
BUSINESS DEVELOPMENT GUIDEJANUARY 2024, VERSION 1.2
ZSCALER AND FORTINET
DEPLOYMENT GUIDE

2©2024 Zscaler, Inc. All rights reserved.
ZSCALER AND FORTINET DEPLOYMENT GUIDE
Contents
Terms and Acronyms 5
About This Document 6
Zscaler Overview 6
Fortinet Overview 6
Audience 6
Soware Versions 6
Prerequisites 6
Request for Comments 7
Zscaler and Fortinet Introduction 8
ZIA Overview 8
ZPA Overview 8
FortiGate Overview 9
FortiNDR Overview 9
Fortinet Resources 9
Traffic Forwarding with FortiGate 10
Configuring GRE and IPSec Tunnels on ZIA 10
Configuring Fortinet for GRE and IPSec 11
Verify Access to FortiOS 11
FortiGate Dashboard 11
Prerequisites to Configuring GRE Tunnels 11
Create GRE Tunnels 12
Configure GRE Tunnel Interfaces 12
Performance SLAs 13
Prerequisites to Configuring Performance SLAs 13
Configuring Performance SLAs 13

3©2024 Zscaler, Inc. All rights reserved.
ZSCALER AND FORTINET DEPLOYMENT GUIDE
Configuring IPSec Tunnels 14
IPSec Wizard 14
Configure IPSec—General 14
Configure IPSec—Phase 1 15
Configure IPSec—Phase 2 15
Verify IPSec Configuration 16
Configuring Firewall Policy 16
Create Firewall Policy 16
Verify Firewall Policies 17
Configuring SD-WAN 17
Create SD-WAN Member for Primary Public Service Edge 17
Create SD-WAN Member for Secondary Public Service Edge 17
Verify SD-WAN Members 18
Configuring SD-WAN Rules 19
Create SD-WAN Rule 19
Verify SD-WAN Rule 20
Verify Configuration with Zscaler Test Page 20
Request Verification Page 20
FortiNDR Integration 21
Zscaler NSS 21
Proxy Sensor 21
NSS Feed Configuration 21
Configuration Issues 21
Base Configuration 21
Web 22
DNS 23
Firewall 24

4©2024 Zscaler, Inc. All rights reserved.
ZSCALER AND FORTINET DEPLOYMENT GUIDE
Cloud NSS 25
Cloud NSS Setup for S3 25
Configuring Cloud NSS for Web Logs 25
Configuring Cloud NSS for Firewall Logs 27
Configuring Cloud NSS for DNS Logs 28
Appendix A: Requesting Zscaler Support 29

ZSCALER AND FORTINET DEPLOYMENT GUIDE
5©2024 Zscaler, Inc. All rights reserved.
Terms and Acronyms
The following table defines acronyms used in this deployment guide. When applicable, a Request for Change (RFC) is
included in the Definition column for your reference.
Acronym Definition
CA Central Authority (Zscaler)
CSV Comma-Separated Values
DLP Data Loss Prevention
DNS Domain Name Service
DPD Dead Peer Detection (RFC 3706)
GRE Generic Routing Encapsulation (RFC2890)
ICMP Internet Control Message Protocol
IdP Identity Provider
IKE Internet Key Exchange (RFC2409)
IPS Intrusion Prevention System
IPSec Internet Protocol Security (RFC2411)
PFS Perfect Forward Secrecy
PSK Pre-Shared Key
SaaS Soware as a Service
SLA Service Level Agreement
SSL Secure Socket Layer (RFC6101)
TLS Transport Layer Security
VDI Virtual Desktop Infrastructure
XFF X-Forwarded-For (RFC7239)
ZPC Zscaler Posture Control (Zscaler)
ZDX Zscaler Digital Experience (Zscaler)
ZIA Zscaler Internet Access (Zscaler)
ZPA Zscaler Private Access (Zscaler)

ZSCALER AND FORTINET DEPLOYMENT GUIDE
6©2024 Zscaler, Inc. All rights reserved.
About This Document
The following sections describe the organizations and requirements of this deployment guide.
Zscaler Overview
Zscaler (NASDAQ: ZS) enables the world’s leading organizations to securely transform their networks and applications for
a mobile and cloud-first world. Its flagship Zscaler Internet Access (ZIA) and Zscaler Private Access (ZPA) services create
fast, secure connections between users and applications, regardless of device, location, or network. Zscaler delivers its
services 100% in the cloud and offers the simplicity, enhanced security, and improved user experience that traditional
appliances or hybrid solutions can’t match. Used in more than 185 countries, Zscaler operates a massive, global cloud
security platform that protects thousands of enterprises and government agencies from cyberaacks and data loss. To
learn more, see Zscaler’s website.
Fortinet Overview
Fortinet (NASDAQ: FTNT) is a driving force in the evolution of cybersecurity and the convergence of networking and
security. Fortinet’s mission is to secure people, devices, and data everywhere, and today they deliver cybersecurity
everywhere you need it with the largest integrated portfolio of over 50 enterprise-grade products. Well over half a million
customers trust Fortinet’s solutions, which are among the most deployed, most patented, and most validated in the
industry. The Fortinet Training Institute, one of the largest and broadest training programs in the industry, is dedicated to
making cybersecurity training and new career opportunities available to everyone. FortiGuard Labs, Fortinet’s elite threat
intelligence and research organization, develops and uses leading-edge machine learning and AI technologies to provide
customers with timely and consistently top-rated protection and actionable threat intelligence. To learn more, refer to
Fortinet’s website.
Audience
This guide is for network administrators, endpoint and IT administrators, and security analysts responsible for deploying,
monitoring, and managing enterprise security systems. For additional product and company resources, see:
• Zscaler Resources
• Fortinet Resources
• Appendix A: Requesting Zscaler Support
Soware Versions
This document was authored using the latest version of Zscaler soware.
Prerequisites
Zscaler Internet Access (ZIA)
• A working instance of ZIA 5.7 or later
• Administrator login credentials to ZIA
Fortinet
• FortiOS 6.2.0 build 0866 (GA) or later
• Administrator login credentials to Fortinet device

