
CPA Evolution
Model Curriculum

Disclaimer: The contents of this publication do not necessarily reect the position or opinion of the American Institute of
CPAs (AICPA), its divisions and its committees, and do not necessarily reect the position or opinion of the National Association
of State Boards of Accountancy (NASBA), its divisions and its committees. This publication is designed to provide accurate and
authoritative information on the subject covered. It is distributed with the understanding that the authors are not engaged in
rendering legal, accounting or other professional services. If legal advice or other expert assistance is required, the services
of a competent professional should be sought.
For more information about the procedure for requesting permission to make copies of any part of this work, please email
copyright@aicpa.org with your request. Otherwise, requests should be written and mailed to the Permissions Department,
AICPA, 220 Leigh Farm Road, Durham, NC 27707–8110.

1 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Contents
3 Introduction
6 Information and Instructions for Use of CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
8 Part I: CPA Evolution Core
8 Section 1: Accounting and Data Analytics Core
8 Module 1: Financial Statements
10 Module 2: Select Financial Statement Accounts
14 Module 3: Select Financial Statement Transactions and Events
16 Module 4: Financial Statement Analysis and Metrics
16 Module 5: Financial Statements and Select Transactions for Not-For-Prot (NFP) Entities
18 Module 6: Financial Statements and Select Transactions for State and Local Governments
19 Module 7: Critical Thinking
19 Module 8: Financial Data Analytics
21 Module 9: Digital Acumen
22 Section 2: Audit and Accounting Information Systems Core
22 Module 1: Audit Environment
24 Module 2: Engagement Planning and Considerations
26 Module 3: Understanding an Entity and its Environment
29 Module 4: Information Technology
30 Module 5: Risk Assessment of Fraud and Noncompliance
31 Module 6: Assessing Risk of Material Misstatement
32 Module 7: Materiality
33 Module 8: Audit Evidence
34 Module 9: Audit Procedures
35 Module 10: Special Considerations
37 Module 11: Audit Conclusion
38 Module 12: Audit Reports
39 Module 13: Other Engagements
41 Module 14: Subsequent Events and Subsequently Discovered Facts
41 Module 15: Digital Acumen
42 Section 3: Tax Core
42 Module 1: Responsibilities in Tax Practice
42 Module 2: Methods of Taxation
42 Module 3: Federal Tax Procedures
43 Module 4: Legal Duties and Responsibilities
44 Module 5: Acquisition and Disposition of Assets
45 Module 6: Federal Taxation of Individuals
47 Module 7: C Corporations
48 Module 8: S Corporations
49 Module 9: Partnerships
50 Module 10: Limited Liability Companies
50 Module 11: Tax-Exempt Organizations
51 Module 12: Technology and Digital Acumen

2 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
52 Part II: CPA Evolution Discipline
52 Section 1: Business Analysis and Reporting (BAR) Discipline
52 Module 1: Accounting Research
52 Module 2: For-Prot Entity Financial Statements
53 Module 3: Select Financial Statement Accounts
54 Module 4: Select Transactions
56 Module 5: Cost accounting
57 Module 6: State and Local Governments
60 Module 7: Employee Benet Plan Accounting
60 Module 8: Planning Techniques
61 Module 9: Financial Statement Analysis
62 Module 10: Advanced Data Analytics
66 Section 2: Information Systems and Controls (ISC) Discipline
66 Module 1: IT Governance and Risk Assessment
69 Module 2: Performing Procedures, Tests of Internal Controls
70 Module 3: SOC Engagements
71 Module 4: Use and Management of Data
72 Module 5: Information Security and Protection of Information Assets
73 Section 3: Tax Compliance and Planning (TCP) Discipline
73 Module 1: Individual Tax Fundamentals and Tax Planning
75 Module 2: Acquisition, Use and Disposition of Assets
76 Module 3: Tax Accounting Methods
77 Module 4: Federal Taxation of Entities
78 Module 5: C Corporations
79 Module 6: S Corporations
80 Module 7: Partnerships
83 Module 8: Tax Planning for Entities
84 Module 9: Trusts
85 Module 10: Tax-Exempt Organizations
85 Module 11: Multijurisdictional Tax Basics
86 Module 12: Technology
86 Module 13: Tax Research
87 Module 14: Personal Financial Advisory Services
89 Appendix
89 Illustrative Accounting Program Structures for Future CPAs

3 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Introduction
Thank you for your interest in the AICPA’s and NASBA’s CPA Evolution Model Curriculum. It
was developed to assist faculty who want to prepare their students for the CPA profession.
It is materially aligned with the Uniform Accountancy Act Model Rules for education and reects
insights gathered through the 2021 CPA Exam Practice Analysis as well as the views of the
subject matter experts who served on the CPA Evolution Model Curriculum Task Forces.
The Task Forces were comprised of over 40 volunteers, including faculty from small schools and
large universities, CPAs in public practice, business and industry and representatives from state
boards of accountancy. The Task Forces met over 50 times over the course of six months. The
AICPA and NASBA would like to extend our gratitude to the Task Forces – they worked tirelessly
to produce a curriculum that is reective of the practice environment, volunteering dozens of
hours of their time.
The CPA Evolution Model Curriculum is comprised of two main components: (1) detailed content
suggestions split into two parts comprised of three sections each with multiple modules, topics,
and learning objectives and (2) examples of course structuring. This CPA-oriented curriculum
is an example, developed at the request of accounting faculty, to provide insight into how an
accounting program might transition in light of CPA Evolution.
The role of today’s CPA has evolved. Newly licensed CPAs need deeper skill sets, more
competencies and greater knowledge of emerging technologies. That’s why the CPA licensure
model is changing. The CPA Evolution initiative, a joint project between the AICPA and NASBA,
aims to transform the CPA licensure model to recognize the rapidly changing skills and
competencies the practice of accounting requires today and will require in the future. Aspiring
CPAs who are college freshmen today will be among the rst to take the updated version of the
Uniform CPA Examination when it launches in 2024.
Accounting educators will play a vital role in preparing students to pursue the CPA license under
this new model. We developed the CPA Evolution Model Curriculum as one example of how an
accounting program might transition to reect the new Core + Disciplines, CPA licensure model.
When targeting our efforts in developing the curriculum, we elected to focus on a university’s
accounting curriculum that is relevant to preparing future CPAs, except for principles of
accounting courses, which are often built into a university’s business pre-requisite curriculum.
This means that independent of the content recommended through the CPA Evolution Model
Curriculum, it is presumed that students will complete coursework in principles of nancial
accounting and principles of managerial accounting, as well as relevant business courses such
as economics, nance and business law.
Part 1 of this CPA Evolution Model Curriculum covers the content necessary for all future CPAs,
regardless of their chosen discipline and Part 2 covers the content relevant for each of the three
separate disciplines. The CPA Evolution Model Curriculum, however, does not specify whether
content should be covered at an undergraduate or graduate level, as this decision will differ
based on the circumstances of each accounting program. Leveraging feedback from the faculty
on the Task Forces, we have provided suggested courses where the content might be taught as
well as instructional time estimates for each topic, however, these are provided for reference only.
We recognize that the courses chosen and time devoted by a program to present these topics are
entirely at the program’s discretion.

4 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Based on these data points, we believe we have developed a curriculum that is actionable
for faculty at programs of all sizes. For universities able to devote more classroom time, like
those with master’s programs, we’ve provided sucient detail to inform a deeper dive into
each topical area.
The CPA Evolution Model Curriculum is specically designed with future CPAs in mind.
We sought to build a curriculum that provides an accounting student with the skills and
competencies required of a newly licensed CPA to meet the needs of the marketplace and
protect the public interest. It should be viewed as a roadmap for faculty seeking to prepare
future CPAs, not a one-size-ts-all approach to accounting education. Again, when reviewing
recommendations within the CPA Evolution Model Curriculum, each accounting program
should consider its unique circumstances and the needs of employers hiring its students.
We want to thank all the faculty that have provided us feedback on CPA Evolution. Your input
was invaluable as we sought to identify and meet the needs of the academy. We look forward
to continuing to work with the academic community throughout this time of transition.
As we work through the next couple of years in dening the new Exam, developing
academic resources, and preparing students and CPA candidates, we want to hear from
you. Please continue to ask us questions and share your feedback by contacting us at
Feedback@EvolutionofCPA.org.
Sincerely,
Jan Taylor-Morris, CPA, CGMA, Ph.D. Daniel J. Dustin, CPA
Academic-in-Residence, AICPA Vice President — State Board Relations,
NASBA

5 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
FOUNDATION
Business program curriculum
including accounting principles
CORE
Business
analysis and
reporting
Information
systems and
controls
Tax compliance
and planning
Accounting and
data analytics
Auditing and AIS
Tax
CPA Evolution Model Curriculum

