
www.wherescape.com
RED and ssis
integration
White Paper

WhereScape White Paper
www.wherescape.com
Overview
• Purpose
• SSIS Introduction
• RED SSIS Loading Feature
Integrating RED & External SSIS Packages
• DTEXEC Method
• RED/DTEXEC Relevant Parameters
• MSSQL 2012 SSIS Catalog
• RED & SSIS Integration Scenarios
Appendix A (Exec_SSIS_Package_Script)
Appendix B (WS_RUN_SSIS_Catalog_Package)
Appendix C (ufn_split_string)
01
01
01
02
02
02
03
03
04
12
13
17

WhereScape White Paper
www.wherescape.com
- 1 -
Overview
Purpose
The purpose of this document is to demonstrate
how quick and easy it is to integrate external
Microsoft SQL Server Integration Services
(SSIS) packages developed using Microsoft tools
like Visual Studio into a RED data warehouse
environment.
There are a number of scenarios where integrating
external ETL processes may be needed, some
potential scenarios are:
Integration with a data source not supported
natively by RED (e.g. SharePoint List, Web
Services)
Integration of Data Quality (DQ) rules into the
workow (e.g. MSSQL Data Quality Services or
DQS)
Complex processing rules where an ETL
package is a better t
By following a few simple steps and applying the
provided base code templates integration between
external SSIS packages and RED can be achieved
within minutes.
SSIS Introduction
Microsoft SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS)
has been around since Microsoft SQL Server
(MSSQL) 2005 having been signicantly enhanced
from its precursor Data Transformation Services
or DTS. In an MSSQL environment SSIS is usually
the default ETL method for moving data into
and between MSSQL databases as it is a bundled
product that can be installed with a MSSQL
instance at no additional cost.
SSIS is a reasonably powerful and exible ETL
offering that can move data efciently between
sources and destinations using a buffering
technique which means that reading and writing
of data can occur in parallel.
SSIS 2005 to 2008R2 versions
From MSSQL 2005 – 2008R2 packages are
developed and deployed individually from Visual
Studio. There are two main options for deploying
and running SSIS without RED.
Packages deployed to MSDB and called by
SQL Agent
Packages deployed to File System and called
by DTEXEC
DTEXEC is the command line method for
executing an SSIS package, DTEXEC can be called
from any batch script and any scheduler service,
including SQL Agent, Windows Task Scheduler or
any other scheduler that can call a batch script.
Because of the difculty in managing SSIS
packages in the MSDB database often the File
System method is used. Because RED natively
supports host (or batch) scripts then it is a very
simple matter to schedule an external SSIS
package from RED and fully integrate the package
into the data warehouse processing.
SSIS 2012 version
In MSSQL 2012, Microsoft have addressed some
of the limitations of using MSDB as a database
repository, by implementing a dedicated SSIS
repository called the “SSIS Catalog” which is
a database with the default name of SSISDB.
Additionally within Visual Studio it is now
RED and ssis
integration

