)
71 1
Cargo 308 47 83 4 285
(385)
12
(43)
197 22
Maintenance test
ferry, positioning,
training and
demonstration
122 2 42 0 190
(66)
0
(0)
74 2
Totals Totals 2,134 279 635 28 30,118
(1, 261)
1,078
(62)
1,028 87
Contents
Leadership Message
2023 Statistical Summary
2023 Airplane Accidents
Accident Summaries
and Rates
CAST/ICAO Common
Taxonomy Team Aviation
Occurence Categories
Fatalities
Regional Statistics
About This Document
Definitions and Terms
The Boeing Company
2023 Statistical
Summary
10
Accident Rates
and Onboard
Fatalities
by Year
Worldwide Commercial Jet Fleet
1959‑2023
Accident Rates and Onboard Fatalities per One Million Departures
Contents
Leadership Message
2023 Statistical Summary
2023 Airplane Accidents
Accident Summaries
and Rates
CAST/ICAO Common
Taxonomy Team Aviation
Occurence Categories
Fatalities
Regional Statistics
About This Document
Definitions and Terms
0
300
600
900
1,200
1,500
0
10
20
30
40
50
2016
2014
2012
2010
2008
2006
2002
2004
1998
2000
1994
1996
1990
1992
1986
1988
1982
2020
2022
2018
1974
1970
1966
1962
1976
1972
1968
1964
1960
1978
1984
1980
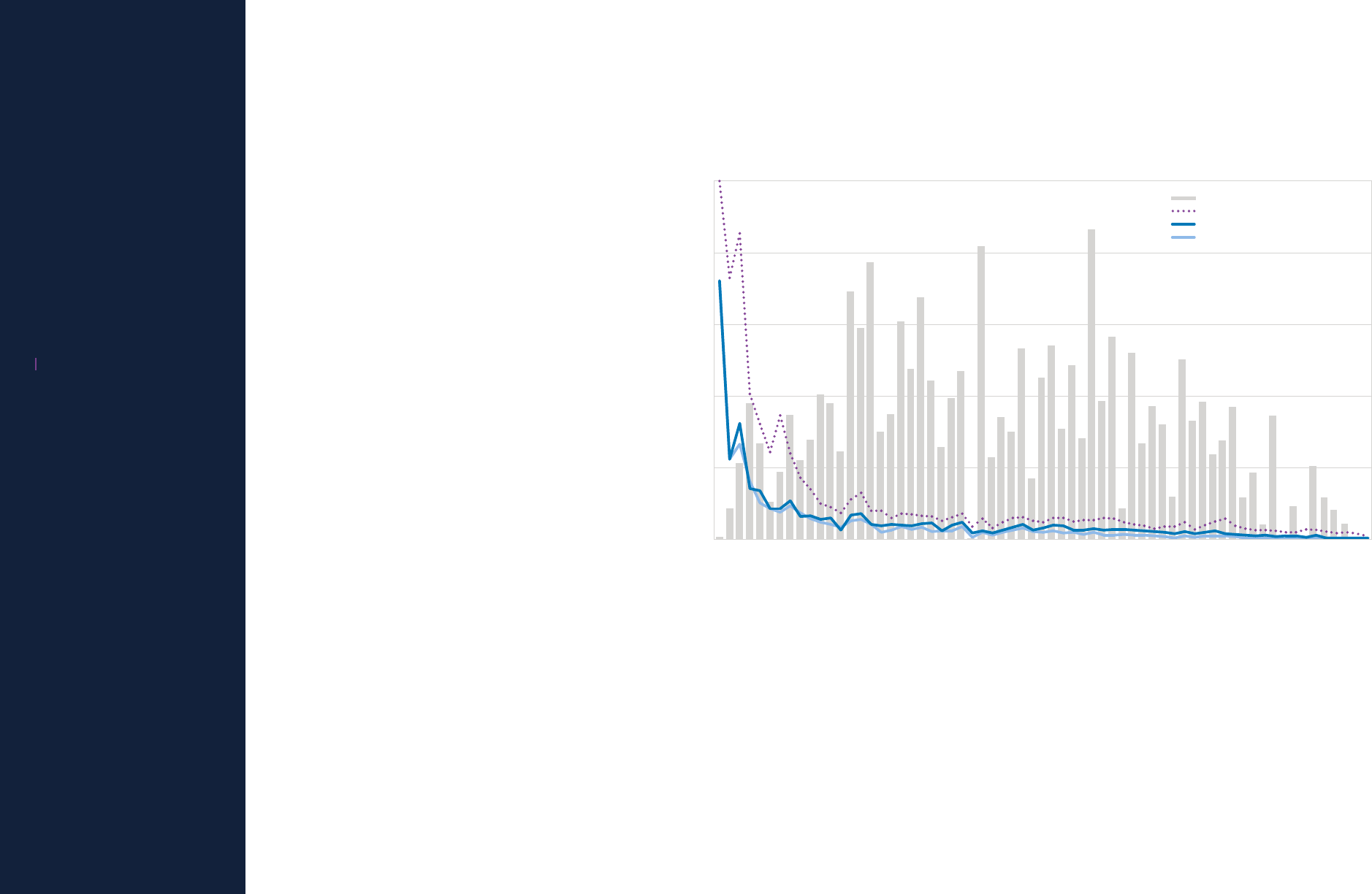
Annual onboard fatalities
Annual accident rate (per million departures)
Onboard fatalities
All accident rate
Hull loss accident rate
Fatal accident rate
The first decade of the jet age saw
dramatic improvements in fatal accident
rates. Since then, safety advancements
across the industry have helped continue
the downward trend. In fact, there were
zero fatal accidents in 2023 – the first
year without a fatal accident since data
collection began in 1959.
The Boeing Company
2023 Statistical
Summary
11
0 1 2 3 5 7 94 6 8 10
Hull loss with fatalities accident rate
Hull loss accident rate — Total bar
*The 707/720, Caravelle, Comet, CV-880-990, Concorde, Mercure,
Trident, VC10, DC-8, BAC1-11, L-1011, and 747-100/-200/-300/SP
have not operated commercially in the last five years.
**These types have accumulated fewer than one million departures.
0.72 / 1.22
3.04 / 5.65
0.77 / 1.45
0.87 / 1.78
2.31 / 4.62
1.28 / 2.98
0.63 / 2.69
0.32 / 0.76
0.13 / 0.53
0.22 / 0.29
0.67 / 1.50
1.89 / 2.53
0.54 / 1.09
1.58 / 3.16
0.13 / 0.40
0.13 / 0.26
0.08 / 0.17
0.03 / 0.16
0.00 / 0.00
0.00 / 0.00
0.00 / 0.00
0.00 / 0.00
0.00 / 0.00
0.00 / 0.00
0.00 / 0.00
0.00 / 0.00
0.08 / 0.08
0.70 / 0.70
0.55 / 1.10
0.0 / 0.57
0.08 / 0.17
0.43 / 1.20
0.26 / 0.80
0.53 / 0.93
Sorted by Year
of Introduction
*No Longer in Service
727
DC-9
737-100/-200
F-28
DC-10/MD-10
A300
MD-80/-90
767
757
BAe 146, RJ-70/-85/-100
A310
737-300/-400/-500
A300-600
A320/321/319/318
F-100/F-70
747-400
MD-11
A340
A330
777
737-600/-700/-800/-900
717
CRJ-700/-900/-1000
EMB-170/-175/-190
**A380
787
**747-8
A350
C-Series/A220
A320/321/319 NEO
737 MAX
A330 NEO
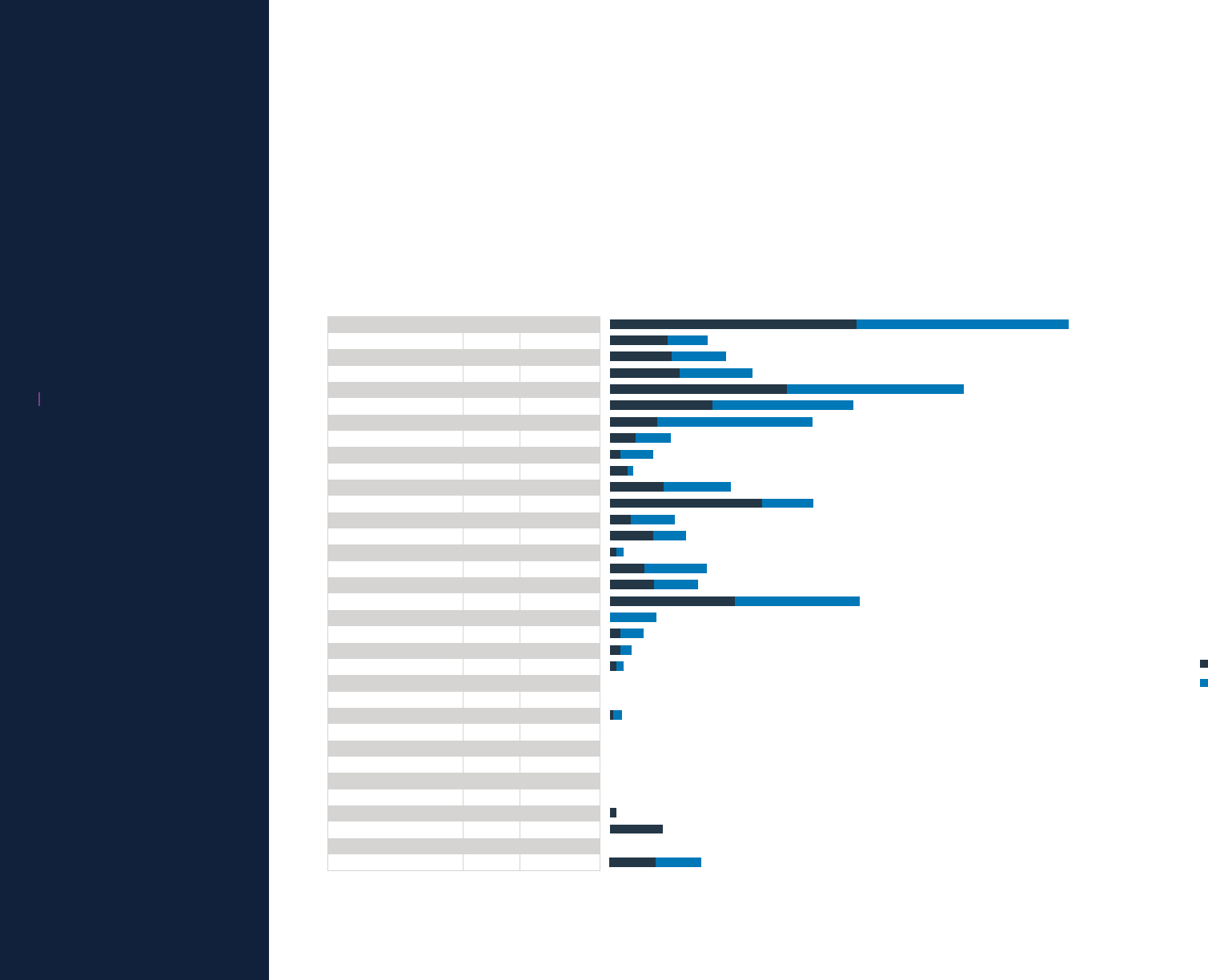
Total
392
94
91
104
42
28
17
36
12
8
18
12
62
7
29
14
10
10
2
6
4
22
0
0
5
0
0
0
0
0
1
2
0
1,028
211
55
48
51
21
12
4
15
3
6
8
9
20
4
13
5
5
5
0
2
2
10
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
2
0
513
Hull Loss
With Fatalities
Hull Loss
Accident Rates by Airplane Type
Hull Loss Accidents | Worldwide Commercial Jet Fleet | 1959‑2023
Hull loss accident rate (per million departures)
Contents
Leadership Message
2023 Statistical Summary
2023 Airplane Accidents
Accident Summaries
and Rates
CAST/ICAO Common
Taxonomy Team Aviation
Occurence Categories
Fatalities
Regional Statistics
About This Document
Definitions and Terms