ZSCALER AND FORTINET DEPLOYMENT GUIDE
7©2024 Zscaler, Inc. All rights reserved.
Request for Comments
• For prospects and customers: Zscaler values reader opinions and experiences. Contact partner-doc-support@
zscaler.com to offer feedback or corrections for this guide.
• For Zscaler employees: Contact z-bd-sa@zscaler.com to reach the team that validated and authored the
integrations in this document.

ZSCALER AND FORTINET DEPLOYMENT GUIDE
8©2024 Zscaler, Inc. All rights reserved.
Zscaler and Fortinet Introduction
Overviews of the Zscaler and Fortinet applications are described in this section.
ZIA Overview
ZIA is a secure internet and web gateway delivered as a service from the cloud. Think of ZIA as a secure internet on-
ramp—just make Zscaler your next hop to the internet via one of the following methods:
• Seing up a tunnel (GRE or IPSec) to the closest Zscaler data center (for offices).
• Forwarding traffic via our lightweight Zscaler Client Connector or PAC file (for mobile employees).
No maer where users connect—a coffee shop in Milan, a hotel in Hong Kong, or a VDI instance in South Korea—they get
identical protection. ZIA sits between your users and the internet and inspects every transaction inline across multiple
security techniques (even within SSL).
You get full protection from web and internet threats. The Zscaler cloud platform supports Cloud Firewall, IPS,
Sandboxing, DLP, and Browser Isolation, allowing you to start with the services you need now and activate others as your
needs grow.
ZPA Overview
ZPA is a cloud service that provides secure remote access to internal applications running on a cloud or data center using
a Zero Trust framework. With ZPA, applications are never exposed to the internet, making them completely invisible
to unauthorized users. The service enables the applications to connect to users via inside-out connectivity rather than
extending the network to them.
ZPA provides a simple, secure, and effective way to access internal applications. Access is based on policies created by
the IT administrator within the ZPA Admin Portal and hosted within the Zscaler cloud. On each user device, soware
called Zscaler Client Connector is installed. Zscaler Client Connector ensures the user’s device posture and extends a
secure microtunnel out to the Zscaler cloud when a user aempts to access an internal application.
Zscaler Resources
The following table contains links to Zscaler resources based on general topic areas.
Name Definition
ZIA Help Portal Help articles for ZIA.
ZPA Help Portal Help articles for ZPA.
Zscaler Tools Troubleshooting, security and analytics, and browser extensions that help
Zscaler determine your security needs.
Zscaler Training and Certification Training designed to help you maximize Zscaler products.
Submit a Zscaler Support Ticket Zscaler Support portal for submiing requests and issues.
If you are using this guide to implement a solution at a government agency, some of the content might be different for your deployment.
Efforts are made throughout the guide to note where government agencies might need different parameters or input. If you have
questions, contact your Zscaler Account representative.

ZSCALER AND FORTINET DEPLOYMENT GUIDE
9©2024 Zscaler, Inc. All rights reserved.
The following table contains links to Zscaler resources for government agencies.
Name Definition
ZIA Help Portal Help articles for ZIA.
ZPA Help Portal Help articles for ZPA.
Zscaler Tools Troubleshooting, security and analytics, and browser extensions that help
Zscaler determine your security needs.
Zscaler Training and Certification Training designed to help you maximize Zscaler products.
Submit a Zscaler Support Ticket Zscaler Support portal for submiing requests and issues.
FortiGate Overview
FortiGate delivers fast, scalable, and flexible SD-WAN on-premises and in the cloud. Fortinet SD-WAN supports cloud-
first, security-sensitive, and global enterprises, as well as the hybrid workforce. The Secure Networking approach uses one
operating system and consolidates SD-WAN and application gateway functions.
FortiNDR Overview
Fortinet’s SaaS-based FortiNDR Cloud leverages AI and machine learning (ML), behavioral, and human analysis to inspect
network traffic to detect malicious behavior early while reducing false positives. FortiNDR Cloud provides unified network
traffic visibility across multi-cloud and hybrid environments as well as distributed workforces and constrained, mission-
critical environments. FortiNDR Cloud automatically identifies anomalous and malicious behavior, provides risk scores,
and shares relevant threat intelligence to assist security teams in prioritizing response efforts.
Fortinet Resources
The following table contains links to Fortinet support resources.
Name Definition
FortiNDR Documentation Online documentation for FortiNDR.
FortiOS Documentation Online documentation for FortiOS.
Fortinet Training & Certification Fortinet solution training and certifications.
Fortinet Support Fortinet solution online support.