6 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Information and Instructions for Use of
CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
The CPA Evolution Model Curriculum is comprised of two parts, each with three sections. The sections are further
divided into modules, topics, and learning objectives.
The topics and learning objectives are presented in tabular format. First, a topical summary is presented with an
estimated range of instruction hours for each topic and the course(s) recommended for delivery of the topic.
Next, the learning objectives relevant to the topic are listed.
Our recommended learning objectives are based on the most recent revisions to Bloom’s Taxonomy of learning. We
recognize that some institutions and faculty may not have adopted or care to implement Bloom’s methodology. We felt
it was important to use a commonly accepted systemic approach to learning objectives, and expect that schools and
faculty may well adapt these recommendations to t their specic institutional and personal professional expectations.
Estimated Hours:
An estimated range of hours are presented, indicating the minimum and maximum hours of instruction recommended
for that topic.
Suggested Course(s):
Suggested courses for each topic are presented as a recommendation by Task Force members. Faculty and programs
should consider their own resources and student needs when choosing where each topic will t best in their programs.
Key to Course Abbreviations:
Abbrev. Course Name
ADA Advanced Data Analytics in Accounting
ADV Advanced Financial Accounting
AMA Advanced Managerial Accounting
AMDA Advanced Managerial Accounting/Data Analytics
AIS Accounting Information Systems
AUD Auditing Principles
DAA Data Analytics in Accounting
EA Emerging Attestation
ECP Entity (Tax) Compliance and Planning
GVT/NFP Government/Not-for-Prot (combined course or separate in one of the two subjects)
ICP Individual (Tax) Compliance and Planning
IMDA Intermediate Managerial Accounting/Data Analytics
INFOSEC Information Security and Forensics
INT Intermediate Accounting 1 or 2 (two courses)
ISAA Information Systems Assurance and Advisory 1 or 2 (two courses)
PFAS Personal Financial Advisory Services
TAX Introduction to Tax for Individuals and Entities
TR Tax Research

7 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
For example, in the illustration shown below, Part 1, Section 1, Module 1, Topic 1, Balance Sheet, is summarized and
an estimate of 3-5 hours is the range of time suggested for delivering this topic and INT (see key on page 6) is the
suggested course. Separate learning objectives for each topic are provided after this summary.
Part I: CPA Evolution Core
Section 1: Accounting and Data Analytics Core
Module 1: Financial statements
Topic 1: Balance sheet
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Dene elements and prepare a for-prot entity’s balance sheet; make needed
adjustments; and perform basic nancial analysis using appropriate technology
(e.g., general ledger software, spreadsheet software/application).
3-5 INT
Learning objective(s):
1. Prepare a classied balance sheet from a trial balance and supporting documentation.
2. Adjust the balance sheet to correct identied errors.
3. Detect, investigate, and correct discrepancies while agreeing the balance sheet amounts to supporting
documentation (see Part I, Section 1, Module 3, Topic 1).
4. Calculate uctuations and ratios and interpret the results while reviewing comparative balance sheets.
Appendix and Other Resources
The Appendix provides a few simple examples of how accounting programs might structure courses to incorporate this
CPA Evolution Model Curriculum.
Many resources are provided by AICPA on the Academic Resource Hub to assist in incorporating new topics or learning
objectives into your existing curriculum.

8 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Part I: CPA Evolution Core
Section 1: Accounting and Data Analytics Core
Module 1: Financial statements
Topic 1: Balance sheet
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Dene elements and prepare a for-prot entity’s balance sheet; make needed
adjustments; and perform basic nancial analysis using appropriate technology
(e.g., general ledger software, spreadsheet software/application).
3-5 INT
Learning objective(s):
1. Prepare a classied balance sheet from a trial balance and supporting documentation.
2. Adjust the balance sheet to correct identied errors.
3. Detect, investigate, and correct discrepancies while agreeing the balance sheet amounts to supporting
documentation (see Part I, Section 1, Module 3, Topic 1).
4. Calculate uctuations and ratios and interpret the results while reviewing comparative balance sheets.
Topic 2: Income statement
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Dene elements and prepare a for-prot entity’s income statement; make
needed adjustments; and perform basic nancial analysis, including Earnings
Per Share (EPS), using appropriate technology (e.g., general ledger software,
spreadsheet software/application).
3-5 INT
Learning objective(s):
1. Prepare the sections of a multiple-step income statement (including operating, nonoperating, discontinued
operations) from a trial balance and supporting documentation.
2. Prepare a single-step income statement from a trial balance and supporting documentation.
3. Adjust the income statement to correct identied errors.
4. Detect, investigate, and correct discrepancies while agreeing the income statement amounts to supporting
documentation (see Part I, Section 1, Module 3, Topic 1).
5. Calculate uctuations and ratios and interpret the results while reviewing comparative income statements.
6. Calculate Earnings Per Share, both basic and fully diluted.

9 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 3: Statements of comprehensive income and changes in equity
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Dene elements of and prepare a statement of comprehensive income and
a statement of changes in equity using appropriate technology (e.g., general
ledger software, spreadsheet software/application).
1-3 INT
Learning objective(s):
1. Recall basic components of other comprehensive income statement.
2. Describe purpose and structure of other comprehensive income statement.
3. Prepare a statement of changes in equity from a trial balance and supporting documentation.
4. Adjust the statement of changes in equity to correct identied errors (see Part I, Section 1, Module 3, Topic 1).
5. Detect, investigate, and correct discrepancies while agreeing the statement of changes in equity amounts to
supporting documentation (see Part I, Section 1, Module 3, Topic 1).
Topic 4: Statement of cash ows
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Prepare a Statement of cash ows under both methods allowed by Generally
Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) and be able to adjust the statement as
needed using appropriate technology (e.g., general ledger software, spreadsheet
software/application), and demonstrate knowledge of individual transactions on
the statement.
3-5 INT
Learning objective(s):
1. Prepare a statement of cash ows using the direct method and required disclosures from supporting documentation.
2. Prepare a statement of cash ows using the indirect method and required disclosures from supporting
documentation.
3. Adjust a statement of cash ows to correct identied errors (see Part 1, Section 1, Module 3, Topic 1).
4. Detect, investigate, and correct discrepancies while agreeing the statement of cash ows amounts to supporting
documentation (see Part I, Section 1, Module 3, Topic 1).
5. Derive the impact of transactions on the statement of cash ows.
Topic 5: Notes to the nancial statements
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Read notes to identify inconsistencies with reported amounts in the nancial
statements and adjust as needed.
1-2 INT
Learning objective(s):
1. Compare the notes to the nancial statements and supporting documentation to identify inconsistencies
and investigate those inconsistencies.
2. Adjust the notes to the nancial statements to correct identied errors and omissions (see Part I, Section 1,
Module 3, Topic 1).

10 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 6: Other
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
List requirements and nancial statements related to for-prot entity nancial
reporting, such as Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) requirements,
and prepare nancial statements using appropriate technology (e.g., general
ledger software, spreadsheet software/application) in accordance with special
purpose frameworks.
5-6 INT
Learning objective(s):
1. List the basic ling requirements (type of ler, type of ling, deadlines for ling) for 10-K, 10-Q and 8-K for publicly
traded companies in the U.S.
2. Recall appropriate nancial statement titles to be used for the nancial statements prepared under a special
purpose framework.
3. Perform calculations to convert cash basis nancial statements to accrual basis nancial statements.
4. Prepare nancial statements using the cash basis of accounting.
5. Prepare nancial statements using a modied cash basis of accounting.
6. Prepare nancial statements using the income tax basis of accounting.
Module 2: Select Financial Statement Accounts
Topic 1: Cash and receivables
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Account for cash, cash equivalents, and trade receivables and allowances
and select and use appropriate technology in calculations, journal entries,
roll-forward schedules, and reconciliations.
3-6 INT
Learning objective(s):
1. Calculate cash and cash equivalents balances to be reported in the nancial statements.
2. Reconcile the cash balance per the bank statement to the general ledger.
3. Investigate unreconciled cash balances to determine whether an adjustment to the general ledger is necessary.
4. Calculate trade receivables and allowances and prepare journal entries.
5. Prepare any required journal entries to record the transfer of trade receivables (secured borrowings, factoring,
assignment, pledging).
6. Prepare a roll-forward of the trade receivables account balance using various sources of information.
7. Reconcile and investigate differences between the subledger and general ledger for trade receivables to determine
whether an adjustment is necessary.

11 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 2: Revenue
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain basics of revenue accounting. Compute and record revenue from a
basic contract.
6-12 INT
Learning objective(s):
1. Recall concepts of accounting for revenue.
2. Determine the amount and timing of revenue to be recognized under a basic contract and prepare journal entries.
Topic 3: Inventory
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Recall basics of inventory accounting and select and use appropriate technology
in calculations, journal entries, roll-forward schedules, and reconciliations.
6-9 INT; IMDA
Learning objective(s):
1. Calculate the carrying amount of inventory and prepare journal entries using various costing methods.
2. Measure impairment losses on inventory.
3. Prepare a roll-forward of the inventory account balance using various sources of information.
4. Reconcile and investigate differences between the subledger and general ledger for inventory to determine
whether an adjustment is necessary.
Topic 4: Property, plant, and equipment
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Account for basic Property, Plant, and Equipment (PPE) transactions and reporting.
Select and use appropriate technology in calculations, journal entries, roll-forward
schedules, and reconciliations.
6-9 INT
Learning objective(s):
1. Calculate the gross and net property, plant, and equipment balances and prepare journal entries.
2. Calculate gains or losses on the disposal of long-lived assets to be recognized in the nancial statements.
3. Measure impairment losses on long-lived assets to be recognized in the nancial statements.
4. Calculate the amounts necessary to prepare journal entries to record a nonmonetary exchange.
5. Determine whether an asset qualies to be reported as held for sale in the nancial statements.
6. Adjust the carrying amount of assets held for sale and calculate the loss to be recognized in the nancial statements.
7. Prepare a roll-forward of the property, plant and equipment account balance using various sources of information.
8. Reconcile and investigate differences between the subledger and general ledger for property, plant, and equipment
to determine whether an adjustment is necessary.
9. Calculate the recorded assets and related liabilities resulting from asset retirement obligations and prepare
journal entries.
10. Calculate the carrying amount of donated assets (nancial assets or long-lived assets) to be reported in the
statement of nancial position.