WhereScape White Paper
www.wherescape.com
- 2 -
possible to build up a solution of packages as
a project and deploy the entire project using
a project deployment manifest, this makes it
much easier to manage change and dependencies
between SSIS packages.
It is still possible to deploy packages to the le
system and use DTEXEC if required however
because the SSIS Catalog has a number of stored
procedures and views to execute and inspect
package meta-data it is now often easier to use the
SSIS Catalog.
Using the SSIS Catalog we can now interact with
SSIS packages using TSQL making it much easier
to write RED code to integrate external SSIS
packages.
RED SSIS Loading Feature
WhereScape RED has supported SSIS loading
of LOAD tables for some time for MSSQL
environments. Buffering performance benets
mean it is often the recommended method for
processing LOAD tables quickly. The SSIS loader
in RED essentially creates a SSIS package on the
y containing:
An OLEDB connection to the:
• Source database (only database sources
supported at the time of writing)
• Data warehouse
A data ow task that maps the source to the
data warehouse LOAD object
RED creates the package at runtime and invokes
SSIS programmatically to run the package. From
within RED it is possible to congure:
Connection settings
• Multiple SSIS database sources
• SSIS connection string per
source database
Load table settings
• Acquisition of a table lock (for faster
BULK operations)
• Commit Interval (rows to commit
per transaction)
• Batch size (control rows per batch)
NOTE: It is possible to output the RED generated
package for logging purposes to the le system. To do
this enter the text FULLLOG in the notes dialog of the
RED SSIS connection being used to load the data. If
run via the scheduler the package will be written to
the Scheduler Work directory.
Integrating RED & External SSIS
Packages
The following is a discussion on how to integrate
a RED data warehouse with an externally managed
SSIS package or solution.
NOTE: Security is an important consideration
and due to complexity is outside the scope of
this document. You will need to consider account
permissions, particularly in a multi-server scenario.
It may be necessary to congure Kerberos when more
than one server hop is required.
DTEXEC Method
When considering integrating RED with versions
prior to MSSQL 2012 the best option is to place
the developed SSIS package on the File System
and call it from a RED Host Script by invoking
DTEXEC. This is relatively simple to do and a
sample is available in the appendices of this
document.
Once the SSIS package has been deployed the host
script can be called by the RED scheduler as a job
task in the usual manner. Normally a LOAD object
would be the data destination, in this case the
connection should be set to Windows and the Load
Type property to “Script based load”. The load
table can then be processed via the host script.