ZSCALER AND FORTINET DEPLOYMENT GUIDE
10©2024 Zscaler, Inc. All rights reserved.
Traffic Forwarding with FortiGate
You can configure FortiGate to forward traffic to Zscaler SSE via GRE or IPSec tunnels.
Configuring GRE and IPSec Tunnels on ZIA
There are three major steps when configuring GRE or IPsec tunnels to ZIA.
1. You must locate which data centers are available to you and the hostname / IP address of the VIP to establish a
tunnel towards. To learn more, see Locating the Hostnames and IP Addresses of Public Service Edges (government
agencies, see Locating the Hostnames and IP Addresses of Public Service Edges).
2. You must configure the tunnel itself on the ZIA side. To learn more about configuring a GRE Tunnel and a VPN
Credential (for an IPsec tunnel), see:
• Configuring GRE Tunnels (government agencies, see Configuring GRE Tunnels)
• Adding VPN Credentials (government agencies, see Adding VPN Credentials)
3. You must add the VPN credential to a location. For GRE, the steps are similar, but instead of selecting a VPN
Credential, select a Static IP Address. To learn more, see Configuring Locations (government agencies, see
Configuring Locations).
If you have problems with any of these steps, open a ticket with Zscaler Support (government agencies, see Zscaler
Support).

ZSCALER AND FORTINET DEPLOYMENT GUIDE
11©2024 Zscaler, Inc. All rights reserved.
Configuring Fortinet for GRE and IPSec
The following sections explain how to configure Fortinet to use GRE and IPSec tunnels.
Verify Access to FortiOS
To connect to the UI using a web browser, you must configure an interface to allow administrative access over HTTPS or
over both HTTPS and HTTP. If you have not changed the admin account password, use the default username, admin, and
leave the password field blank.
Figure 1. FortiOS Login
FortiGate Dashboard
The dashboard displays various widgets with important system information and allows you to configure some system
options. The System Information widget lists information relevant to the FortiGate system, including hostname, serial
number, and firmware. The Licenses widget lists the status of various licenses, such as FortiCare Support and IPS.
Figure 2. FortiGate Dashboard
Prerequisites to Configuring GRE Tunnels
While most of the tasks to configure your FortiGate can be accomplished using the UI, this configuration guide makes use
of advanced features that require the CLI for portions of the configuration.
ZSCALER AND FORTINET DEPLOYMENT GUIDE
12©2024 Zscaler, Inc. All rights reserved.
Create GRE Tunnels
GRE tunnels are configured using the FortiGate CLI. In the following configuration, remote-gw is the IP address of your
Zscaler tunnel and local-gw is the IP address of your FortiGate’s ISP facing interface.
This step creates the GRE tunnels and adds them as interfaces to the FortiGate.
cong system gre-tunnel edit "GRE-SITE1"
set interface "wan1"
set remote-gw 199.168.148.131
set local-gw 72.52.82.217
next
edit "GRE-SITE2"
set interface "wan1"
set remote-gw 104.129.194.38
set local-gw 72.52.82.217
next
end
Configure GRE Tunnel Interfaces
This next step configures the newly created FortiGate interfaces. In this config, ip is an address in a /30 subnet provided
by Zscaler for the express purpose of GRE tunnel connectivity.
cong system interface
edit "GRE-SITE1"
set ip 172.17.12.129 255.255.255.252
set allowaccess ping set type tunnel
set interface "wan1"
next
edit "GRE-SITE2"
set ip 172.17.12.133 255.255.255.252
set allowaccess ping set type tunnel
set interface "wan1"
next
end

ZSCALER AND FORTINET DEPLOYMENT GUIDE
13©2024 Zscaler, Inc. All rights reserved.
Performance SLAs
This section explains how to configure Layer-7 Health Checks (aka HTTP Ping).
Prerequisites to Configuring Performance SLAs
If you have not yet done so, configure SD-WAN interfaces as described in Configuring SD-WAN. You cannot configure
performance SLAs on your FortiGate unless SD-WAN is enabled and at least one interface is marked as an SD-WAN
member interface.
Configuring Performance SLAs
You must use the CLI to enable Performance SLA health checks on your new GRE tunnels:
cong system virtual-wan-link
cong health-check
edit "Zscaler_VPNTEST"
set server "gateway.zscalerbeta.net"
set protocol http
set http-get "v/vpntest"
set interval 10000
set failtime 10
set members 1 2
congure sla
edit 1
set latency-threshold 250
set jitter-threshold 100
set packetloss-threshold 5
next
end
next
end
end
The rest of this document only uses the HTTP interface.