The Boeing Company
2023 Statistical
Summary
12
The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) and the Commercial
Aviation Safety Team (CAST), which includes government ocials and
aviation industry leaders, have jointly chartered the CAST/ICAO Common
Taxonomy Team (CICTT). CICTT includes experts from several air
carriers; aircraft manufacturers; engine manufacturers; pilot associations;
regulatory authorities; transportation safety boards; ICAO; and members
from Canada, the European Union, France, Italy, the Netherlands, the
United Kingdom, and the United States. CICTT is co-chaired by one
representative each from ICAO and CAST.
The team is charged with developing common taxonomies and
definitions for aviation accident and incident reporting systems.
Common taxonomies and definitions establish a standard industry
language, thereby improving the quality of information and
communication. With this common language, the aviation community’s
capacity to focus on common safety issues is greatly enhanced.
The CICTT Aviation Occurrence Taxonomy is designed to permit an
assignment of multiple categories as necessary to describe the accident
or incident. Since 2001, the Occurrence Validation Study Group (OVSG),
formerly Safety Indicator Steering Group (SISG), has met annually to
assign CICTT occurrence categories to the prior year’s accidents.
In a separate activity, the CAST assigned each fatal accident to a single
principal category. Those accident assignments and a brief description of
the categories are reported in the following chart.
The CAST’s use of principal categories has been instrumental in focusing
industry and government eorts and resources on accident prevention.
Charts using principal categories are used by the CAST to identify changes
to historical risk and to help to determine if the safety enhancements put in
place are eective.
For a complete description of the categories, go to
www.intlaviationstandards.org.
CAST/ICAO Common Taxonomy Team Aviation
Occurrence Categories
Contents
Leadership Message
2023 Statistical Summary
2023 Airplane Accidents
Accident Summaries
and Rates
CAST/ICAO Common
Taxonomy Team Aviation
Occurence Categories
Fatalities
Regional Statistics
About This Document
Definitions and Terms