WhereScape White Paper
www.wherescape.com
- 3 -
The DTEXEC utility is installed with the
“Integration Service Instance” option while
installing SQL Server.
The DTEXEC command prompt utility is used to
congure and execute SQL Server Integration
Services packages. The DTEXEC utility provides
access to the entire package conguration
and execution features, such as parameters,
connections, properties, variables, logging, and
progress indicators.
Syntax
DTEXEC /option [value] [/option [value]]...
Syntax Rules
All options must start with a slash (/) or a
minus sign (-). The options that are shown here
start with a slash (/), but the minus sign (-) can
be substituted.
An argument must be enclosed in quotation
marks if it contains a space. If the argument is
not enclosed in quotation marks, the argument
cannot contain white space.
Doubled quotation marks within quoted strings
represent escaped single quotation marks.
Options and arguments are not case-sensitive,
except for passwords.
Read more about DTEXEC options here:
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/
hh231187.aspx
RED/DTEXEC Relevant Parameters
/FILE “packageFilePath” - specify the location of the
package
/REPORTING EW - display which messages to report;
Errors (E) and Warnings (W) for the error log (if this
command isn’t specied the default is EWP – Errors,
Warnings & Progress)
/CONN “connectionManager”;”connectionString” -
Optional: used to change the connection string in the
package
/SET \package.variables[“variable”].value;”value” -
Optional: used to set parameters in the package
/SET \package.connections[“connectionManager”].
properties[connectionstring];”connectionString”-
used to set the connection string if it is
parameterised.
NOTE: Each line of the host script must be less than
255 characters long otherwise when it is processed by
RED it will cut off the end and throw an error.
MSSQL 2012 SSIS Catalog
With the implementation of the SSIS Catalog it
is now possible to invoke a package with TSQL,
which from a RED perspective is much simpler
and easier to integrate and also manage the SSIS
packages cleanly. At this point we need to cover off
some specics as to the mechanisms provided to
do so.
Within the SSIS Catalog there are a number of
stored procedures and views by which we can
execute a package and monitor its progress and
state. Basically the process follows 4 steps:
1. Create a package execution “container”
2. Set the required package parameter values
& environments
3. Execute the package itself
4. Monitor progress and state via Catalog
views
A couple of important things to note:
By creating the package execution you obtain
an execution id that is used by the following
processes to identify the particular execution
instance of the package
If the package itself fails then the execute
package procedure will not necessarily return
an error, so we have to check the SSIS Catalog
WhereScape White Paper
www.wherescape.com
- 4 -
views to ascertain the execution state and the
error details
In order to make the calling procedure wait
until the package execution completes then
conguring the SSIS “SYNCHRONIZED”
execution parameter to TRUE is important
As there are several procedure calls to the
SSIS Catalog and subsequent checking of the
processing state of the package it is much easier
to create a general wrapper procedure within RED
which can then be called by subsequent custom
procedures where specic input parameters such
as the package name can be supplied.
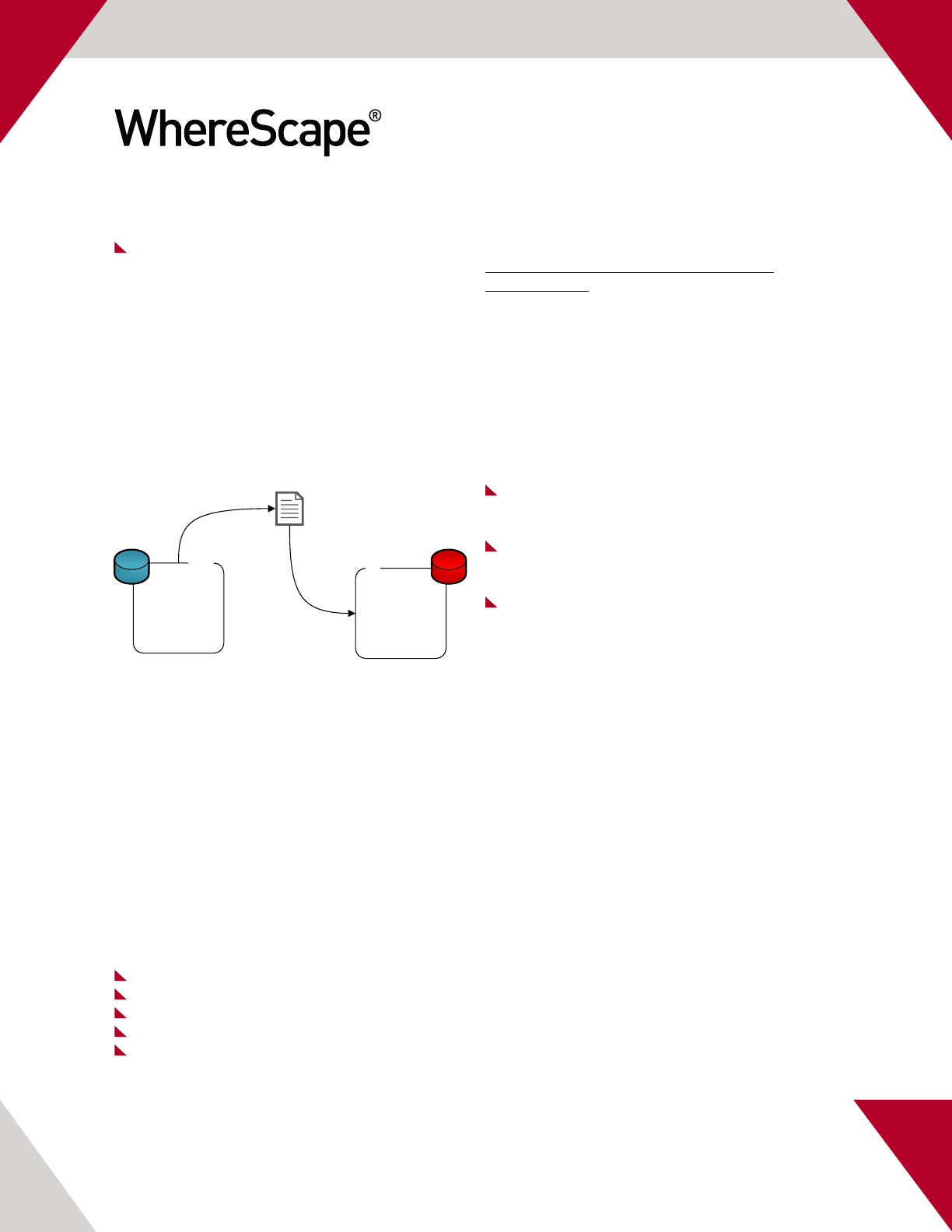
Diagram 1.0 – SSIS & RED integration via wrapper sproc
We have created a modiable wrapper procedure
called “WS_RUN_SSIS_Catalog_Package ” this
procedure accepts input parameters as to which
SSIS package to execute, the SSIS project, logging
levels etc. The code for “WS_RUN_SSIS_Catalog_
Package ” is supplied in appendix B of this
document.
SSIS Catalog Procedure details
The following SSIS Catalog procedures and views
have been used in the wrapper procedure:
[catalog].[create_execution]
[catalog].[environment_references]
[catalog].[set_execution_parameter_value]
[catalog].[start_execution]
[catalog].[executions]
Links to further explanation of these objects can
be found here:
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/
hh479588.aspx
RED & SSIS Integration Scenarios
We have seen that RED supports SSIS loading for
LOAD objects and that we can provide customised
conguration settings against those load objects
if needed however there are some scenarios where
this use case does not t. Potential scenarios may
be things like:
Integration with a data source not supported
natively by RED (e.g. SharePoint List, Web
Services)
Integration of Data Quality (DQ) rules into
the workow (e.g. MSSQL Data Quality Services
(DQS))
Complex processing rules where an ETL
package is a better t
When one of these scenarios occurs then we
want the external packages to be scheduled and
execute synchronously within the RED workow
so that there is only one place we need to check
if something goes wrong. This has been possible
from MSSQL 2005 but has been made much easier
in MSSQL 2012.
Scenario One – DTEXEC Method
Steps:
1. In Red create a host script called EXEC_SSIS
Package_Script containing the DTEXEC
command to run the package as per the sample
in APPENDIX A
2. In the properties of the host script set default
connection to Windows
3. Add for error catching in RED at the end of the
dtexec command: > %FILELOG% 2>&1
Ws_Exec_SSIS_Catalog_Package
RED
Load
Stage
Da taS tore
SSISDB
Sprocs
Views