ZSCALER AND FORTINET DEPLOYMENT GUIDE
14©2024 Zscaler, Inc. All rights reserved.
Configuring IPSec Tunnels
The rest of this section only uses the web UI.
IPSec Wizard
To create the VPN, go to VPN > IPsec Wizard and create a new tunnel using a pre-existing template. Name the VPN. The
tunnel name cannot include any spaces or exceed 13 characters.
Figure 3. IPSec Wizard—Step 1
Configure IPSec—General
Configure the Network seings, as shown in the following figure. The Dynamic DNS entry is the hostname to the Public
Service Edge you want to use.
Figure 4. IPSec Wizard—Step 2

ZSCALER AND FORTINET DEPLOYMENT GUIDE
15©2024 Zscaler, Inc. All rights reserved.
Configure IPSec—Phase 1
Configure your seings to match the following figure. The Pre-Shared Key (PSK) is unique per site. The Local ID is the
FQDN you configured in the earlier sections.
Figure 5. IPSec Wizard—Step 3
Configure IPSec—Phase 2
Configure your seings to match the following figure. When completed, save these seings.
Figure 6. IPSec Wizard—Step 4

ZSCALER AND FORTINET DEPLOYMENT GUIDE
16©2024 Zscaler, Inc. All rights reserved.
Verify IPSec Configuration
Aer saving your seings, you see your tunnels Up. If they are not established, recheck your Pre-Shared Key.
Figure 7. Verify IPSec configuration
Configuring Firewall Policy
The following sections describe how to configure firewall policies.
Create Firewall Policy
When you create a Firewall policy, seings should match the configuration shown in the following figure. Your Outgoing
Interface might have a different name, so adjust this seing to match your internet-facing link.
Figure 8. Configure Firewall Policy

ZSCALER AND FORTINET DEPLOYMENT GUIDE
17©2024 Zscaler, Inc. All rights reserved.
Verify Firewall Policies
Repeat the steps in the following section, as shown in the following figure.
Figure 9. Verify Firewall Policies
Configuring SD-WAN
Configure the primary and secondary ZIA Public Service Edge as a member of the SD-WAN.
Create SD-WAN Member for Primary Public Service Edge
Configure the primary Public Service Edge as a SD-WAN member, with a cost of 5.
Figure 10. Config SD-WAN for Primary Public Service Edge
Create SD-WAN Member for Secondary Public Service Edge
Configure the primary Public Service Edge as a SD-WAN member, with a cost of 10. Having a higher cost than the prior
SD-WAN member determines this SD-WAN member to be secondary (or as a backup).
Figure 11. Config SD-WAN for Secondary Public Service Edge

ZSCALER AND FORTINET DEPLOYMENT GUIDE
18©2024 Zscaler, Inc. All rights reserved.
Verify SD-WAN Members
Aer both SD-WAN members are configured, verify the configuration. Your screen is similar to the following figure.
Figure 12. Verify SD-WAN Members

ZSCALER AND FORTINET DEPLOYMENT GUIDE
19©2024 Zscaler, Inc. All rights reserved.
Configuring SD-WAN Rules
This section describes how to configure a SD-WAN rule. This ties the Performance SLA probe to each SD-WAN member
for the primary and secondary Public Service Edge.
Create SD-WAN Rule
By using a strategy of Lowest Cost (SLA), this determines which Public Service Edge is the active primary and which Public
Service Edge is the standby secondary.
Figure 13. Configure SD-WAN Rule

ZSCALER AND FORTINET DEPLOYMENT GUIDE
20©2024 Zscaler, Inc. All rights reserved.
Verify SD-WAN Rule
Aer you have configured your SD-WAN rule, verify your configuration. Your screen is similar to the following.
Figure 14. Verify SD-WAN Rule
Verify Configuration with Zscaler Test Page
The following sections describe verifying the configuration with a Zscaler test page.
Request Verification Page
Use the URL hps://ip.zscaler.com to confirm if you are transiting ZIA. This is what you see if you are not going through
ZIA.
Figure 15. Non-working Example
If you are transiting ZIA, you should see the following:
Figure 16. Working Example