12 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 5: Intangible assets
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Recall basics of accounting for intangible assets and select and use appropriate
technology in calculations, journal entries, roll-forward schedules, and
reconciliations.
3-6 INT
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify the criteria for recognizing intangible assets in the balance sheet and classify intangible assets
as either nite-lived or indenite-lived.
2. Calculate the carrying amount of nite-lived intangible assets reported in the nancial statements
(initial measurement, amortization, and impairment) and prepare journal entries.
3. Prepare a roll-forward of the nite-lived intangible asset account balance using various sources of information.
Topic 6: Investments
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Classify, measure, account for, and report investments in nancial instruments
using appropriate technology.
3-6 INT
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify investments that are eligible or required to be reported at fair value in the nancial statements.
2. Calculate the carrying amount of investments measured at fair value and prepare journal entries
(excluding impairment).
3. Calculate gains and losses to be recognized in net income or other comprehensive income for investments
measured at fair value and prepare journal entries.
4. Calculate investment income to be recognized in net income for investments measured at fair value and
prepare journal entries.
5. Measure impairment losses to be recognized on applicable investments reported at fair value in the nancial
statements.
6. Identify investments that are eligible to be reported at amortized cost in the nancial statements.
7. Calculate the carrying amount of investments measured at amortized cost and prepare journal entries
(excluding impairment).
8. Measure impairment losses to be recognized on investments reported at amortized cost in the nancial
statements.
9. Identify when the equity method of accounting can be applied to an investment.
10. Calculate the carrying amount of equity method investments and prepare journal entries (excluding impairment).
11. Measure impairment losses to be recognized in the nancial statements on equity method investments.

13 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 7: Current liabilities and other payables
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Compute and report current liabilities, and select and use appropriate technology
in calculations, journal entries, and reconciliations.
3-6 INT
Learning objective(s):
1. Calculate the amount of payables (including accounts payable, dividends payable) and accrued liabilities (including
accrued wages, accrued vacation, accrued bonuses) and prepare journal entries.
2. Reconcile and investigate differences between the subledger and general ledger for accounts payable and accrued
liabilities to determine whether an adjustment is necessary.
3. Identify and calculate liabilities arising from exit or disposal activities and determine the timing of recognition in the
nancial statements.
Topic 8: Long-term debt
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Classify and account for long-term debt throughout the life cycle of the debt,
including basic classication and effects of modications to the original debt
agreement and debt extinguishment. Select and use appropriate technology in
calculations, journal entries, roll-forward schedules, and reconciliations.
3-6 INT
Learning objective(s):
1. Determine the classication of debt.
2. Classify a nancial instrument as either debt or equity, based on its characteristics.
3. Calculate the interest expense attributable to notes and bonds payable reported in the nancial statements
(including discounts, premiums, or debt issuance costs).
4. Calculate the carrying amount of notes and bonds payable and prepare journal entries.
5. Perform debt covenant calculations as stipulated in a debt agreement to ascertain compliance. Focus on using
nal nancial statements to complete calculations to determine current period debt covenant compliance.
6. Classify a change to a debt instrument as either a modication of terms or an extinguishment of debt.
7. Describe when a change to the terms of a debt instrument qualies as a troubled debt restructuring.
8. Determine the implications of a violation of a debt covenant.
Topic 9: Equity
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Prepare journal entries to recognize equity transactions in the nancial statements. 3-4 INT
Learning objective(s):
1. Prepare journal entries to recognize sales of equity interest transactions in the nancial statements.
2. Prepare journal entries to recognize declaration of cash dividends (common and preferred) and stock splits.
3. Prepare journal entries to recognize treasury stock transactions.
4. Prepare journal entries to recognize retirement of equity interests.

14 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 10: Current and deferred income tax expense
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Recall basic concepts of accounting for income taxes and calculate the
amounts to be reported in related specic income tax accounts on the
income statement and balance sheet.
3-5 INT
Learning objective(s):
1. Recall concepts of accounting for income taxes (e.g., temporary differences vs. permanent differences;
valuation allowance accounts).
2. Recall the criteria for recognizing or adjusting a valuation allowance for a deferred tax asset in the nancial
statements.
3. Calculate the income tax expense, current taxes payable/receivable and deferred tax liabilities/assets to be reported
in the nancial statements.
4. Recall the accounting treatment for uncertainty in income taxes.
Module 3: Select Financial Statement Transactions and Events
Topic 1: Accounting changes and error corrections
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
To the extent the underlying subject matter is in Section 1: Accounting and Data
Analytics Core, describe underlying concepts associated with changes and error
corrections and prepare journal entries for those accounting changes in principle
or estimates, and for error corrections.
2-4 INT
Learning objective(s):
1. Describe concepts related to error corrections/prior period adjustments/change in estimates.
2. Calculate a required adjustment to the nancial statements due to an accounting change or error correction and
determine whether it requires prospective or retrospective application.
3. Prepare journal entries to record error corrections, changes in estimates, and prior period adjustments.
4. Derive the impact to the nancial statements and related note disclosures of an accounting change or an
error correction.
Topic 2: Commitments and contingencies
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Recall basics of reporting of commitments and contingencies. 1-2 INT
Learning objective(s):
1. Recall the recognition and disclosure criteria used to identify commitments and contingencies.
2. Calculate contingencies reported and prepare journal entries as needed.
3. Review supporting documentation to determine whether a commitment or contingency requires recognition
or disclosure in the nancial statements.

15 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 3: Lease transactions (lessee)
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Recall criteria for lease classication by lessees, compute amounts, and prepare
journal entries for lessees at the appropriate time.
3-6 INT
Learning objective(s):
1. Recall concepts of accounting for leases including lease classication for lessee.
2. Determine the amount and timing of lease accounting to be recognized under a simple lease contract
and prepare journal entries for lessee.
Topic 4: Subsequent events
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify, calculate, and determine reporting for subsequent events. 1-2 INT; AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify a subsequent event and recall its appropriate accounting treatment.
2. Calculate required adjustments to nancial statements and/or note disclosures based on identied
subsequent events.
3. Derive the impact to the nancial statements and required note disclosures due to identied subsequent events.
Topic 5: Fair value measurements
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify techniques to measure and use concepts and hierarchy for fair value. 1-2 DAA; INT
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify the valuation techniques used to measure fair value.
2. Use the fair value hierarchy to determine the classication of a fair value measurement.
3. Use of accounting estimates in fair value measurements and decision-making.
4. Use the fair value concepts (e.g., highest, and best use, market participant assumptions, unit of account)
to measure the fair value of assets and liabilities.
Topic 6: Foreign currency transactions
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Dene foreign currency transaction concepts and calculate gains or losses from
transactions denominated in foreign currencies.
2-3 INT
Learning objective(s):
1. Calculate transaction gains or losses recognized from monetary transactions denominated in a foreign currency.

16 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Module 4: Financial Statement Analysis and Metrics
Topic 1: Capital structure and working capital
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Compute nancial statement ratios and other metrics using appropriate
technology and interpret the effect of transactions on the metrics.
2-4 INT; IMDA
Learning objective(s):
1. Calculate debt and equity related ratios.
2. Calculate the metrics associated with the working capital components, such as current ratio, quick ratio, cash
conversion cycle, inventory turnover, and receivables turnover.
3. Interpret an effect of a proposed or past transaction on a nancial statement metric.
Topic 2: Budgeting/nancial and nonnancial measures of performance management
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify, calculate, and analyze a variety of measures to assess an entity’s
nancial performance using appropriate technology.
5-7 DAA; IMDA
Learning objective(s):
1. Calculate the difference between budgeted and actual nancial data to determine variances.
2. Calculate nancial and nonnancial measures appropriate to analyze specic aspects of an entity’s performance
(e.g., economic value added, costs of quality-prevention vs. appraisal vs. failure).
3. Determine which nancial and nonnancial measures are appropriate to analyze specic aspects of an entity’s
performance and risk prole (e.g., return on equity, return on assets and contribution margin).
Module 5: Financial Statements and Select Transactions for Not-For-Prot (NFP) Entities
Topic 1: Statement of nancial position
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)**
Recall purpose and objectives and prepare a statement of nancial position for
nongovernmental, NFP, and be able to make necessary adjustments.
2-4 INT; GVT/NFP
Learning objective(s):
1. Recall the purpose and objectives of the statement of nancial position for a nongovernmental, not-for-prot entity.
2. Prepare a statement of nancial position for a nongovernmental, not-for-prot entity from a trial balance and
supporting documentation.
3. Calculate net asset balances for a nongovernmental, not-for-prot entity and prepare journal entries.
4. Adjust the statement of nancial position for a nongovernmental, not-for-prot entity to correct identied errors.

17 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 2: Statement of activities
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)**
Recall purpose and objectives and prepare a statement of activities
for nongovernmental, NFP, and be able to make necessary adjustments.
2-4 INT; GVT/NFP
Learning objective(s):
1. Recall the purpose and objectives of the statement of activities for a nongovernmental, not-for-prot entity.
2. Prepare a statement of activities for a nongovernmental, not-for-prot entity from a trial balance and
supporting documentation.
3. Adjust the statement of activities for a nongovernmental, not-for-prot entity to correct identied errors.
Topic 3: Statement of cash ows
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)**
Recall purpose and objectives and prepare a statement of cash ows
for nongovernmental, NFP, and be able to make necessary adjustments.
2-4 INT; GVT/NFP
Learning objective(s):
1. Recall the purpose and objectives of the statement of cash ows for a nongovernmental, not-for-prot entity.
2. Prepare a statement of cash ows and required disclosures using the indirect method for a nongovernmental,
not-for-prot entity.
3. Adjust the statement of cash ows for a nongovernmental, not-for-prot entity to correct identied errors.
Topic 4: Notes to NFP nancial statements
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)**
Prepare and adjust, as needed, notes to the nancial statements
for nongovernmental, NFP organizations.
0.5-1 INT; GVT/NFP
Learning objective(s):
1. Prepare the notes to the nancial statements of a nongovernmental, not-for-prot entity using
supporting documentation.
2. Adjust the notes to the nancial statements of a nongovernmental, not-for-prot entity to correct identied
errors and omissions.