WhereScape White Paper
www.wherescape.com
- 5 -
If the connection strings need to be changed the following code can be used:
DTEXEC /FILE “packageFilePath” /REPORTING E /CONN “connectionManager”;”connectionString”
The following example can be used to change 2 connection strings.
DTEXEC /FILE C:\temp\test_package.dtsx /REPORTING E /CONN FlatFileConnectionManager;”C:\
temp\test_File.txt” /CONN Red;”Data Source=MyServer\MyInstance;Initial Catalog=Red7;Integrated
Security=SSPI;”
Variables can also be used to break up the code (ideally use if the line will be over 255 characters long).
For example:
SET CONNAME1=Package.Connections[Red].Properties[ConnectionString]
SET DATSOURCE1=Data Source=MyServer\MyInstance;Initial Catalog=Red;Integrated Security=SSPI
SET CONNAME2=Package.Connections[“FlatFileConnectionManager”].Properties[ConnectionString]
SET DATSOURCE2=C:\temp\test_File.txt
DTEXEC /FILE C:\temp\test_package.dtsx /REPORTING E /SET \%CONNAME1%;\””%DATSOURCE1%;”\” /
SET \%CONNAME2%;\””%DATSOURCE2%”\” > %FILELOG% 2>&1

WhereScape White Paper
www.wherescape.com
- 6 -
4. In RED build a load table with columns based on the SSIS package output.
5. In the properties of the load table set the following:
Connection: windows
Load type: script based load
Script name: EXEC_SSIS_Package_Script