The Boeing Company
2023 Statistical
Summary
13 Note: Principal categories as assigned by CAST. See “Definitions and Terms” for included and excluded event details. For a complete description of CAST/ICAO Common Taxonomy Team (CICTT) Aviation Occurrence Categories, go to www.intlaviationstandards.org.
Fatalities by CICTT Aviation Occurrence Categories
Fatal Accidents | Worldwide Commercial Jet Fleet | 2014‑2023
8 2 5 1 1 1 3 1 1 3 11
ARC Abnormal Runway Contact
CTOL Collision With Obstacle(s) During Takeo and Landing
CFIT Controlled Flight Into or Toward Terrain
FUEL Fuel Related
ICE Icing
LOC-I Loss of Control — Inflight
MAC Midair/Near Midair Collision
OTHR Other
RAMP Ground Handling
RE Runway Excursion (Takeo or Landing)
RI-VAP Runway Incursion – Vehicle, Aircraft or Person
SCF-NP System/Component Failure or Malfunction (Non-Powerplant)
SCF-PP System/Component Failure or Malfunction (Powerplant)
USOS Undershoot/Overshoot
CFITFUEL
0
SCF-NP
1
LOC-I
1
RAMP MAC
0
7
4
35
RE
(RE, USOS, ARC)
9
CTOL
5
0
12
0
0
3
RI-VAP
0
5
SCF-PP
1
0
OTHR
0
1
ICE
CFITFUELSCF-NPLOC-I RAMP MACRE
(RE, USOS, ARC)
CTOL RI-VAP SCF-PPOTHR
ICE
0
200
400
600
800
1000
Fatalities
Number of fatal accidents (28 total)
External fatalities (Total 62)
Onboard fatalities (Total 1,078)
706
157
122
71
Contents
Leadership Message
2023 Statistical Summary
2023 Airplane Accidents
Accident Summaries
and Rates
CAST/ICAO Common
Taxonomy Team Aviation
Occurence Categories
Fatalities
Regional Statistics
About This Document
Definitions and Terms

The Boeing Company
2023 Statistical
Summary
14
3
4
2
3 3
1
0
2
10
0
174
17
347
278
71
0
100
91
0
200
100
300
400
500
0
5
10
15
20
25
Taxi
load/unload,
parked,
tow
Takeo Initial
climb
Climb
(flaps up)
Cruise Descent Initial
approach
Final
approach
Landing
Distribution of fatal accidents and onboard fatalities | 2014 through 2023
Fatal accidents
Onboard fatalities
Fatal accidents
Onboard fatalities
Fatal Accidents
and Fatalities
by Phase of
Flight
Worldwide Commercial Jet Fleet
2014‑2023
Percentage of Fatal Accidents and Onboard Fatalities | 2014-2023
Distribution of Fatal Accidents and Onboard Fatalities | 2014-2023
Taxi, load/
unload,
parked,
tow
21% 43%
Takeo
Initial
climb
Climb
(flaps up) Cruise Descent
Initial
approach
Final
approach Landing
Fatal accidents 11% 14% 7% 11% 11% 4% 0% 7% 36%
Onboard fatalities 0% 16% 2% 32% 26% 7% 0% 9% 8%
18% 17%
Exposure
(percentage
of flight time
estimated for a
1.5-hour flight) 1% 1% 14% 57%
Initial
approach
fix
11%
Final
approach
fix
12% 3% 1%
Note: Percentages may not sum to 100% because of numerical rounding.
Contents
Leadership Message
2023 Statistical Summary
2023 Airplane Accidents
Accident Summaries
and Rates
CAST/ICAO Common
Taxonomy Team Aviation
Occurence Categories
Fatalities
Regional Statistics
About This Document
Definitions and Terms
While cruising at altitude makes up the
majority of time in the air, this phase of
flight accounts for 11% of all fatal accidents.
Conversely, the landing phase accounts
for only 1% of flight time, but 36% of
all fatal accidents. Most safety-related
improvements over the past few decades
have focused on the taxi, climb, approach
and landing phases.
The Boeing Company
2023 Statistical
Summary
15
North America,
Central America
and Caribbean
(NACC)
Europe and
North Atlantic
(EUR/NAT)
Western
and Central
Africa
(WACAF)
Eastern and
Southern Africa
(ESAF)
Middle East
(MID)
Asia and Pacific
(APAC)
South
America
(SAM)
Regional Statistics
This section organizes accident data into
seven regions aligned with the ICAO’s
annual Safety Report. Each region is
dierent in terms of air travel growth rates,
operational profiles and other important
factors, and the data is reflected with those
factors in mind. However, all regions share
one common trend – the continued decline
in accident rates across recent decades.
Accident statistics are aligned with
operators and their home state of operation.
This regional data perspective provides
additional safety data for ICAO members
as they develop and implement their global,
regional and national aviation safety plans.
Contents
Leadership Message
2023 Statistical Summary
2023 Airplane Accidents
Accident Summaries
and Rates
CAST/ICAO Common
Taxonomy Team Aviation
Occurence Categories
Fatalities
Regional Statistics
About This Document
Definitions and Terms