18 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 5: Select transactions: nonreciprocal transfers
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)**
Recall and identify transfers and promises to give to a nongovernmental,
not-for-prot and be able to calculate effect on net assets.
0.5-1 INT; GVT/NFP
Learning objective(s):
1. Recall the recognition requirements associated with conditional and unconditional promises to give (pledges)
for a nongovernmental, not-for-prot entity.
2. Identify transfers to a nongovernmental, not-for-prot entity acting as an agent or intermediary that are not
recognized as contributions in the statement of activities.
3. Calculate increases in net assets attributable to contributions for a nongovernmental, not-for-prot entity.
** For programs with a GVT/NFP or similar course, these topics would likely be taught in this course. For programs without the GVT/NFP course, depending
on the programs’ objectives, they could elect to add some level of this topic into INT or could decide that this topic could be developed in an internship or other
post-graduation studies/experiences.
Module 6: Financial Statements and Select Transactions for State and Local Governments
Topic 1: State and local government concepts
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Recall the measurement focus and basis of accounting used by state and local
governments for fund and government-wide nancial reporting.
3-4 INT; GVT/NFP
Learning objective(s):
1. Recall authoritative guidance setting body for governmental accounting standards.
2. Recall the types of governmental entities and differentiate the regulation and reporting for each.
3. Recall the measurement focus and basis of accounting used by state and local governments for fund and
government-wide nancial reporting.
4. Determine the appropriate fund(s) that a state or local government should use to record its activities.
19 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Module 7: Critical Thinking
Topic 1: Critical thinking
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify nancial data risks and opportunities using relevant facts to make
appropriate nancial decisions.
2-4 DAA; IMDA
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify how nancial data and nonnancial metrics are linked to the nancial performance and forecasting.
2. Identify nancial opportunities and risks using relevant nancial data and nonnancial metrics.
3. Identify internal and external stakeholders in nancial related decision processes.
4. Identify outcome probabilities and weightings in nancial related decision processes.
5. Recognize potential decision-making biases in nancial related decision processes.
6. Describe alternative questions and answers in nancial related decision processes.
Module 8: Financial Data Analytics
Topic 1: Logical thinking
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Dene main logical thinking concepts related to nancial data analytics. 2-4 DAA; IMDA
Learning objective(s):
1. Dene conditional thinking in nancial data analytics.
2. Identify appropriate conditional logic statements in nancial analysis.
3. Identify what conditions are met in a conditional statement related to nancial analysis.
4. Explain relational concepts (e.g., normalization, integrity, cell referencing) in nancial data.
5. Explain the different types of codes (e.g., relational, functional, object-oriented) related to nancial data.
6. Identify universal code concepts (e.g., loop) in nancial data.
Topic 2: Financial data
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain main components of nancial data and extract-transform-load (ETL)
processes.
5-7 DAA; IMDA
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify basic concepts of nancial data analytics.
2. Explain the dimensions or characteristics of nancial data.
3. Dene the ETL process and principles of ETL as related to nancial data.
4. Dene the goals of the ETL process related to nancial data.
5. Identify methods to cleanse, prepare, and transform structured nancial raw data.
20 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 3: Data mining of structured nancial data
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain main concepts of data mining related to nancial data. 3-6 DAA; IMDA
Learning objective(s):
1. Dene data mining of structured nancial data.
2. Describe correlations, patterns, and anomalies in structured nancial data.
Topic 4: Analysis of nancial data
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Describe data analysis concepts and models. 6-9 DAA; IMDA
Learning objective(s):
1. Describe the analytical maturity model (descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive).
2. Determine and interpret appropriate descriptive analysis, mins, max, means, median, standard deviation, and
distribution shapes.
3. Determine and interpret appropriate diagnostic data analysis, correlations, patterns, and anomalies.
Topic 5: Visualization
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Describe data visualization techniques. 6-9 DAA; IMDA
Learning objective(s):
1. Describe the various types of data relationships.
2. Describe the data visualization techniques used to identify patterns, trends, and correlations.
3. Match the appropriate data visualization method to specic data sets and circumstances.

21 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 6: Communicating accounting data results
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Demonstrate ability to communicate accounting data analysis results. 6-12 DAA; IMDA
Learning objective(s):
1. Demonstrate written communication skills (i.e., memos, emails, social media, reports, disclosures).
2. Demonstrate oral communication skills (i.e., mock interviews, role-playing, presentations).
3. Demonstrate visual communication skills (i.e., interpretation, mind maps, infographics, choosing appropriate
visualizations, design best practices).
4. Demonstrate interpersonal communication skills (i.e., listening, situational awareness, emotional intelligence).
5. Explain key performance indicators (KPIs) on a dashboard.
6. List assumptions used in analysis of data for nancial decisions.
7. Identify targeted audience and scope of analysis.
Topic 7: Data ethics
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Demonstrate awareness of data ethics issues. 3-9 DAA; IMDA
Learning objective(s):
1. Summarize data ownership concepts.
2. Demonstrate awareness of common issues associated with data ownership.
3. Summarize required informed consent, local regulations, and jurisdictions as related to data privacy.
4. Describe various regulatory data privacy frameworks.
5. Identify common pitfalls in data visualization.
6. Dene common data and analysis biases.
7. Dene Articial Intelligence (AI).
8. Describe the role of AI in data analysis and processing.
Module 9: Digital Acumen
Topic 1: Digital acumen
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Demonstrate knowledge of, and the essential ability to respond to change in,
the world of digital tools and technologies.
1-2 DAA; IMDA; INT
Learning objective(s):
1. Recall how to identify prevailing technological trends and anticipate their impact on accounting and
nancial reporting.
2. Recall existing technological trends that are impacting accounting and nancial reporting.
3. Identify common technological applications and their uses when delivering services relative to accounting
and nancial reporting.

22 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Part I: CPA Evolution Core
Section 2: Audit and Accounting Information Systems Core
Module 1: Audit Environment
Topic 1: Nature and scope: audit and other engagements
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify the nature, scope, and objectives of the different types of audit
engagements and identify the factors for consideration in engagements in
another country or within special-purpose framework.
2-4 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify the nature, scope, and objectives of the different types of audit engagements, including issuer and
nonissuer audits.
2. Identify the nature, scope, and objectives of engagements performed in accordance with Government
Accountability Oce Government Auditing Standards (GAGAS).
3. Identify the requirements under GAGAS related to reporting on internal controls over nancial reporting (ICOFR)
and compliance with provisions of the law, regulations, contracts, and grant agreements that have a material effect
on the nancial statements.
4. Identify the factors an auditor should consider when reporting on the audit of nancial statements prepared in
accordance with a special-purpose framework, including cash basis, tax basis, regulatory basis, contractual basis,
or other basis.
Topic 2: Audit-related research
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain basics of audit-related research and identify appropriate
authoritative guidance.
1-3 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Explain the importance of audit-related research and appropriate techniques for conducting it.
2. Identify the appropriate authoritative guidance (e.g., PCAOB AS, AICPA AU-C) and resources for audit research.

23 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 3: AICPA Code of Professional Conduct
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Describe, recognize threat to, and apply the principles, rules, and interpretations
included in the AICPA Code of Professional Conduct.
2-3 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Describe the principles, rules, and interpretations included in the AICPA Code of Professional Conduct.
2. Recognize situations that present threats to compliance with the AICPA Code of Professional Conduct, including
threats to independence.
3. Apply the principles, rules, and interpretations included in the AICPA Code of Professional Conduct to given
situations.
4. Apply the Conceptual Framework for both members in public practice or in business included in the AICPA Code
of Professional Conduct to situations that could present threats to compliance with the rules included in the Code.
5. Apply the Conceptual Framework for Independence included in the AICPA Code of Professional Conduct to
situations that could present threats to compliance with the rules included in the Code.
Topic 4: Other ethical frameworks
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Describe other ethical frameworks which auditors are required to comply with
beyond the AICPA Code of Professional Conduct and apply as needed.
0.5-1 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Describe other ethical frameworks which auditors are required to comply with beyond the Code
(e.g., SEC, GAO, DOL).
2. Recognize threats to compliance with other frameworks.
3. Apply requirements and independence rules of other ethical frameworks to situations that present
threats to compliance.
Topic 5: Licensing
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain the role and authority of state boards of accountancy. 0.5-1 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Explain the role and authority of state boards of accountancy in licensing CPAs.
2. Explain state reciprocity and cross-border practice considerations.

24 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 6: Professional skepticism and professional judgment
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Describe concepts of professional skepticism and professional judgment
and the impediments to exercising both.
1-1.5 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Describe the concepts of professional skepticism and professional judgment.
2. Describe personal bias and other impediments to acting with professional skepticism, such as threats, incentives,
and judgment-making shortcuts.
Module 2: Engagement Planning and Considerations
Topic 1: Pre-engagement activities
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify the preconditions necessary for accepting or retaining a client,
and other engagement terms, conditions, and requirements.
0.5-1 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify the preconditions needed for accepting or continuing an engagement.
2. Identify the factors affecting the acceptance or continuance of an engagement.
3. Perform procedures to conrm that a common understanding of the terms of an engagement exist with
management and those charged with governance.
4. Document the terms of an engagement in a written engagement letter or other suitable form of written agreement.
Topic 2: Requirements for engagement documentation
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain the elements of and requirements for sucient and appropriate
engagement documentation.
0.5-2 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify the elements that comprise sucient appropriate documentation for an engagement.
2. Identify the requirements for the assembly and retention of documentation for an engagement.
3. Prepare documentation that is sucient to enable an experienced auditor having no previous connection with an
engagement to understand and describe the nature, timing, extent, and results of procedures performed and the
signicant ndings and conclusions reached.