WhereScape White Paper
www.wherescape.com
- 7 -
6. In the package set the destination of the SSIS package to the load table you created in RED
7. Also make sure the mappings match up to the load table

WhereScape White Paper
www.wherescape.com
- 8 -
8. Load the table to make sure the SSIS package completes successfully and loads the data from the
package into the load table.
SQL SERVER 2012 DTEXEC Catalog
DTEXEC can also call packages stored in SSISDB using the following format:
DTEXEC /ISSERVER \”catalogName”\”folderName”\”projectName”>\”packageFileName” /SERVER “server” /
REPORTING EW /ENV “EnvironmentName”
Example:
DTEXEC /ISSERVER “\SSISDB\MyFolder\MyProject\MyPackage.dtsx” /SERVER “MyServer” /REPORTING
EW
Scenario Two - SSIS Catalog Method
This option can be used if you have SQL Server 2012 and the SSIS Package in the SSIS Catalog:

WhereScape White Paper
www.wherescape.com
- 9 -
Steps:
1. In RED create a custom stored procedure called WS_RUN_SSIS_Catalog_Package (see Appendix B for
code). This will read the package details from a RED parameter and run the SSIS package.
This procedure accepts details about which package to run as a delimited string, the delimiter being
pipe “|”.
The parameter string should be in the format:
Folder|Project|Package|Environment_name|logging_level|Synchronised_exec
Example – Specifying all options
MyFolder|MyProject|MyPackage.dtsx|MyEnvironment|1|1
Example – Specifying minimum options
MyFolder|MyProject|MyPackage.dtsx
Optional Parameters:
Environment_name – if no environment is used this can be left blank
Logging_level – if not specied this will default to 1
Synchronised_exec – if not specied this will default to 1
2. In RED create a parameter called pSSIS_Package and enter the package string.
3. In RED build a load table with columns from the result of the SSIS package.
4. In the properties of the load table set the following:
Connection – Windows
Load type – Externally Loaded
Pre-Load Action - Truncate
Post Load Procedure – WS_RUN_SSIS_Catalog_Package

WhereScape White Paper
www.wherescape.com
- 10 -
NOTE: If you have multiple packages and want to use the same stored procedure and parameter then the new
package parameter value can be written to by setting the following additional options:
Pre-Load Action – Both Truncate and Execute Pre-Load SQL
Pre-Load SQL:
DECLARE @RC int
EXECUTE @RC = [dbo].[WsParameterWrite]
parameter,
parameter_value,
comment
For example:
DECLARE @RC int
EXECUTE @RC = [dbo].[WsParameterWrite]
‘pSSIS_Package’,
‘MyFolder|MyProject|MyPackage.dtsx||1|1’,
‘updated from load procedure’ + CAST(GETDATE AS VARCHAR)
WhereScape White Paper
www.wherescape.com
- 11 -
5. Set the destination of the SSIS package to the load table you created in RED
6. Make sure the mappings match up to the load table
7. Load the table to make sure the SSIS package completes successfully and loads the data
from the package into the load table.
8. Now schedule the Load table as part of the desired RED job