ZSCALER AND FORTINET DEPLOYMENT GUIDE
21©2024 Zscaler, Inc. All rights reserved.
FortiNDR Integration
Fortinet NDR solutions combine AI-driven and human analysis to detect and respond to known and unknown network
threats. This integration uses logs from Zscaler Internet Access.
This document describes the Zscaler setup needed for log ingestion.
• Zscaler NSS
• Proxy sensor
• NSS feed configuration
Refer to supplemental online documentation for details needed on the Fortinet platform:
• FortiNDR Cloud
• Zscaler setup
Zscaler NSS
Nanolog Streaming Service (NSS) is a Zscaler-provided utility to download logs. Zscaler requires the deployment of virtual
machines—one each for web and firewall logs. Customers that have already deployed NSS VMs for external log ingestion
can use the same ones for FortiNDR Cloud. If you do not have NSS installed, see the Zscaler help pages or contact Zscaler
Support for help.
Proxy Sensor
NSS forwards logs using the syslog protocol. The proxy sensor is designed to receive these logs and upload them to the
same destination as FortiNDR Cloud sensors. Aer ingested, the Zscaler events are mostly treated the same as Zeek
events.
NSS Feed Configuration
Aer the NSS and proxy sensor instances have been deployed, feeds must be configured to enable loing. See Zscaler’s
About NSS Feeds (government agencies, see About NSS Feeds) if you need help.
Configuration Issues
It is important that the feeds are configured correctly. If the system is not configured correctly, there is data loss. In the
worst case scenario, it can cause problems with the ingest pipeline.
Base Configuration
All feeds share the same base configuration:
The Docker Container must be run from a system that is separate from the NSS log server.
ZSCALER AND FORTINET DEPLOYMENT GUIDE
22©2024 Zscaler, Inc. All rights reserved.
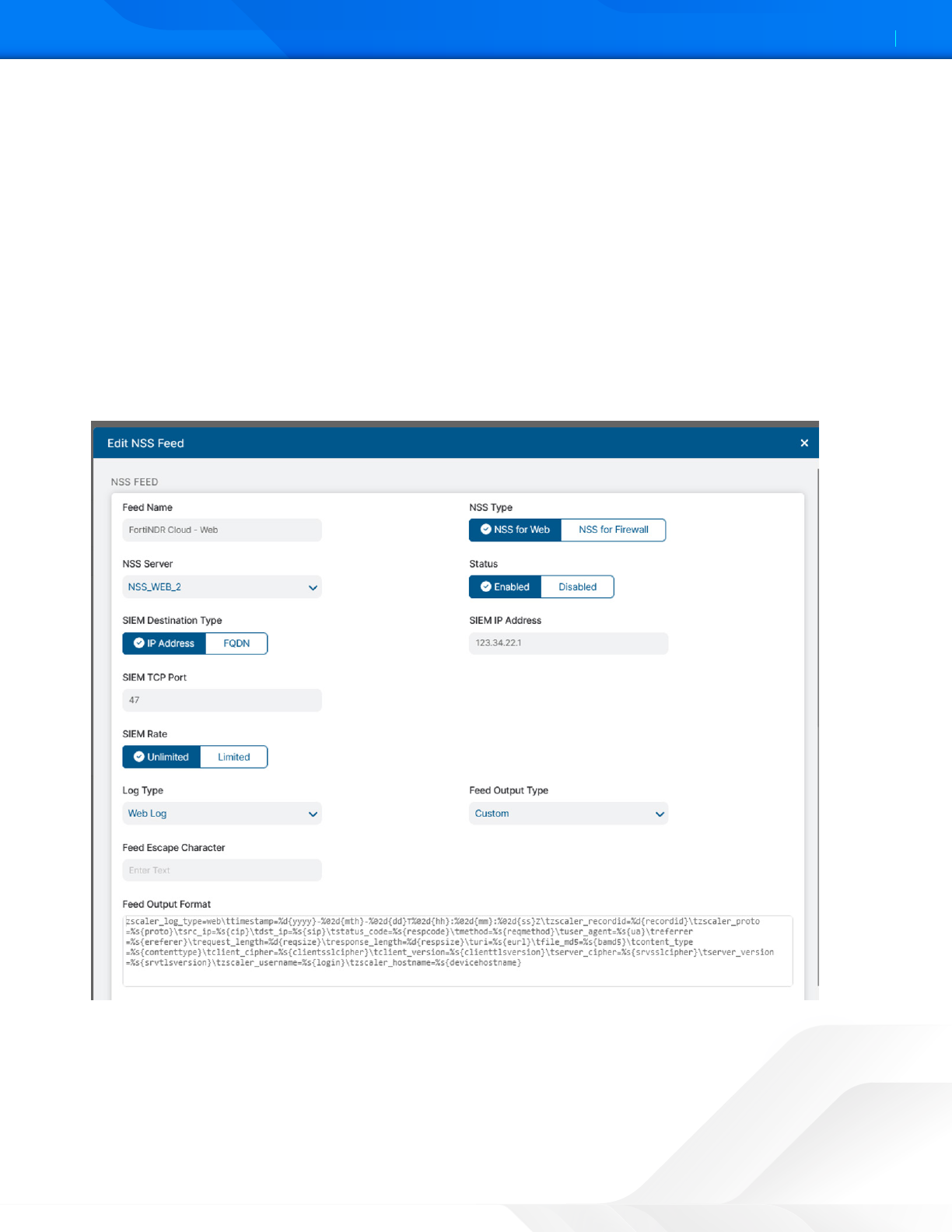
Web
1. Feed Name: FortiNDR Cloud - Web
2. NSS Type: NSS for Web
3. Log Type: Web Log
4. Feed Output Format:
zscaler_log_type=web\ttimestamp=%d{yyyy}-%02d{mth}-%02d{dd}T%02d{hh}:%02d{mm}:%02d{ss}
Z\tzscaler_recordid=%d{recordid}\tzscaler_proto=%s{proto}\tsrc_ip=%s{cip}\tdst_
ip=%s{sip}\tstatus_code=%s{respcode}\tmethod=%s{reqmethod}\tuser_agent=%s{ua}\
treferrer=%s{ereferer}\trequest_length=%d{reqsize}\tresponse_length=%d{resp-
size}\turi=%s{eurl}\tle_md5=%s{bamd5}\tcontent_type=%s{contenttype}\tclient_ci-
pher=%s{clientsslcipher}\tclient_version=%s{clienttlsversion}\tserver_cipher=%s{s-
rvsslcipher}\tserver_version=%s{srvtlsversion}\tzscaler_username=%s{login}\
tzscaler_hostname=%s{devicehostname}
Figure 17. Web NSS feed