25 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 3: Firm quality control system
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Recognize and apply a rm’s internal system of quality control. 0.5-1 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Recognize a CPA rm’s responsibilities for its accounting and auditing practice’s system of quality control.
2. Apply quality control procedures on an engagement.
Topic 4: Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify key provisions of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 related to the
engagement.
1-3 AUD; AIS
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify and dene key corporate governance provisions of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 related to an audit.
2. Identify regulatory deciencies within a client entity by using the requirements associated with the Sarbanes-Oxley
Act of 2002.
Topic 5: Planning the engagement
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain the purpose of an engagement strategy and prepare a plan. 1-2 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Explain the purpose and signicance of the overall engagement strategy for an engagement.
2. Identify additional consideration for an initial audit (predecessor auditor inquiries, opening balances).
3. Prepare a plan for an engagement starting with the prior-year engagement plan or with a template incorporating
known business, economic, standard changes for the current year.
4. Prepare supporting planning related materials (e.g., client assistance request listings, time budgets) for an
engagement plan starting with the prior-year engagement plan or with a template.

26 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 6: Planning for and using the work of others
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify considerations when using the work of others. 0.5-1 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify the factors to consider in determining the extent to which an engagement team can use the work of the
internal audit function, IT auditor, auditor’s specialist, or a component auditor.
Topic 7: Planning communications with the client
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify matters and types of communication needed during planning. 0.5-1 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify the matters related to the planned scope and timing of an engagement that should be communicated to
management and those charged with governance.
2. Identify the types of the presentation materials and supporting schedules for use in communicating the planned
scope and timing of an engagement to management and those charged with governance.
Module 3: Understanding an Entity and its Environment
Topic 1: Understanding an entity and its environment: external factors
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify relevant external factors and explain their impact on the entity’s business. 2-4 AUD; AIS; IMDA
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify the relevant external factors (e.g., industry, regulation, applicable nancial reporting framework and
technology) that impact an entity and/or the inherent risk of material misstatement, and document the procedures
performed to obtain that understanding.
2. Describe the business cycle (trough, expansion, peak, recession) and leading, coincident, and lagging indicators of
economic activity (e.g., bond yields, new housing starts, personal income, and unemployment).
3. Recall the characteristics of market types (e.g., perfect competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, monopoly)
as well as the common competitive strategies in each type.
4. Explain the impact on an entity’s industry and operations due to changes in government scal policies, monetary
policies, regulations, and trade controls.
5. Recognize the impact of market inuences on an entity’s business strategy, operations, and risk (e.g., increasing
investment and nancial leverage, innovating to develop new product offerings, seeking new foreign and domestic
markets, and undertaking productivity or cost-cutting initiatives).
6. Determine the impact of signicant transactions (e.g., business combinations and divestitures, product line
diversication, production sourcing and public and private offerings of securities) on the engagement.

27 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 2: Understanding an entity and its environment: internal factors
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify relevant internal factors and explain their impact on the entity’s risk of
material misstatement.
2-3 AUD; AIS
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify the relevant internal factors that dene the nature of an entity, including the impact on the risk of material
misstatement (e.g., its operations, ownership and governance structure, investment and nancing plans, selection
of accounting policies, objectives, and strategies).
2. Describe the corporate governance structure within an organization (e.g., tone at the top, policies, steering
committees, oversight, and ethics).
Topic 3: Business processes and controls
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify major business processes and related controls. 4-6 AUD; AIS; IMDA
Learning objective(s):
1. Describe the types and purposes of accounting and nancial reporting systems along with the related tools and
software, and the benets they provide to an entity’s business processes.
2. Classify business process controls by type (e.g., preventive vs. detective, automated vs. manual).
3. Identify the sequence of steps and the information, documents, tools, and technology commonly used in key
business processes (e.g., sales, cash collections, purchasing, disbursements, human resources, payroll, production,
treasury, xed assets, general ledger, and reporting).
4. Identify an appropriate mix of business process controls (e.g., segregation of duties, input edit checks, authorization
and approval, verications, physical controls, controls over standing data, spreadsheet controls, reconciliations, and
supervisory controls) to prevent or detect errors in transactions.
5. Identify the structured and unstructured data needed to perform data analytics related to a key business process
and identify the appropriate analytic technique for a given purpose.
6. Perform a walkthrough of a signicant business process and document (e.g., ow charts, process diagrams,
narratives, including interfaces) the ow of relevant transactions and data from initiation through nancial
statement reporting and disclosure.

28 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 4: Enterprise risk management (ERM)
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Dene and apply enterprise risk management (ERM) within the context of the
COSO ERM framework.
2-3 AIS
Learning objective(s):
1. Dene ERM within the context of the COSO ERM framework, including the purpose and objectives of the
framework.
2. Use the COSO ERM framework to identify risk/opportunity scenarios in an entity.
3. Describe the relationship among risk, business strategy and performance within the context of the
COSO ERM framework.
Topic 5: Limitations of controls and risk of management override
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Describe the limitations of internal controls. 1-3 AUD; AIS
Learning objective(s):
1. Describe the limitations of internal controls and the potential impact on the risk of material misstatement of an
entity’s nancial statements.
2. Identify and document the risks associated with management override of internal controls and the potential impact
on the risk of material misstatement of an entity’s nancial statements.
Topic 6: COSO internal control framework
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Dene internal control and apply COSO internal control framework to identify
risks and controls.
3-5 AUD; AIS
Learning objective(s):
1. Dene internal control within the context of the COSO internal control framework, including the purpose, objectives,
and limitations of the framework.
2. Identify and dene the components, principles, and underlying structure of the COSO internal control framework.
3. Apply the COSO internal control framework to identify entity-level risks (inherent and residual) related to an
organization’s compliance, operations, and reporting (internal and external, nancial, and nonnancial) objectives.
4. Apply the COSO internal control framework to identify risks related to fraudulent nancial and nonnancial
reporting, misappropriation of assets and illegal acts, including the risk of management override of controls.
5. Apply the COSO internal control framework to identify controls to meet an entity’s compliance, operations, and
reporting (internal and external, nancial, and nonnancial) objectives at the entity and sub-unit level.
29 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 7: Understanding Systems and Organization Controls (SOC) Reports
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain implications of an entity using a service organization. 3-4 AUD; AIS
Learning objective(s):
1. Explain the differences between SOC 1® and SOC 2® engagements and how SOC engagements are different from
other attestation engagements.
2. Recognize the type and relevance of the report of the examination of controls at a service organization, starting
with a report example.
3. Identify the factors that a user entity and user auditor should consider when evaluating the controls at a service
organization.
Module 4: Information Technology
Topic 1: Understanding of information technology (IT)
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain the role of IT within the organization. 1-3 AUD; AIS
Learning objective(s):
1. Explain the role that IT personnel, processes and strategies play in IT governance and in supporting an entity’s
overall vision, strategy, and business objectives.
2. Identify hardware, software, databases, networks, mobile technology, etc. used by an entity.
3. Describe the advantages, disadvantages, risks, and other considerations associated with cloud computing and IT
outsourcing arrangements, including the use of System and Organization Controls (SOC) for service organizations
reports from third parties.
4. Identify the role and benets of information systems (e.g., enterprise resource planning, e-commerce, and supply
chain management systems).
Topic 2: Understanding an entity’s IT environment
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Describe an entity’s IT environment and its impact on the nancial reporting. 1-3 AUD; AIS
Learning objective(s):
1. Describe an entity’s IT environment (application systems and IT infrastructure database,
operating system, network).
2. Identify implications to risk of outsourced IT environment components.
3. Identify the IT-related signicant business processes and data ows that directly or indirectly impact
an entity’s nancial statements.

30 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 3: Control environment, IT general controls and entity-level controls
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify and document signicant components of entity-level controls, including IT. 1-3 AUD; AIS
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify and document the signicant components of an entity’s control environment (entity-level), including
its IT general controls and application controls.
2. Identify the categories of IT general controls and pervasive impact on nancial reporting.
3. Identify the types of IT application controls and impact on nancial reporting.
4. Describe the testing strategies used in selecting, developing, and implementing new information systems.
5. Recognize effective IT control activities, including manual, IT dependent and automated controls, as well as
preventive, detective, and corrective controls.
Module 5: Risk Assessment of Fraud and Noncompliance
Topic 1: Assessing risks due to fraud and noncompliance
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Assess risks due to fraud, including discussions among the engagement team
about the risk of material misstatement due to fraud or error, and describe the
accountant’s responsibilities with respect to laws and regulations and perform
tests of compliance.
1-3 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Assess risks of material misstatement of an entity’s nancial statements due to fraud or error (e.g., during a
brainstorming session), leveraging the combined knowledge and understanding of the engagement team.
2. Describe the accountant’s responsibilities with respect to laws and regulations that have a direct effect on the
determination of material amounts or disclosures in an entity’s nancial statements for an engagement.
3. Describe the accountant’s responsibilities with respect to laws and regulations that are fundamental to an entity’s
business but do not have a direct effect on the entity’s nancial statements in an engagement.
4. Perform tests of compliance with laws and regulations that have a direct effect on material amounts or disclosures
in an entity’s nancial statements in an engagement.
5. Perform tests of compliance with laws and regulations that are fundamental to an entity’s business, but do not have
a direct effect on the entity’s nancial statements for an engagement.