WhereScape White Paper
www.wherescape.com
- 12 -
Appendix A (EXEC_SSIS_Package_Script)
The following script is a base template for calling DTEXEC from a RED host script:
@echo off
SETLOCAL ENABLEDEPLAYEDEXPANSION
SETLOCAL ENABLEEXTENSIONS
REM **********************************************************
REM ***** LOAD A TABLE FROM AN SSIS PACKAGE
REM *****
REM **********************************************************
REM **********************************************************
REM ***** NOTE: The following environment variables will be set
REM ***** WSL_SEQUENCE = a unique sequence number for the scheduler
REM ***** WSL_WORKDIR = the work directory dened in the connection
REM ***** WSL_SERVER = the server dened in the connection
REM ***** WSL_DATABASE = the database dened in the connection
REM ***** WSL_USER = the dss user dened in the connection
REM ***** WSL_PWD = the dss password dened in the connection
REM **********************************************************
SET LOAD_FILE= DRIVE:\DIR\*.dat
SET LOAD_TABLE=load_table
SET FILECTL=%WSL_WORKDIR%\wsl%WSL_SEQUENCE%.ctl
SET FILELOG=%WSL_WORKDIR%\wsl%WSL_SEQUENCE%.log
SET FILEAUD=%WSL_WORKDIR%\wsl%WSL_SEQUENCE%.aud
REM **********************************************************
REM ************* RUN SSIS ***********************************
REM **********************************************************
DTEXEC /FILE “C:\MyFolder\MyPackage.dtsx” /REPORTING EW > %FILELOG% 2>&1
FOR /F “tokens=*” %%a IN (‘TYPE %FILELOG%’) DO IF “%%a”==”DTExec: The package execution returned DTSER_
FAILURE (1).” (SET pResult=-2 )
FOR /F “tokens=*” %%a IN (‘type %FILELOG%’) DO IF “%%a”==”DTExec: The package execution returned DTSER_
SUCCESS (0).” (SET pResult=1 )
IF %pResult% EQU 1 GOTO LABEL_OKAY
:LABEL_FAIL
ECHO -2
ECHO SSIS Processing Failed. See error log for details (%FILELOG%)
TYPE %FILELOG% >&2
EXIT
:LABEL_OKAY
ECHO 1
ECHO SSIS Package Processed Successfully.
TYPE %FILELOG% >&2
EXIT

WhereScape White Paper
www.wherescape.com
- 13 -
Appendix B (WS_RUN_SSIS_Catalog_Package)
The following is the code for the SSISDB Catalog wrapper stored procedure:
-- ==============================================================================
-- DBMS Name : SQL Server
-- Script Name : WS_RUN_SSIS_Catalog_Package
-- Description : Run SSIS Catalog Packages
-- Generated by : WhereScape RED
-- Generated for : WhereScape Ltd
-- Author : WhereScape Ltd
-- ==============================================================================
-- Notes / History
--
CREATE PROCEDURE WS_RUN_SSIS_Catalog_Package
@p_sequence integer
, @p_job_name varchar(256)
, @p_task_name varchar(256)
, @p_job_id integer
, @p_task_id integer
, @p_return_msg varchar(256) OUTPUT
, @p_status integer OUTPUT
AS
SET XACT_ABORT OFF -- Turn off auto abort on errors
SET NOCOUNT ON -- Turn off row count messages
--===============================================================
-- Control variables used in most programs
--===============================================================
DECLARE
@v_msgtext varchar(256) -- Text for audit_trail
, @v_step integer -- return code
, @v_update_count integer -- no of records updated
, @v_insert_count integer -- no of records inserted
, @v_count integer -- General counter
, @v_return_status integer -- Query result status
, @v_row_count integer -- Query returned row count
, @v_db_code varchar(10) -- Database error code
, @v_db_msg varchar(100) -- Database error message
--===============================================================
-- Main
--===============================================================
SET @v_step = 100
SET @v_update_count = 0
SET @v_insert_count = 0