ZSCALER AND FORTINET DEPLOYMENT GUIDE
23©2024 Zscaler, Inc. All rights reserved.
DNS
1. Feed Name: FortiNDR Cloud - DNS
2. NSS Type: NSS for Firewall
3. Log Type: DNS Logs
4. Feed Output Format:
zscaler_log_type=dns\ttimestamp=%d{yyyy}-%02d{mth}-%02d{dd}T%02d{hh}:%02d{mm}:%02d{ss}
Z\tzscaler_recordid=%d{recordid}\tsrc_ip=%s{cip}\tdst_ip=%s{sip}\tdst_port=%d{sport}\
tquery=%s{req}\tqtype_name=%s{reqtype}\tresponse=%s{res}\tzscaler_username=%s{login}\
tzscaler_hostname=%s{devicehostname}
Figure 18. DNS NSS feed

ZSCALER AND FORTINET DEPLOYMENT GUIDE
24©2024 Zscaler, Inc. All rights reserved.
Firewall
1. Feed Name: FortiNDR Cloud - Firewall
2. NSS Type: NSS for Firewall
3. Log Type: Firewall Logs
4. Feed Output Format:
zscaler_log_type=rewall\ttimestamp=%d{yyyy}-%02d{mth}-%02d{dd}
T%02d{hh}:%02d{mm}:%02d{ss}Z\tzscaler_recordid=%d{recordid}\tsrc_ip=%s{c-
sip}\tsrc_port=%d{csport}\tdst_ip=%s{cdip}\tdst_port=%d{cdport}\tdura-
tion=%d{durationms}\tprotocol=%s{ipproto}\tservice=%s{nwsvc}\trequest_
bytes=%ld{outbytes}\tresponse_bytes=%ld{inbytes}\tzscaler_username=%s{login}\
tzscaler_hostname=%s{devicehostname}
Figure 19. Firewall NSS feed
ZSCALER AND FORTINET DEPLOYMENT GUIDE
25©2024 Zscaler, Inc. All rights reserved.
Cloud NSS
Zscaler Cloud NSS is a managed service from Zscaler. When using Cloud NSS, you do not need to deploy the NSS Virtual
Machines. Cloud NSS sends logs to a HTTP endpoint or an S3 bucket. The integration with FortiNDR is through the S3
bucket path. Check with your Zscaler Account team to ensure you have this subscription enabled.
Cloud NSS Setup for S3
The S3 bucket that Zscaler sends logs to is customer-owned. Zscaler accesses it via credentials provided by the customer
setup. Ensure that access to the S3 bucket is restricted with proper permissions.
Ensure that you have the following to configure Zscaler Cloud NSS. Contact Fortinet Support to obtain these values.
• AWS Access Id
• AWS Secret Key
• S3 Folder URL
Using S3 requires the correct set of permissions and configuration. To learn more, see the Zscaler and S3 Deployment
Guide, section Zscaler Cloud NSS with Amazon S3, on seing up S3 to work with Cloud NSS.
Configuring Cloud NSS for Web Logs
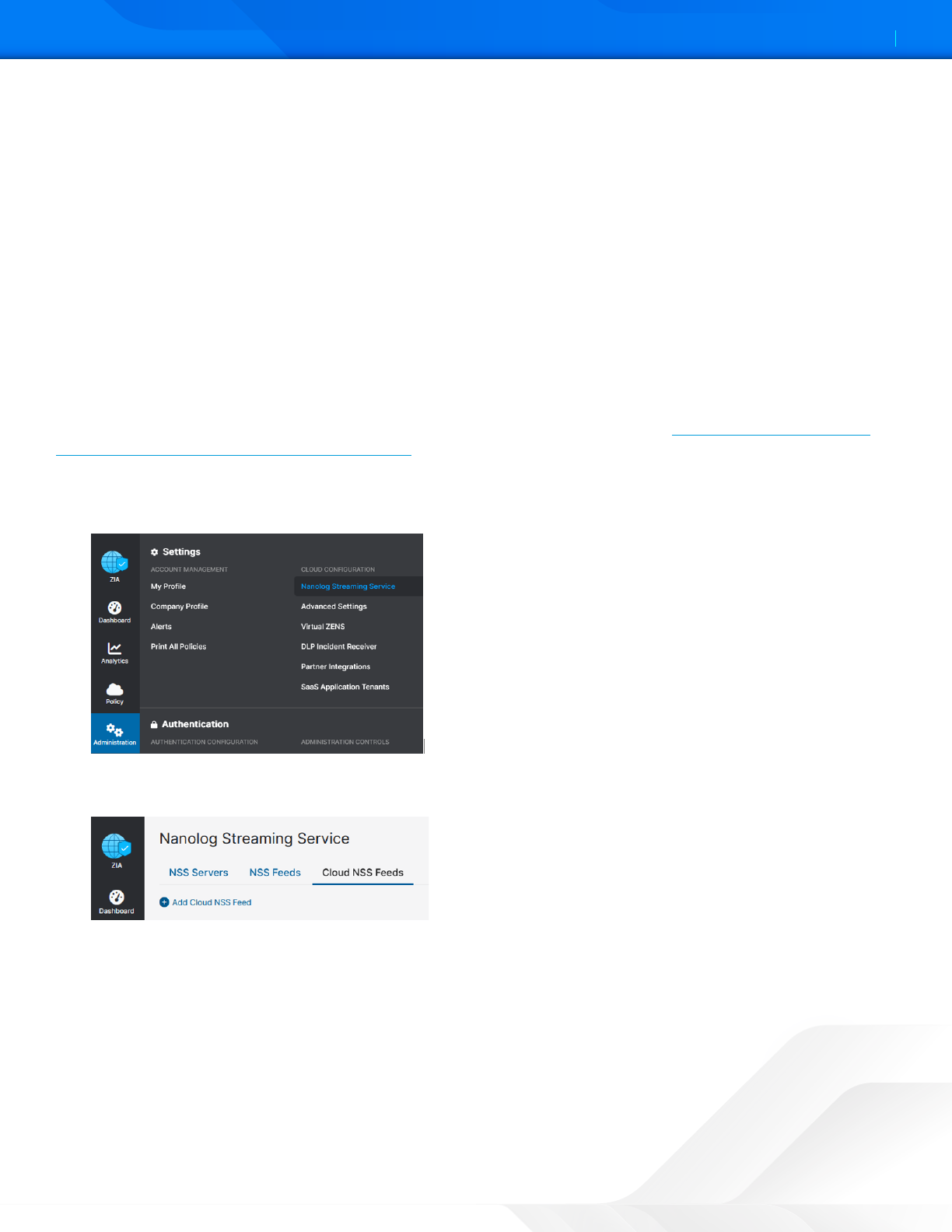
1. Log in as an administrator and go to Administration > Nanolog Streaming Service.
Figure 20. Log in as an administrator
2. Go to Cloud NSS Feeds and click Add Cloud NSS Feed.
Figure 21. Cloud NSS Feeds