31 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Module 6: Assessing Risk of Material Misstatement
Topic 1: Impact of risks at the nancial statement level
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify, document, and analyze the impact of risks of material misstatement. 1-2 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify and document the assessed impact of risks of material misstatement at the nancial statement level,
taking into account the effect of relevant controls.
2. Analyze identied risks to detect those that relate to an entity’s nancial statements as a whole (as contrasted to
the relevant assertion level).
Topic 2: Impact of risks for each relevant assertion at the class of transaction, account balance
and disclosure levels
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify, document, and analyze risks and related controls at the relevant
assertion level.
2-4 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify and document risks and related controls at the relevant assertion level for signicant classes of
transactions, account balances, and disclosures in an entity’s nancial statements.
2. Analyze the potential impact of identied risks at the relevant assertion level for signicant classes of transactions,
account balances, and disclosures in an entity’s nancial statements, taking account of the controls the auditor
intends to test.
3. Recognize the potential impact of lower complexity and higher complexity signicant accounting estimates
on the risk of material misstatement, including the indicators of management bias.
Topic 3: Risk associated with IT
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Describe IT-related risks. 1-2 AUD; AIS
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify IT-related risks, including cybersecurity risks, and describe mitigating strategies given risk severity,
probability, and costs.
2. Describe the risks associated with an inadequate change control and change management process for an entity’s
information systems and processes, including acquisition, integration, and outsourcing.

32 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 4: Response to identied risks
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Analyze risk of material misstatement, analyze transactions, and use audit data
analytics outputs to develop audit procedures in response to identied risks.
1-3 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Develop planned audit procedures that are responsive to identied risks of material misstatement due to fraud or
error at the relevant assertion level for signicant classes of transactions and account balances.
2. Analyze the risk of material misstatement, including the potential impact of individual and cumulative
misstatements, to provide a basis for developing planned audit procedures.
3. Analyze transactions that may have a higher risk of material misstatement from audit data analytic outputs (e.g.,
reports and visualizations) by determining relationships among variables and interpreting results to provide a basis
for developing planned audit procedures.
Module 7: Materiality
Topic 1: Materiality for the nancial statements as a whole
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Describe and calculate materiality as it relates to the nancial statements
as a whole.
1-2 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Describe materiality as it relates to the nancial statements as a whole.
2. Calculate materiality for an entity’s nancial statements as a whole.
3. Calculate the materiality level (or levels) to be applied to classes of transactions, account balances, and disclosures
in an audit of an issuer or nonissuer.
Topic 2: Materiality for tolerable misstatement and performance materiality
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Describe and calculate tolerable misstatement. 1-2 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Describe the use of tolerable misstatement or performance materiality in an audit of an issuer or nonissuer.
2. Calculate tolerable misstatement or performance materiality for the purposes of assessing the risk of material
misstatement and determining the nature, timing, and extent of further audit procedures in an audit of an
issuer or nonissuer.

33 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Module 8: Audit Evidence
Topic 1: Tests of controls
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Determine the need for tests of controls on an engagement. 0.5-1 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Based on the nature of the engagement, determine the need for tests of controls in an audit engagement.
Topic 2: Sucient appropriate evidence
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Determine the sources and evaluate whether evidence is sucient and
appropriate given the nature of the audit engagement.
2-4 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Determine the sources of sucient appropriate evidence (e.g., generated from management’s nancial reporting
system, obtained from management specialists, obtained from external sources, or developed by the audit team
from internal or external sources).
2. Identify procedures to validate the completeness and accuracy of data and information obtained from management
(e.g., tying information back to original sources such as general ledger, subledger or external information sources,
validate search or query criteria used to obtain data, etc.).
3. Exercise professional skepticism and professional judgment while analyzing the data and information to be used
as evidence to determine whether it is suciently reliable and corroborates or contradicts the assertions in the
nancial statements and the objectives of the engagement and modify planned procedures accordingly.
4. Evaluate whether sucient appropriate evidence has been obtained to achieve the objectives of the
planned procedures.

34 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Module 9: Audit Procedures
Topic 1: General procedures to obtain sucient appropriate evidence
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Describe and perform general procedures to test controls and to obtain sucient
and appropriate audit evidence to support the auditor’s conclusion.
3-6 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Describe the purpose and application of sampling techniques including the use of automated tools and audit data
analytic techniques to identify signicant events or transactions that may impact the nancial statements.
2. Use sampling techniques to extrapolate the characteristics of a population from a sample of items.
3. Use observation and inspection to obtain evidence.
4. Use recalculation (e.g., manually or using automated tools and techniques) to test the mathematical accuracy of
information to obtain evidence.
5. Use reperformance to independently execute procedures or controls to obtain evidence.
6. Inquire of management and others to gather evidence and document the results.
7. Analyze responses obtained during structured interviews or informal conversations with management and others,
including those in nonnancial roles, and ask relevant and effective follow-up questions to understand their
perspectives and motivations.
Topic 2: Analytical procedures
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Perform analytical procedures. 1-3 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Determine the suitability of substantive analytical procedures to provide evidence to support an identied assertion.
2. Develop an expectation of recorded amounts or ratios when performing analytical procedures and determine
whether the expectation is suciently precise to identify a misstatement in the entity’s nancial statements
or disclosures.
3. Perform analytical procedures during engagement planning.
4. Perform analytical procedures near the end of an audit engagement that assist the auditor when forming an overall
conclusion about whether the nancial statements are consistent with the auditor’s understanding of the entity.
5. Evaluate the reliability of data from which an expectation of recorded amounts or ratios is developed when
performing analytical procedures.
6. Evaluate the signicance of the differences of recorded amounts from expected values when performing
analytical procedures.

35 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 3: External conrmations
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Conduct external conrmations and analyze responses. 1-2 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Conrm signicant account balances and transactions using appropriate tools and techniques (e.g., conrmation
services, electronic conrmations, manual conrmations) to obtain relevant and reliable evidence.
2. Analyze external conrmation responses in the audit of an issuer or nonissuer to determine the need for follow-up
or further investigation.
Topic 4: Audit data analytics
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Describe the use of audit data analytics. 4-6 AUD; AIS
Learning objective(s):
1. Verify the accuracy and completeness of data sets that are used in an engagement to complete planned
procedures.
2. Determine the attributes, structure and sources of data needed to complete audit data analytic procedures.
3. Identify procedures using outputs (e.g., reports and visualizations) from audit data analytic techniques to determine
relationships among variables.
4. Summarize the capabilities needed in tools that support data modeling and analysis.
Module 10: Special Considerations
Topic 1: Accounting estimates
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Perform audit procedures related to accounting estimates. 0.5-1 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Recalculate and reperform procedures to validate the inputs and assumptions of an entity’s signicant accounting
estimates with a higher risk of material misstatement or complexity, such as fair value estimates.
2. Perform procedures (e.g., reviewing the work of a specialist and procedures performed by the engagement team) to
validate an entity’s calculations and detailed support for signicant accounting estimates in an audit of an issuer or
nonissuer, including consideration of information that contradicts assumptions made by management.
3. Evaluate the reasonableness of signicant accounting estimates with a lower risk of material misstatement or
complexity in an audit or an issuer or nonissuer.

36 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 2: Investments in securities
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Perform audit procedures related to investments. 0.5-1 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify the considerations relating to the measurement and disclosure of the fair value of investments in securities
in an audit of an issuer or nonissuer.
2. Test management’s assumptions, conclusions, and adjustments related to the valuation of investments in
securities in an audit of an issuer or nonissuer.
Topic 3: Inventory and inventory held by others
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Perform audit procedures related to inventory. 1-2 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Analyze management’s instructions and procedures for recording and controlling the results of an entity’s physical
inventory counting in an audit of an issuer or nonissuer.
2. Observe the performance of inventory counting procedures, inspect the inventory and perform test counts to verify
the ending inventory quantities in an audit of an issuer or nonissuer.
Topic 4: Litigation, claims, and assessments
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Perform audit procedures related to litigation, claims, and assessments. 0.5-1 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Perform appropriate audit procedures, such as inquiring of management and others, reviewing minutes, and
sending external conrmations, to detect the existence of litigation, claims, and assessments in an audit of an
issuer or nonissuer.
Topic 5: An entity’s ability to continue as a going concern
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify factors impacting entity’s ability to continue as a going concern. 0.5-1 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify factors that should be considered while performing planned procedures that may indicate substantial
doubt about an entity’s ability to continue as a going concern for a reasonable period of time.
2. Consideration of management’s evaluation and reasonableness thereof, and the impact on the audit
(including reporting implications).
37 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 6: Related parties and related party transactions
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Perform related party procedures. 0.5-1 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Perform procedures to identify related party relationships and transactions, including consideration of signicant
unusual transactions and transactions with executive ocers.
Module 11: Audit Conclusion
Topic 1: Misstatements and internal control deciencies
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Determine the effect of identied misstatements. 1-2 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Prepare a summary of corrected and uncorrected misstatements.
2. Determine the effect of uncorrected misstatements on an entity’s nancial statements in an engagement.
3. Determine the effect of identied misstatements on the assessment of internal control over nancial reporting
in an audit of an issuer or nonissuer.
4. Evaluate the signicance of internal control deciencies on the risk of material misstatement of nancial
statements in an audit of an issuer or nonissuer.
Topic 2: Communication of internal control related matters
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify and communicate matters related to deciencies
and material weaknesses.
1-2 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify the matters related to deciencies and material weaknesses in internal control that should be
communicated to those charged with governance and management for an engagement and the timing
of such communications.
2. Prepare written communication of the internal control deciencies and material weaknesses that are required
to be communicated in writing to those charged with governance and management.