The Boeing Company
2023 Statistical
Summary
16
Regional Accident Counts
APAC 1959-2023 2014-2023
All Accidents 399 67
Fatal Accidents 128 7
Onboard Fatalities 7,197 532
External Fatalities 271 2
Hull Loss Accidents 195 20
Fatal Accidents
CICTT Category 2014-2023
CFIT 0
CTOL 0
FUEL 0
ICE 0
LOC-I 3
MAC 0
OTHR 0
RAMP 1
RE (RE, USOS, ARC) 3
RI-VAP 0
SCF-NP 0
SCF-PP 0
Accident Rates per One Million Departures
0
10
20
30
40
50
Accident rate Hull loss accident rate Fatal accident rate
1994-2003
2004-2013
2014-2023
2.57
1.32
0.74
0.22
0.82
0.08
0.25
1.71
0.75
Contents
Leadership Message
2023 Statistical Summary
2023 Airplane Accidents
Accident Summaries
and Rates
CAST/ICAO Common
Taxonomy Team Aviation
Occurence Categories
Fatalities
Regional Statistics
About This Document
Definitions and Terms
Asia and Pacific (APAC)
Percentage of Fatal Accidents and Onboard Fatalities | 2014-2023
Taxi, load/
unload,
parked,
tow
14% 42%
Takeo
Initial
climb
Climb
(flaps up) Cruise Descent
Initial
approach
Final
approach Landing
Fatal accidents 14% 14% 0% 14% 14% 0% 0% 14% 28%
Onboard fatalities 0% 11% 0% 35% 30% 0% 0% 18% 4%
11% 22%
Exposure
(percentage
of flight time
estimated for a
1.5-hour flight) 1% 1% 14% 57%
Initial
approach
fix
11%
Final
approach
fix
12% 3% 1%
Note: Percentages may not sum to 100% because of numerical rounding.

The Boeing Company
2023 Statistical
Summary
17
Regional Accident Counts
ESAF 1959-2023 2014-2023
All Accidents 72 11
Fatal Accidents 16 1
Onboard Fatalities 1,064 157
External Fatalities 10 0
Hull Loss Accidents 44 4
Fatal Accidents
CICTT Category 2014-2023
CFIT 0
CTOL 0
FUEL 0
ICE 0
LOC-I 0
MAC 0
OTHR 0
RAMP 0
RE (RE, USOS, ARC) 0
RI-VAP 0
SCF-NP 1
SCF-PP 0
Eastern and Southern Africa (ESAF)
Accident Rates per One Million Departures
0
10
20
30
40
50
1994-2003
2004-2013
2014-2023
Accident rate Hull loss accident rate Fatal accident rate
12.68
9.06
2.71
1.42
1.81
0.36
1.55
5.03
3.92
Contents
Leadership Message
2023 Statistical Summary
2023 Airplane Accidents
Accident Summaries
and Rates
CAST/ICAO Common
Taxonomy Team Aviation
Occurence Categories
Fatalities
Regional Statistics
About This Document
Definitions and Terms
Percentage of Fatal Accidents and Onboard Fatalities | 2014-2023
Taxi, load/
unload,
parked,
tow
0% 0%
Takeo
Initial
climb
Climb
(flaps up) Cruise Descent
Initial
approach
Final
approach Landing
Fatal accidents 0% 0% 0% 100% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0%
Onboard fatalities 0% 0% 0% 100% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0%
0% 0%
Exposure
(percentage
of flight time
estimated for a
1.5-hour flight) 1% 1% 14% 57%
Initial
approach
fix
11%
Final
approach
fix
12% 3% 1%
Note: Percentages may not sum to 100% because of numerical rounding.
The Boeing Company
2023 Statistical
Summary
18
Regional Accident Counts
EUR/NAT 1959-2023 2014-2023
All Accidents 508 74
Fatal Accidents 142 6
Onboard Fatalities 8,069 135
External Fatalities 146 38
Hull Loss Accidents 217 21
Fatal Accidents
CICTT Category 2014-2023
CFIT 1
CTOL 0
FUEL 0
ICE 1
LOC-I 1
MAC 0
OTHR 0
RAMP 1
RE (RE, USOS, ARC) 1
RI-VAP 1
SCF-NP 0
SCF-PP 0
Percentage of Fatal Accidents and Onboard Fatalities | 2014-2023
Taxi, load/
unload,
parked,
tow
16% 50%
Takeo
Initial
climb
Climb
(flaps up) Cruise Descent
Initial
approach
Final
approach Landing
Fatal accidents 16% 0% 16% 0% 16% 0% 0% 0% 50%
Onboard fatalities 0% 0% 8% 0% 85% 0% 0% 0% 5%
8% 5%
Exposure
(percentage
of flight time
estimated for a
1.5-hour flight) 1% 1% 14% 57%
Initial
approach
fix
11%
Final
approach
fix
12% 3% 1%
Note: Percentages may not sum to 100% because of numerical rounding.
Accident Rates per One Million Departures
0
10
20
30
40
50
Accident rate Hull loss accident rate Fatal accident rate
1.84
0.81
0.57
0.30
0.51
0.09
0.26
1.80
1.05
1994-2003
2004-2013
2014-2023
Contents
Leadership Message
2023 Statistical Summary
2023 Airplane Accidents
Accident Summaries
and Rates
CAST/ICAO Common
Taxonomy Team Aviation
Occurence Categories
Fatalities
Regional Statistics
About This Document
Definitions and Terms
Europe and North Atlantic (EUR/NAT)