ZSCALER AND FORTINET DEPLOYMENT GUIDE
26©2024 Zscaler, Inc. All rights reserved.
3. In the Add Cloud NSS Feed dialog:
a. Enter a Feed Name.
b. Select NSS for Web.
c. Status: Enabled.
d. SIEM Rate: Unlimited.
e. SIEM Type: S3.
f. Enter information gathered for S3 Folder URL, AWS Access Id, and AWS Secret Key.
g. Enter a dummy HTTP key and value pair. This is required.
h. In the Formaing section, choose Web Log, Custom type, and enter ,\" as the feed escape character.
i. Feed Output Format:
zscaler_log_type=web\ttimestamp=%d{yyyy}-%02d{mth}-%02d{dd}T%02d{hh}:%02d{mm}:%02d{ss}
Z\tzscaler_recordid=%d{recordid}\tzscaler_proto=%s{proto}\tsrc_ip=%s{cip}\tdst_
ip=%s{sip}\tstatus_code=%s{respcode}\tmethod=%s{reqmethod}\tuser_agent=%s{ua}\
treferrer=%s{ereferer}\trequest_length=%d{reqsize}\tresponse_length=%d{resp-
size}\turi=%s{eurl}\tle_md5=%s{bamd5}\tcontent_type=%s{contenttype}\tclient_ci-
pher=%s{clientsslcipher}\tclient_version=%s{clienttlsversion}\tserver_cipher=%s{s-
rvsslcipher}\tserver_version=%s{srvtlsversion}\tzscaler_username=%s{login}\
tzscaler_hostname=%s{devicehostname}
Figure 22. Web Cloud NSS feed