38 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 3: Written representations
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify the written representation to be obtained from management. 0.5-1 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify the written representations that should be obtained from management or those charged with governance
in an engagement.
Module 12: Audit Reports
Topic 1: Auditor’s opinion
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify types of opinions and modications. 2-4 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify the factors that an auditor should consider when forming an opinion on an entity’s nancial statements.
2. Identify the type of opinion that an auditor should render on the audit of an issuer or nonissuer’s nancial
statements, including unmodied (or unqualied), qualied, adverse, or disclaimer of opinion.
3. Identify the factors that an auditor should consider when it is necessary to modify the audit opinion on an issuer
or nonissuer’s nancial statements, including when the nancial statements are materially misstated and when the
auditor is unable to obtain sucient appropriate audit evidence.
Topic 2: Auditor’s report over nancial statements
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify and apply the appropriate form, order, and content of an auditor’s report
over the nancial statements.
1-2 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify and apply the appropriate form, order, and content of an auditor’s report for an audit of an issuer
or nonissuer’s nancial statements, including the appropriate use of emphasis-of-matter and other-matter
(i.e., explanatory) paragraphs.
2. Identify the factors that would affect the comparability or consistency of nancial statements, including a change
in accounting principle, the correction of a material misstatement, and a material change in classication.
3. Describe the auditor’s responsibilities related to other information included in documents with audited
nancial statements.
4. Identify the factors an auditor should consider when reporting on supplementary information included in
or accompanying an entity’s nancial statements.

39 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 3: Audit of internal control integrated with an audit of nancial statements
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify and apply the appropriate form, order, and content of an auditor’s report
over internal controls.
1-2 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify the factors that an auditor should consider when forming an opinion on the effectiveness of internal control
in an audit of internal control.
2. Identify and apply the appropriate form, order, and content of a report on the audit of internal control, including
report modications and the use of separate or combined reports for the audit of an entity’s nancial statements
and the audit of internal control.
Module 13: Other Engagements
Topic 1: General standards for attestation reports
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain general standards for attestation reports. 0.25-1 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify the nature, scope, and objectives of attestation engagements and accounting and review
service engagements.
2. Identify the factors that a practitioner should consider when issuing an examination or review report
for an attestation engagement.
Topic 2: Agreed-upon procedures reports
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain factors for consideration in agreed-upon procedures engagement. 0.25-1 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify the factors that a practitioner should consider when issuing an agreed-upon procedures report for an
attestation engagement.

40 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 3: Preparation and compilation engagements
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain factors for consideration in a preparation engagement and in
compilation engagement.
0.25-0.5 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify the factors that an accountant should consider when performing a preparation engagement.
2. Identify the factors that an accountant should consider when reporting on an engagement to compile an
entity’s nancial statements, including the proper form and content of the compilation report.
3. Identify and apply the appropriate form and content for a report for an engagement to compile an entity’s
nancial statements, starting with a report example (e.g., an illustrative report from professional standards).
Topic 4: Review reports
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain factors for consideration in a review engagement. 0.25-0.5 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify the factors that an accountant should consider when reporting on an engagement to review
an entity’s nancial statements, including the proper form and content of the review report.
2. Identify and apply the appropriate form and content for a report for an engagement to review an entity’s
nancial statements, starting with a report example (e.g., an illustrative report from professional standards).
3. Identify the factors an auditor should consider when reporting on an engagement to review interim
nancial information.
Topic 5: Reporting on compliance
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain factors for consideration when reporting on compliance. 0.5-1 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Recall the factors that an auditor should consider when reporting on compliance with aspects of contractual
agreements or regulatory requirements in connection with an audit of an entity’s nancial statements.

41 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Module 14: Subsequent Events and Subsequently Discovered Facts
Topic 1: Subsequent events and subsequently discovered facts
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Perform procedures to identify subsequent events and identify their impact
on the nancial statements and disclosure.
1-2 AUD
Learning objective(s):
1. Recall the impact of subsequently discovered facts on the auditor’s report.
2. Perform procedures to identify subsequent events that should be reected in an entity’s current period nancial
statements and disclosures.
3. Determine whether identied subsequent events are appropriately reected in an entity’s nancial statements
and disclosures.
Module 15: Digital Acumen
Topic 1: Digital acumen
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify technological trends, applications, and their uses in audit and
assurance services.
2-6 AUD; AIS
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify prevailing technological trends and anticipate their impact on audit and assurance.
2. Recall existing technological trends that are impacting audit and assurance.
3. Identify common technological applications and their uses when delivering services relative to audit and assurance.
Topic 2: Application of digital technologies
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Use existing and emerging technologies to perform basic audit and assurance
related tasks and procedures.
9-15 AUD; AIS
Learning objective(s):
1. Use existing and emerging technologies (e.g, computer aided audit tools; robotic process automation; data mining
tools) to perform basic audit and assurance related tasks and procedures
42 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Part I: Core
Section 3: Tax Core
Module 1: Responsibilities in Tax Practice
Topic 1: Internal Revenue Code and regulations related to tax return preparers
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Recall and apply the regulations governing practice before the Internal Revenue
Service (IRS).
3-4 TAX
Learning objective(s):
1. Recall the regulations governing practice before the IRS.
2. Apply the regulations governing practice before the IRS given a specic scenario.
3. Identify tax return preparers.
4. Recognize situations that would result in federal tax return preparer penalties.
5. Apply potential federal tax return preparer penalties given a specic scenario.
6. Explain the responsibilities of the payer vs. the tax preparer and that preparer is responsible for results
of technology usage.
7. Describe the purpose and key elements of the Circular 230 and the Statements on Standards for Tax Services.
Module 2: Methods of Taxation
Topic 1: Methods of taxation
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Describe methods of taxation. 1-2 TAX
Learning objective(s):
1. Distinguish between various types of taxes (income, employment, estate and gift, sales, property, etc.).
2. Recall concepts related to allocation and apportionment of taxable income between states.
Module 3: Federal Tax Procedures
Topic 1: Audits, appeals, and judicial process
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain audits, appeals, and judicial process. 0.5-1 TA X
Learning objective(s):
1. Explain the audit and appeals process as it relates to federal tax matters.
2. Explain the different levels of the judicial process as they relate to federal tax matters.
3. Identify options available to a taxpayer within the audit and appeals process given a specic scenario.
4. Identify options available to a taxpayer within the judicial process given a specic scenario.

43 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 2: Substantiation and disclosure of tax positions
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain importance of substantiation and disclosure of tax positions. 0.5-1 TAX
Learning objective(s):
1. Summarize the requirements for the appropriate disclosure of a federal tax return position.
2. Identify situations in which disclosure of federal tax return positions is required.
3. Identify whether substantiation is sucient given a specic scenario.
4. Recall situations that would result in taxpayer penalties relating to federal tax returns or other
statements/positions taken before the IRS (basics of what is substantial authority and including penalties
for not ling information returns).
Topic 3: Authoritative hierarchy
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain authoritative hierarchy in tax guidance. 0.5-1 TAX
Learning objective(s):
1. Summarize the appropriate hierarchy of authority for federal tax purposes.
2. Dene the importance of tax research and appropriate techniques for conducting tax research in
authoritative literature.
3. Explain the types of primary authority provided by each branch of government and ranking of these authorities.
4. Explain the difference between primary and secondary authority and the relevance to resolving tax issues.
5. Be able to nd primary and secondary authority to resolve basic to intermediate level tax issues.
Module 4: Legal Duties and Responsibilities
Topic 1: Common law duties and liabilities to clients and third parties
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain the tax return preparers’ common law duties and liabilities to clients
and third parties and identify violations.
0.5-1 TAX
Learning objective(s):
1. Summarize the tax return preparers’ common law duties and liabilities to clients and third parties.
2. Identify situations which result in violations of the tax return preparers’ common law duties and liabilities
to clients and third parties.

44 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 2: Privileged communications, condentiality, and privacy acts
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain rules regarding privileged communications, condentiality,
and privacy acts.
1-2 TAX
Learning objective(s):
1. Summarize the rules regarding privileged communications as they relate to tax practice.
2. Identify situations in which communications regarding tax practice are considered privileged.
Module 5: Acquisition and Disposition of Assets
Topic 1: Tax basis of assets
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Calculate tax basis of assets, as well as depreciation and depletion using
current and emerging tax preparer technology. Determine holding periods,
compare tax benets, recall basics of cost recovery, and reconcile balances
in accumulated depreciation.
3-4 TAX
Learning objective(s):
1. Calculate the tax basis of an asset.
2. Develop the basis of assets purchased for use in trade or business which is a routine part of the daily operations of
a business and is an integral part of calculating the depreciation deduction taken on an entity’s tax return (e.g., basis
of property cost with various components, basis of property converted from personal use to revenue-producing
property, basis of multi-unit property).
3. Determine the holding period of a disposed asset for classication of tax gain or loss.
4. Calculate tax depreciation (cost recovery) for tangible business property and tax amortization of intangible assets.
5. Calculate depletion for federal income tax purposes.
6. Compare tax benets of the different expensing options or tax depreciation for federal income tax purposes.
7. Recall the basics of cost recovery and how it differs from depreciation used for GAAP.
8. Reconcile the activity in the beginning and ending accumulated tax depreciation account.