The Boeing Company
2023 Statistical
Summary
19
Regional Accident Counts
MID 1959-2023 2014-2023
All Accidents 148 19
Fatal Accidents 41 3
Onboard Fatalities 2,353 62
External Fatalities 128 2
Hull Loss Accidents 76 5
Fatal Accidents
CICTT Category 2014-2023
CFIT 0
CTOL 0
FUEL 0
ICE 0
LOC-I 2
MAC 0
OTHR 0
RAMP 0
RE (RE, USOS, ARC) 0
RI-VAP 1
SCF-NP 0
SCF-PP 0
Accident Rates per One Million Departures
0
10
20
30
40
50
Accident rate Hull loss accident rate Fatal accident rate
1994-2003
2004-2013
2014-2023
8.64
5.34
2.42
0.40
1.78
0.24
0.85
5.56
1.53
Contents
Leadership Message
2023 Statistical Summary
2023 Airplane Accidents
Accident Summaries
and Rates
CAST/ICAO Common
Taxonomy Team Aviation
Occurence Categories
Fatalities
Regional Statistics
About This Document
Definitions and Terms
Middle East (MID)
Percentage of Fatal Accidents and Onboard Fatalities | 2014-2023
Taxi, load/
unload,
parked,
tow
0% 100%
Takeo
Initial
climb
Climb
(flaps up) Cruise Descent
Initial
approach
Final
approach Landing
Fatal accidents 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 100%
Onboard fatalities 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 100%
0% 100%
Exposure
(percentage
of flight time
estimated for a
1.5-hour flight) 1% 1% 14% 57%
Initial
approach
fix
11%
Final
approach
fix
12% 3% 1%
Note: Percentages may not sum to 100% because of numerical rounding.

The Boeing Company
2023 Statistical
Summary
20
Regional Accident Counts
NACC 1959-2023 2014-2023
All Accidents 702 75
Fatal Accidents 210 6
Onboard Fatalities 7,228 116
External Fatalities 416 3
Hull Loss Accidents 281 19
Fatal Accidents
CICTT Category 2014-2023
CFIT 0
CTOL 0
FUEL 0
ICE 0
LOC-I 2
MAC 0
OTHR 1
RAMP 1
RE (RE, USOS, ARC) 0
RI-VAP 0
SCF-NP 1
SCF-PP 1
Accident Rates per One Million Departures
0
10
20
30
40
50
Accident rate Hull loss accident rate Fatal accident rate
1.38
0.58 0.40
0.23
0.38
0.07
0.19
1.21
0.89
1994-2003
2004-2013
2014-2023
Contents
Leadership Message
2023 Statistical Summary
2023 Airplane Accidents
Accident Summaries
and Rates
CAST/ICAO Common
Taxonomy Team Aviation
Occurence Categories
Fatalities
Regional Statistics
About This Document
Definitions and Terms
North America, Central America and Caribbean (NACC)
Percentage of Fatal Accidents and Onboard Fatalities | 2014-2023
Taxi, load/
unload,
parked,
tow
33% 32%
Takeo
Initial
climb
Climb
(flaps up) Cruise Descent
Initial
approach
Final
approach Landing
Fatal accidents 16% 33% 0% 16% 0% 0% 0% 16% 16%
Onboard fatalities 0% 96% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 2% 0%
96% 2%
Exposure
(percentage
of flight time
estimated for a
1.5-hour flight) 1% 1% 14% 57%
Initial
approach
fix
11%
Final
approach
fix
12% 3% 1%
Note: Percentages may not sum to 100% because of numerical rounding.