ZSCALER AND FORTINET DEPLOYMENT GUIDE
27©2024 Zscaler, Inc. All rights reserved.
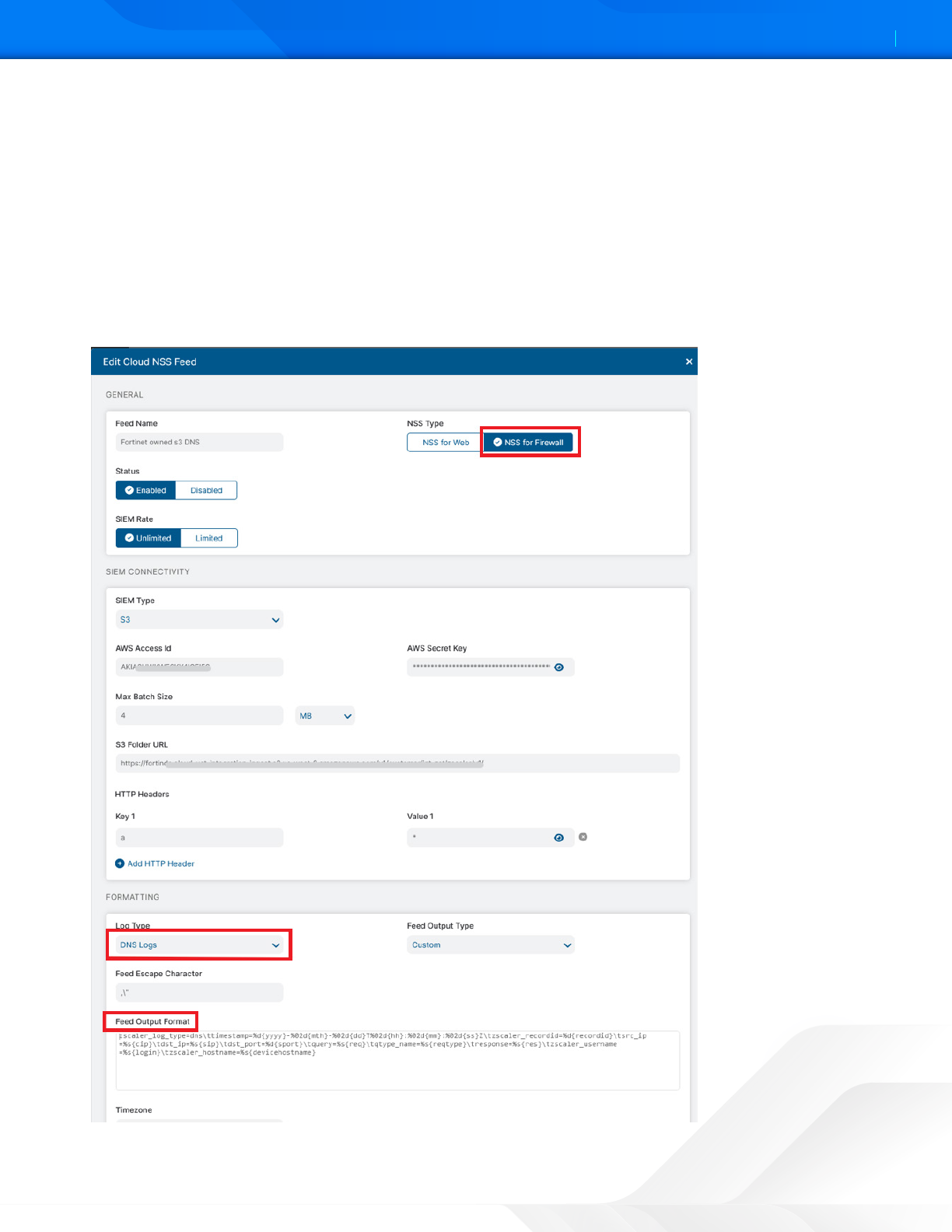
Configuring Cloud NSS for Firewall Logs
To configure Firewall logs, follow similar configuration steps for the Web Log with the following exceptions.
1. NSS Type: NSS for Firewall.
2. Log Type: Firewall Logs.
3. Feed Output Format:
zscaler_log_type=rewall\ttimestamp=%d{yyyy}-%02d{mth}-%02d{dd}
T%02d{hh}:%02d{mm}:%02d{ss}Z\tzscaler_recordid=%d{recordid}\tsrc_ip=%s{c-
sip}\tsrc_port=%d{csport}\tdst_ip=%s{cdip}\tdst_port=%d{cdport}\tdura-
tion=%d{durationms}\tprotocol=%s{ipproto}\tservice=%s{nwsvc}\trequest_
bytes=%ld{outbytes}\tresponse_bytes=%ld{inbytes}\tzscaler_username=%s{login}\
tzscaler_hostname=%s{devicehostname}
Figure 23. Firewall Cloud NSS feed
ZSCALER AND FORTINET DEPLOYMENT GUIDE
28©2024 Zscaler, Inc. All rights reserved.
Configuring Cloud NSS for DNS Logs
To configure DNS logs, follow similar configuration steps for the Web Log with the following exceptions.
1. NSS Type: NSS for Firewall.
2. Log Type: DNS Logs.
3. Feed Output Format:
zscaler_log_type=dns\ttimestamp=%d{yyyy}-%02d{mth}-%02d{dd}T%02d{hh}:%02d{mm}:%02d{ss}
Z\tzscaler_recordid=%d{recordid}\tsrc_ip=%s{cip}\tdst_ip=%s{sip}\tdst_port=%d{sport}\
tquery=%s{req}\tqtype_name=%s{reqtype}\tresponse=%s{res}\tzscaler_username=%s{login}\
tzscaler_hostname=%s{devicehostname}
Figure 24. DNS Cloud NSS feed

ZSCALER AND FORTINET DEPLOYMENT GUIDE
29©2024 Zscaler, Inc. All rights reserved.
Appendix A: Requesting Zscaler Support
If you need Zscaler Support to provision certain services or to help troubleshoot configuration and service issues, it is
available 24/7/365.
To contact Zscaler Support:
1. Go to Administration > Seings > Company Profile.
Figure 25. Collecting details to open support case with Zscaler TAC
2. Copy your Company ID.
Figure 26. Company ID

ZSCALER AND FORTINET DEPLOYMENT GUIDE
30©2024 Zscaler, Inc. All rights reserved.
3. With your company ID information, you can open a support ticket. Go to Dashboard > Support > Submit a Ticket.
Figure 27. Submit a ticket