WhereScape White Paper
www.wherescape.com
- 14 -
--===============================================================
--Process Package
--***************************************************************
DECLARE
@v_return_msg VARCHAR(MAX)
, @param_string VARCHAR(8000)
, @execution_id BIGINT
, @package VARCHAR(8000)
, @project VARCHAR(8000)
, @folder VARCHAR(8000)
, @environment_name VARCHAR(8000)
, @environment_id BIGINT
, @logging_level SMALLINT
, @syncronised_exec SMALLINT
, @delimiter VARCHAR(255)
, @ssis_error_txt VARCHAR(255)
-- set variable defaults
SELECT
@v_return_status = 0
, @delimiter = ‘|’ -- delimiter for split function
-- set variable from the parameter containing details of the package
SET @param_string = (SELECT dbo.WsParameterReadF (‘pSSIS_Package’))
-- set input variable values
SELECT
@folder = (SELECT Item FROM dbo.ufn_split_string (@param_string,@delimiter) WHERE Ordinal = 1)
, @project = (SELECT Item FROM dbo.ufn_split_string (@param_string,@delimiter) WHERE Ordinal = 2)
, @package = (SELECT Item FROM dbo.ufn_split_string (@param_string,@delimiter) WHERE Ordinal = 3)
, @environment_name = (SELECT Item FROM dbo.ufn_split_string (@param_string,@delimiter) WHERE Ordinal = 4)
, @logging_level = (SELECT ISNULL(Item,1) FROM dbo.ufn_split_string (@param_string,@delimiter) WHERE Ordinal
= 5) -- default logging = basic (1)
, @syncronised_exec = (SELECT ISNULL(Item,1) FROM dbo.ufn_split_string (@param_string,@delimiter) WHERE
Ordinal = 6) -- default sync = true (1)
SELECT @environment_id = (SELECT reference_id FROM [SSISDB].[catalog].[environment_references] WHERE
environment_name = @environment_name AND environment_folder_name = @folder)
SELECT @environment_name = CASE WHEN @environment_name IS NULL THEN 1 ELSE @environment_name
END,
@logging_level = CASE WHEN @logging_level IS NULL THEN 1 ELSE @logging_level END,
@syncronised_exec = CASE WHEN @syncronised_exec IS NULL THEN 1 ELSE @syncronised_exec END
BEGIN TRY
BEGIN
-- create package execution container
EXEC [SSISDB].[catalog].[create_execution]
@package_name = @package
, @execution_id = @execution_id OUTPUT

WhereScape White Paper
www.wherescape.com
- 15 -
, @folder_name = @folder
, @project_name = @project
, @reference_id = @environment_id
, @use32bitruntime = FALSE;
-- set logging level paramter value
EXEC [SSISDB].[catalog].[set_execution_parameter_value]
@execution_id
, @object_type = 50 -- execution param
, @parameter_name = N’LOGGING_LEVEL’
, @parameter_value = @logging_level;
-- set sync/non-sync execution mode
EXEC [SSISDB].[catalog].[set_execution_parameter_value]
@execution_id -- execution_id from catalog.create_execution
, @object_type = 50 -- execution param
, @parameter_name = N’SYNCHRONIZED’
, @parameter_value = @syncronised_exec;
-- set your own custom paramter values here if required
-- execute the package itself
EXEC [SSISDB].[catalog].[start_execution] @execution_id;
END
-- if a an execution error occurs then raise a custom error message
-- note: if an ssis error occurs the sprocs will succeed which is why we need this step
IF EXISTS (
SELECT 1
FROM [SSISDB].[catalog].[executions]
WHERE execution_id = @execution_id
AND [status] IN (4, 6) -- failure, ended unexpectedly statuses
)
BEGIN
SET @ssis_error_txt = ‘SSIS Package error occurred. Check SSIS catalog view [catalog].[operation_
messages] for details. SELECT * FROM [SSISDB].[catalog].[operation_messages] WHERE operation_id = ‘ + CAST (@
execution_id AS VARCHAR(64))
RAISERROR(@ssis_error_txt,16,1)
END
-- set the success return values
SET @v_return_status = ISNULL(ERROR_NUMBER(),0)
SET @v_return_msg = ‘SSIS Package execution succeeded. Check SSIS catalog view [catalog].[executions] for
details. execution id = ‘ + CAST (@execution_id AS VARCHAR(64))
END TRY
-- catch the error if it occurs
BEGIN CATCH
-- set the error return values