The Boeing Company
2023 Statistical
Summary
21
Regional Accident Counts
SAM 1959-2023 2014-2023
All Accidents 211 21
Fatal Accidents 74 3
Onboard Fatalities 3,250 76
External Fatalities 212 2
Hull Loss Accidents 145 12
Fatal Accidents
CICTT Category 2014-2023
CFIT 0
CTOL 1
FUEL 1
ICE 0
LOC-I 0
MAC 0
OTHR 0
RAMP 0
RE (RE, USOS, ARC) 0
RI-VAP 1
SCF-NP 0
SCF-PP 0
Accident Rates per One Million Departures
4.78
3.08
1.50
0.85
1.70
0.21
0.55
2.21
1.48
0
10
20
30
40
50
Accident rate Hull loss accident rate Fatal accident rate
1994-2003
2004-2013
2014-2023
Contents
Leadership Message
2023 Statistical Summary
2023 Airplane Accidents
Accident Summaries
and Rates
CAST/ICAO Common
Taxonomy Team Aviation
Occurence Categories
Fatalities
Regional Statistics
About This Document
Definitions and Terms
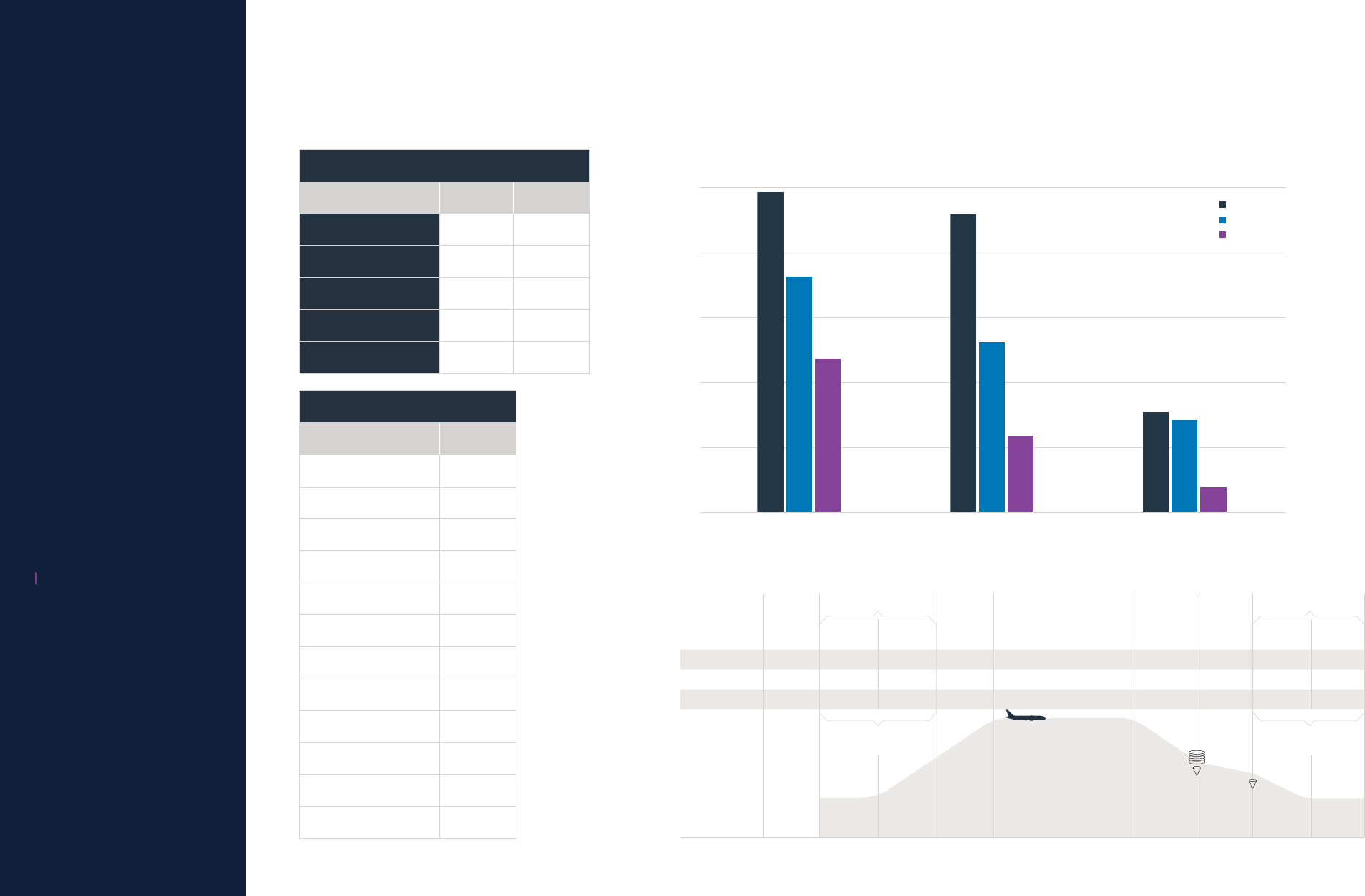
South America (SAM)
Percentage of Fatal Accidents and Onboard Fatalities | 2014-2023
Taxi, load/
unload,
parked,
tow
66% 0%
Takeo
Initial
climb
Climb
(flaps up) Cruise Descent
Initial
approach
Final
approach Landing
Fatal accidents 0% 33% 33% 0% 0% 33% 0% 0% 0%
Onboard fatalities 0% 0% 6% 0% 0% 93% 0% 0% 0%
6% 0%
Exposure
(percentage
of flight time
estimated for a
1.5-hour flight) 1% 1% 14% 57%
Initial
approach
fix
11%
Final
approach
fix
12% 3% 1%
Note: Percentages may not sum to 100% because of numerical rounding.
The Boeing Company
2023 Statistical
Summary
22
Regional Accident Counts
WACAF 1959-2023 2014-2023
All Accidents 94 12
Fatal Accidents 24 2
Onboard Fatalities 957 0
External Fatalities 78 15
Hull Loss Accidents 70 6
Fatal Accidents
CICTT Category 2014-2023
CFIT 0
CTOL 0
FUEL 0
ICE 0
LOC-I 0
MAC 1
OTHR 0
RAMP 0
RE (RE, USOS, ARC) 1
RI-VAP 0
SCF-NP 0
SCF-PP 0
Accident Rates per One Million Departures
0
10
20
30
40
50
Accident rate Hull loss accident rate Fatal accident rate
49.44
46.03
26.21
11.85
15.34
3.95
14.11
36.29
23.69
1994-2003
2004-2013
2014-2023
Contents
Leadership Message
2023 Statistical Summary
2023 Airplane Accidents
Accident Summaries
and Rates
CAST/ICAO Common
Taxonomy Team Aviation
Occurence Categories
Fatalities
Regional Statistics
About This Document
Definitions and Terms
Western and Central Africa (WACAF)
Percentage of Fatal Accidents and Onboard Fatalities | 2014-2023
Taxi, load/
unload,
parked,
tow
0% 50%
Takeo
Initial
climb
Climb
(flaps up) Cruise Descent
Initial
approach
Final
approach Landing
Fatal accidents 0% 0% 0% 0% 50% 0% 0% 0% 50%
Onboard fatalities 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0%
0% 0%
Exposure
(percentage
of flight time
estimated for a
1.5-hour flight) 1% 1% 14% 57%
Initial
approach
fix
11%
Final
approach
fix
12% 3% 1%
Note: Percentages may not sum to 100% because of numerical rounding.

The Boeing Company
2023 Statistical
Summary
24
The accident statistics presented in this summary are confined to
worldwide commercial jet airplanes that are heavier than 60,000
pounds (27,216 kilograms) maximum gross weight. Within that set of
airplanes, there are two groups excluded:
1. Airplanes manufactured in the Commonwealth of Independent States
(CIS), the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), or the People’s
Republic of China (PRC) due to lack of operational data.
2. Commercial airplanes operated in military service. (However, if a
military-owned commercial jet transport is used for civilian
commercial service, that data will be included in this summary.)
The following airplanes are included in the statistics:
Boeing
707/720
727
737
747
757
767
777
787
717
DC-8
DC-9
DC-10/MD-10
MD-11
MD-80/-90
Airbus
A300
A300-600
A310
A320/321/319/318
A330
A340
A350
A380
A220/C Series
BAE SYSTEMS (Avro)
Avro RJ70/85/100
BAE SYSTEMS (BAC)
Concorde
One-Eleven
VC10
BAE SYSTEMS (HS)
BAe 146
Comet 4
Trident
Bombardier
CRJ700/900/1000
Aerospatiale
Caravelle
Embraer
E170/175
E190/195
Fokker
F28
F70
F100
Lockheed
L-1011
Dassault Aviation
Mercure
General Dynamics
(Convair)
CV-880/-990
Flight operations data for Boeing airplanes is developed internally from
airline operator reports. Flight operations data for non-Boeing airplanes
is compiled by Cirium. The source of jet airplane inventory data is
Jet Information Services Inc.
Accident data is obtained, when available, from government accident
reports. Otherwise, information is from operators, manufacturers, various
government and private information services, and press accounts.
Readers may note that cumulative accident totals from year to year may
not exactly correlate with the expected change from the previous year’s
accidents. This is a result of periodic audits of the entire accident history
for updates to the data.
Definitions related to the development of statistics in this summary are
primarily based on corresponding ICAO, U.S. National Transportation
Safety Board (NTSB) and Flight Safety Foundation (FSF) terms, as
explained in the next section.
Contents
Leadership Message
2023 Statistical Summary
2023 Airplane Accidents
Accident Summaries
and Rates
CAST/ICAO Common
Taxonomy Team Aviation
Occurence Categories
Fatalities
Regional Statistics
About This Document
Definitions and Terms
About This Document

The Boeing Company
2023 Statistical
Summary
25
Definitions
Airplane Accident
An occurrence associated with the operation of an airplane that takes
place between the time any person boards the airplane with the intention
of flight and such time as all such persons have disembarked, in which:
• The airplane sustains substantial damage.
• Death or serious injury results from:
- Being in the airplane.
- Direct contact with the airplane or anything attached thereto.
- Direct exposure to jet blast.
Excluded Airplanes
Airplanes manufactured in the CIS, USSR or the PRC are excluded
because of the lack of operational data. Commercial airplanes operated
in military service are generally excluded. (If a military-owned commercial
jet transport is used for civilian commercial service, that data is included in
this summary.)
Excluded Events
• Fatal and nonfatal injuries from natural causes.
• Fatal and nonfatal self-inflicted injuries or injuries inflicted by
other persons.
• Fatal and nonfatal injuries of stowaways hiding outside the areas
normally available to the passengers and crew.
• Nonfatal injuries resulting from atmospheric turbulence, normal
maneuvering, loose objects, boarding, disembarking, evacuation, and
maintenance and servicing.
• Nonfatal injuries to persons not aboard the airplane.
• Occurrences classified as missing, unknown or undetermined
(CICTT occurrence category UNK) are not included in this
publication until otherwise determined by the ocial ICAO
Annex 13 investigation.
Note: The exclusion of the UNK occurrence category is in alignment
with industry eorts to identify, prioritize and reduce global high-risk
categories of occurrences such as those identified in ICAO’s Global
Aviation Safety Plan (GASP).
(See the “CAST/ICAO Common Taxonomy Team Aviation Occurrence
Categories” section.)
Contents
Leadership Message
2023 Statistical Summary
2023 Airplane Accidents
Accident Summaries
and Rates
CAST/ICAO Common
Taxonomy Team Aviation
Occurence Categories
Fatalities
Regional Statistics
About This Document
Definitions and Terms

The Boeing Company
2023 Statistical
Summary
26
Excluded Events (continued)
The following occurrences are not considered airplane accidents:
• Those that are the result of experimental flight tests. (However,
maintenance flight tests, ferry, positioning, training and demonstration
flights are not excluded.)
• Those that are the result of a hostile action, including sabotage,
hijacking, terrorism and military action.
Note: This is generally consistent with the ICAO and the NTSB definition
of an accident. (See the “Referenced ICAO and NTSB Definition” section.)
The dierences are:
1. The ICAO and NTSB references to “aircraft” were changed to
“airplane” and references to propellers and rotors were eliminated.
2. This publication excludes events that result in nonfatal injuries from
atmospheric turbulence, normal maneuvering, etc.; nonfatal injuries
to persons not aboard the airplane; and any events that result from
an experimental flight test or from hostile action, such as sabotage,
hijacking, terrorism and military action.
Note: Within this publication, the term “accident” is used interchangeably
with “airplane accident.”
Destroyed
The estimated or likely cost of repairs would have exceeded 50% of the
new value of the airplane had it still been in production at the time
of the accident.
Note: This definition is consistent with the FSF definition. NTSB defines
“destroyed” as damaged due to impact, fire or in-flight failures to an extent
not economically repairable.
Fatal Injury
Any injury that results in death within 30 days of the accident.
Note 1: This is consistent with both the ICAO and the NTSB definitions.
Note 2: External fatalities include on-ground fatalities as well as fatalities
on other aircraft involved.
Contents
Leadership Message
2023 Statistical Summary
2023 Airplane Accidents
Accident Summaries
and Rates
CAST/ICAO Common
Taxonomy Team Aviation
Occurence Categories
Fatalities
Regional Statistics
About This Document
Definitions and Terms
Definitions

The Boeing Company
2023 Statistical
Summary
27
Major Accident
An accident in which any of three conditions is met:
• The airplane was destroyed.
• There were multiple fatalities.
• There was one fatality and the airplane was substantially damaged.
Note: This definition is consistent with the NTSB definition. It also is
generally consistent with FSF, except that the FSF definition specifies that
fatalities include only occupants of the airplane. ICAO does not normally
define the term “major accident.”
Serious Injury
An injury that is sustained by a person in an accident and that:
• Requires hospitalization for more than 48 hours, commencing
within seven days from the date the injury was received.
• Results in a fracture of any bone (except simple fractures of
fingers, toes or nose).
• Causes severe hemorrhage, nerve, muscle or tendon damage.
• Involves injury to any internal organ.
• Involves second- or third-degree burns or any burns aecting
more than 5% of the body surface.
• Involves verified exposure to infectious substances or
injurious radiation.
Note: This is generally consistent with the ICAO definition. It is also
consistent with the NTSB definition except for the last bullet, which is
not included in the NTSB definition.
Contents
Leadership Message
2023 Statistical Summary
2023 Airplane Accidents
Accident Summaries
and Rates
CAST/ICAO Common
Taxonomy Team Aviation
Occurence Categories
Fatalities
Regional Statistics
About This Document
Definitions and Terms
Definitions

The Boeing Company
2023 Statistical
Summary
28
Substantial Damage
Damage or failure that adversely aects the structural strength,
performance, or flight characteristics of the airplane, and that would
normally require major repair or replacement of the aected component.
Substantial damage is not considered to be:
• Engine failure or damage limited to an engine,
if only one engine fails or is damaged.
• Bent fairings or cowlings.
• Dents in the skin.
• Small puncture holes in the skin.
• Damage to wheels.
• Damage to tires.
• Damage to flaps.
• Damage to engine accessories.
• Damage to brakes.
• Damage to wingtips.
Note 1: This definition is generally consistent with the NTSB definition of
substantial damage except it (1) deletes the reference to “small puncture
holes in the fabric” and “ground damage to rotor or propeller blades,” and
(2) deletes “damage to landing gear” from the list of items not considered
to be substantial damage.
Note 2: ICAO does not define the term “substantial damage.” Still, the
definition is generally consistent with the ICAO definition of damage or
structural failure contained within part (B) of the ICAO accident definition.
Note 3: Boeing does not consider damage to be substantial if repairs
to an event airplane enable it to be flown to a repair base within 48 hours
of the event.
Contents
Leadership Message
2023 Statistical Summary
2023 Airplane Accidents
Accident Summaries
and Rates
CAST/ICAO Common
Taxonomy Team Aviation
Occurence Categories
Fatalities
Regional Statistics
About This Document
Definitions and Terms
Definitions