WhereScape White Paper
www.wherescape.com
- 16 -
SET @v_return_status = ISNULL(ERROR_NUMBER(),0)
SET @v_return_msg = ERROR_MESSAGE()
END CATCH
SELECT @v_count = @@SPID
SELECT
@v_return_status = @v_return_status
, @v_row_count = @@ROWCOUNT
--===============================================================
-- Handle Error
--===============================================================
IF @v_return_status <> 0
BEGIN
SET @v_db_code = CONVERT(varchar, @v_return_status)
SELECT @v_db_msg = description FROM master.dbo.sysmessages
WHERE error = @v_return_status
SET @p_return_msg = ‘Unhandled Exception in WS_RUN_SSIS_Catalog_Package at step ‘
+ CONVERT(varchar,@v_step) + SUBSTRING(@v_db_msg,1,150)
EXEC @v_return_status = WsWrkAudit ‘F’,@p_job_name,@p_task_name,
@p_sequence,@p_return_msg,@v_return_msg,@v_return_msg,@p_task_id,@p_job_id
SET @p_status = -3
RETURN 0
END
--***************************************************************
--End of custom code.
--===============================================================
--===============================================================
--All Done report the results and return.
--p_status is the return code. Valid values are:
-- 1 successful completion
-- -2 failed with error
-- -3 failed with unhandled error
--p_return_msg is a 256 character message which should
-- provide a summary of the result of this procedure.
--===============================================================
SET @v_step = 200
SET @p_status = 1
SET @p_return_msg = ‘WS_RUN_SSIS_Catalog_Package completed. ‘
+ @v_return_msg
RETURN 0

WhereScape White Paper
www.wherescape.com
- 17 -
Appendix C (ufn_split_string)
CREATE FUNCTION dbo.ufn_split_string
(
@List AS VARCHAR(MAX)
, @Delimiter AS VARCHAR(255) = NULL
)
RETURNS @List_table TABLE (
Ordinal INT NOT NULL
, Item VARCHAR(8000) NOT NULL
)
AS
BEGIN
DECLARE
@DelimPos1 AS INT
, @DelimPos2 AS INT
, @DelimLen AS INT
, @Ord AS INT
SELECT
-- Initialise vars
@DelimPos1 = 0
, @DelimPos2 = 0
, @DelimLen = 0
, @Ord = 1
-- Intialise input params to defaults
, @Delimiter = CASE ISNULL(@Delimiter, ‘’)
WHEN ‘’ THEN ‘,’
ELSE @Delimiter
END
SELECT
-- Initialise vars
@DelimLen = LEN(@Delimiter)
, @DelimPos1 = -LEN(@Delimiter) + 1
IF (@List IS NOT NULL)
BEGIN
SELECT @DelimPos2 = CHARINDEX(@Delimiter, @List)
WHILE (@DelimPos2 > 0)
BEGIN
INSERT INTO @List_table (
Ordinal
, Item
)
VALUES
(
@Ord
, SUBSTRING(@List, @DelimPos1 + @DelimLen, @DelimPos2 - @DelimPos1 - @DelimLen)
)

WhereScape White Paper
www.wherescape.com
- 18 -
SELECT
@DelimPos1 = @DelimPos2
, @DelimPos2 = CHARINDEX(@Delimiter, @List, @DelimPos2 + @DelimLen)
, @Ord = @Ord + 1
END
INSERT INTO @List_table (
Ordinal
, Item
)
VALUES
(
@Ord
, SUBSTRING(@List, @DelimPos1 + @DelimLen, LEN(@List) - @DelimPos1)
)
END
RETURN
END
Version 02
About WhereScape
The pioneer in data warehouse automation software, WhereScape empowers organizations constrained by time, money or lack of resources,
to deliver business value from their decision support infrastructure – including enterprise data warehouses, business facing data marts, and
big data solutions. WhereScape has global operations in the USA, UK, Singapore, and New Zealand. www.wherescape.com