The Boeing Company
2023 Statistical
Summary
29
Accident Rates
In general, this expression is a measure of accidents per million departures.
Departures (or flight cycles) are used as the basis for calculating rates
because there is a stronger statistical correlation between accidents
and departures than there is between accidents and flight-hours, or
between accidents and the number of airplanes in service, or between
accidents and passenger miles or freight miles. Airplane departures data
is continually updated and revised as new information and estimating
processes become available. These form the baseline for the measure of
accident rates, and, as a consequence, rates may vary between editions
of this publication.
Airplane Collisions
Events involving two or more airplanes are counted as separate events,
one for each airplane. For example, destruction of two airplanes in a
collision is considered to be two separate accidents.
Fatal Accident
An accident that results in fatal injury.
Hull Loss
Airplane totally destroyed or damaged and not repaired. Hull loss also
includes, but is not limited to, events in which:
• The airplane is missing. An aircraft is considered to be missing
when the ocial search has been terminated and the wreckage
has not been located.
• The airplane is completely inaccessible.
State of Operation
Regional data is reported based on the ICAO member state that serves as
the headquarters location of the operator involved in the accident.
*The terms on this page were created by Boeing for this publication and do not have corresponding equivalents in ICAO or NTSB.
Contents
Leadership Message
2023 Statistical Summary
2023 Airplane Accidents
Accident Summaries
and Rates
CAST/ICAO Common
Taxonomy Team Aviation
Occurence Categories
Fatalities
Regional Statistics
About This Document
Definitions and Terms
Boeing Terms*

The Boeing Company
2023 Statistical
Summary
30
Accident
ICAO defines an “accident” as follows:
Accident. An occurrence associated with the operation of an aircraft that,
in the case of a manned aircraft, takes place between the time any person
boards the aircraft with the intention of flight until such time as all such
persons have disembarked, or in the case of an unmanned aircraft, takes
place between the time the aircraft is ready to move with the purpose of
flight until such time as it comes to rest at the end of the flight and the
primary propulsion system is shut down, in which:
A. A person is fatally or seriously injured as a result of:
• Being in the aircraft.
• Direct contact with any part of the aircraft, including parts which
have become detached from the aircraft.
• Direct exposure to jet blast, except when the injuries are from
natural causes, self-inflicted or inflicted by other persons, or when
the injuries are to stowaways hiding outside the areas normally
available to the passengers and crew.
B. The aircraft sustains damage or structural failure which:
• Adversely aects the structural strength, performance or flight
characteristics of the aircraft.
• Would normally require major repair or replacement of the
aected component, except for engine failure or damage, when
the damage is limited to a single engine (including its cowlings
or accessories), to propellers, wingtips, antennas, probes,
vanes, tires, brakes, wheels, fairings, panels, landing gear doors,
windscreens, the aircraft skin (such as small dents or puncture
holes), or for minor damages to main rotor blades, tail rotor
blades, landing gear, and those resulting from hail or bird strike
(including holes in the radome).
C. The aircraft is missing or is completely inaccessible.
NTSB defines an “aircraft accident” as follows:
Aircraft accident means an occurrence associated with the operation
of an aircraft that takes place between the time any person boards the
aircraft with the intention of flight and all such persons have disembarked,
and in which any person suers death or serious injury, or in which the
aircraft receives substantial damage. For purposes of this part, the
definition of “aircraft accident” includes “unmanned aircraft accident,”
as defined in 49 CFR 830.2.
Contents
Leadership Message
2023 Statistical Summary
2023 Airplane Accidents
Accident Summaries
and Rates
CAST/ICAO Common
Taxonomy Team Aviation
Occurence Categories
Fatalities
Regional Statistics
About This Document
Definitions and Terms
Referenced ICAO and NTSB Definitions

The Boeing Company
2023 Statistical
Summary
31
Safety Management System (SMS)
ICAO defines an “SMS” as follows:
An SMS is a systematic approach to managing safety, including
the necessary organizational structures, accountabilities, policies
and procedures. Visit www.icao.int/safety/SafetyManagement for
more information.
Serious Injury
ICAO defines “serious injury” as follows:
Serious injury. An injury that is sustained by a person in an accident
and which:
A. Requires hospitalization for more than 48 hours, commencing
within seven days from the date the injury was received.
B. Results in a fracture of any bone (except simple fractures of
fingers, toes or nose).
C. Involves lacerations that cause severe hemorrhage, nerve,
muscle or tendon damage.
D. Involves injury to any internal organ.
E. Involves second- or third-degree burns, or any burns aecting
more than 5% of the body surface.
F. Involves verified exposure to infectious substances or
injurious radiation.
NTSB defines “serious injury” as follows:
Serious injury means any injury that:
1. Requires hospitalization for more than 48 hours, commencing within
seven days from the date the injury was received.
2. Results in a fracture of any bone (except simple fractures of fingers,
toes or nose).
3. Causes severe hemorrhages, nerve, muscle or tendon damage.
4. Involves any internal organ.
5. Involves second- or third-degree burns, or any burns aecting more
than 5% of the body surface.
Substantial Damage
NTSB defines “substantial damage” as follows:
Substantial damage means damage or failure that adversely aects the
structural strength, performance, or flight characteristics of the aircraft,
and which would normally require major repair or replacement of the
aected component. Engine failure or damage limited to an engine if
only one engine fails or is damaged, bent fairings or cowling, dented
skin, small puncture holes in the skin or fabric, ground damage to rotor or
propeller blades, and damage to landing gear, wheels, tires, flaps, engine
accessories, brakes, or wingtips are not considered “substantial damage”
for the purpose of this part.
ICAO does not define the term “substantial damage.”
Contents
Leadership Message
2023 Statistical Summary
2023 Airplane Accidents
Accident Summaries
and Rates
CAST/ICAO Common
Taxonomy Team Aviation
Occurence Categories
Fatalities
Regional Statistics
About This Document
Definitions and Terms
Referenced ICAO and NTSB Definitions

Copyright © 2024 Boeing. All rights reserved. 328585 8/24
2023
Statistical
Summary