45 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Module 6: Federal Taxation of Individuals
Topic 1: Gross income
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain components of and calculate gross income using appropriate
tax preparer technology.
2-3 TAX
Learning objective(s):
1. Calculate the amounts that should be routinely included in, or excluded from, an individual’s gross income as
reported on federal Form 1040 — U.S. Individual Income Tax Return.
2. Analyze client-provided documentation to determine the appropriate amount of gross income to be reported on
federal Form 1040 — U.S. Individual Income Tax Return.
Topic 2: Reporting of items from pass-through entities
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Describe reporting of items from pass-through entities and report on federal
Form 1040, using appropriate tax preparer technology.
2-3 TAX
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify income, expenses, gains, and losses recognized from pass-through entities, dened as partnership, S
corporations, LLCs, sole proprietorships, and disregarded entities. For example: a) Identify information received
from a partnership (e.g., non-separately stated items, separately stated items, guaranteed payments), b) Identify
information received from an S corporation (e.g., non-separately stated items, separately stated items, taxable
fringe benets), c) Identify information received from a sole proprietorship (i.e., what is reported on schedule C v.
what is reported as an above-the-line adjustment to calculate AGI, self-employment income and tax).
2. Prepare relevant sections of federal Form 1040 — U.S. Individual Income Tax Return based on the information
provided on Schedule K-1.
Topic 3: Adjustments and deductions to arrive at adjusted gross income and taxable income
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Calculate adjustments and deductions to arrive at adjusted gross income
and taxable income using appropriate tax preparer technology.
2-3 TAX
Learning objective(s):
1. Calculate the amount of adjustments and deductions to arrive at adjusted gross income (AGI) and taxable income
(TI) on federal Form 1040 — U.S. Individual Income Tax Return.
2. Analyze client-provided documentation to determine the validity of the deductions taken to arrive at adjusted gross
income (e.g., 50% self-employment tax, deductible IRAs, self-employed individual health insurance) or taxable
income (e.g., mortgage interest, charitable contributions, property taxes, state income taxes) and nondeductible
items (e.g., gambling losses in excess of winnings, credit card interest) on federal Form 1040 — U.S. Individual
Income Tax Return.
3. Recall that a 20% deduction exists for qualied business income deduction (QBI).

46 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 4: Loss limitations
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify and calculate deductible and nondeductible losses by an individual
and possible limitations using appropriate tax preparer technology.
1-2 TAX
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify and/or calculate deductible and nondeductible losses by an individual. For example, determine losses on
sale of investments and Sec. 1211 limitation or losses not allowed (e.g., personal property sales or hobby losses).
2. Identify loss limitations, passive activity loss limitations, and at-risk limitations as it applies to ow-through entities.
Topic 5: Filing status
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Describe ling status types and related concepts. 1-2 TAX
Learning objective(s):
1. Recall taxpayer ling status for federal income tax purposes.
2. Recall relationships meeting the denition of dependent for purposes of determining taxpayer ling status.
3. Identify taxpayer ling status for federal income tax purposes given a specic scenario.
Topic 6: Computation of tax and credits
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Describe and compute tax credits and tax liability for an individual using
appropriate tax preparer technology.
1-2 TAX
Learning objective(s):
1. Recall credits available for use on individual’s Form 1040 and calculation of tax liability. Examples include
refundable tax credits, nonrefundable tax credits, difference between tax credit and tax deduction, tax assessed
other than income tax (net investment income tax), and calculate tax due or tax refund.
2. Recall and dene minimum requirements for individual federal estimated tax payments to avoid penalties.
3. Calculate the tax liability based on an individual’s taxable income for federal income tax purposes.
4. Calculate the impact of the tax deductions and tax credits and their effect on federal Form 1040 — U.S. Individual
Income Tax Return.
5. List the basic elements and explain operation of the foreign tax credit, the child and dependent tax credit, the
earned income credit, and education credits.

47 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 7: Sole proprietorships
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain taxation of sole proprietors. 0.5-1 TAX
Learning objective(s):
1. Explain the basic income and self-employment tax obligations of self-employed individuals.
Module 7: C Corporations
Topic 1: Computations of taxable income, tax liability, and allowable credits
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Calculate taxable income, tax liability, and allowable credits using appropriate
tax preparer technology.
3-4 TAX
Learning objective(s):
1. Calculate taxable income and tax liability for a C corporation.
2. Calculate the credits allowable as a reduction of tax for a C corporation.
3. Calculate the dividend received deduction at different ownership levels.
4. Explain the rationale for a dividend received deduction.
Topic 2: Net operating losses
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain and calculate net operating losses using appropriate tax preparer
technology.
1-2 TAX
Learning objective(s):
1. Calculate the current-year net operating or capital loss of a C corporation.
2. Dene a net operating loss (NOL) and its characteristics.
3. Prepare a net operating and/or capital loss carryforward schedule for a C corporation.
Topic 3: Differences between book and tax income (loss)
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Calculate differences between book and tax income (loss) for an M-1
and M-3 schedules using appropriate tax preparer technology.
2-3 TAX
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify permanent vs. temporary differences to be reported on Schedule M-1 and/or M-3.
2. Calculate the book/tax differences and report them on a Schedule M-1 or M-3.
3. Prepare a schedule M-1 or M-3 for a business entity.
4. Reconcile the differences between book and taxable income (loss) of a business entity.

48 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Module 8: S Corporations
Topic 1: Eligibility and election
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain eligibility requirements for an S corporation election and related concepts. 0.5-1 TAX
Learning objective(s):
1. Recall eligibility requirements/eligible shareholders for an S corporation for federal income tax purposes.
2. Explain the procedures to make a valid S corporation election for federal income tax purposes.
3. Identify situations in which S corporation status would be revoked or terminated for federal income tax purposes.
Topic 2: Determination of ordinary business income (loss) and separately stated items
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify and calculate ordinary business income (loss) and separately stated items
for an S corporation using appropriate tax preparer technology.
3-4 TAX
Learning objective(s):
1. Calculate ordinary business income (loss) and separately stated items for an S corporation for federal income
tax purposes.
2. Identify capital loss/gains, interest income, and dividend income for separate report on Form 1120S/Schedule K-1.
3. Determine what constitutes non-separately stated items of income and expense (e.g., payroll expenses,
sales income).
4. Distinguish book depreciation from accelerated modied accelerated cost recovery system (MACRS) depreciation
from Sec. 179 deductions.
5. Calculate book depreciation and accelerated MACRS depreciation.
6. Identify nondeductible expenses (e.g., governmental penalties, client entertainment).
7. Identify tax-exempt income (e.g., municipal bond interest).
8. Analyze components of S corporation income/deductions to determine classication as ordinary business income
(loss) or separately stated items on federal Form 1120S — U.S. Income Tax Return for an S Corporation.
9. Recall that if an S corporation was previously a C corporation, there is potential for entity-level taxation.
10. Explain the importance of paying reasonable comp to shareholder/employee.
11. Analyze both the accumulated adjustment account and the other adjustments account of an S corporation
for federal income tax purposes.

49 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 3: Basis of shareholder’s interest
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Calculate increases and decreases to shareholder basis and identify their
allocation to S corporation owners using appropriate tax preparer technology.
1-1.5 TAX
Learning objective(s):
1. Calculate increase/decrease to shareholder basis resulting from share of ordinary business income (loss).
2. Calculate increase/decrease to shareholder basis resulting from share of separately stated items.
3. Calculate increase/decrease to shareholder basis resulting from share of nondeductible expenses.
4. Calculate increase/decrease to shareholder basis resulting from share of tax-exempt income.
5. Calculate increase/decrease to shareholder basis resulting from existing debt basis.
6. Identify how income and losses are allocated to owners.
Module 9: Partnerships
Topic 1: Determination of ordinary business income (loss) and separately stated items
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify and calculate ordinary business income (loss) and separately stated
items for a partnership using appropriate tax preparer technology.
1-1.5 TAX
Learning objective(s):
1. Calculate ordinary business income (loss) and separately stated items for a partnership for federal income
tax purposes.
2. Identify capital loss/gains, interest income, and dividend income for separate report on Form 1065/Schedule K-1.
3. Determine what constitutes non-separately stated items of income and expense (e.g., payroll expenses,
sales income).
4. Distinguish book depreciation from accelerated MACRS depreciation from Sec. 179 deductions.
5. Calculate book depreciation and accelerated MACRS depreciation.
6. Identify nondeductible expenses (e.g., governmental penalties, client entertainment).
7. Identify types of tax-exempt income (e.g., municipal bond interest).
8. Analyze components of partnership income/deductions to determine classication as ordinary business income
(loss) or separately stated items on federal Form 1065 — U.S. Return of Partnership Income.

50 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 2: Basis of partner’s interest and basis of assets contributed to the partnership
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Calculate increases and decreases to partner basis and identify their allocation
partners using appropriate tax preparer technology.
1-1.5 TAX
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify how income and losses are allocated to partners.
2. Calculate increase/decrease to partner basis resulting from share of ordinary business income (loss).
3. Calculate increase/decrease to partner basis resulting from share of separately stated items.
4. Calculate increase/decrease to partner basis resulting from share of nondeductible expenses.
5. Calculate increase/decrease to partner basis resulting from share of tax-exempt income.
6. Calculate increase/decrease to partner basis resulting from liabilities incurred through routine business
operations (e.g., accounts payable, accrued expenses, repayment of existing loans).
Module 10: Limited Liability Companies
Topic 1: Limited liability companies
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Describe concepts related to the taxation of limited liability companies. 0.25-0.5 TAX
Learning objective(s):
1. Recall the tax classication options for a limited liability company for federal income tax purposes.
2. Explain the basics of the “check the box” rules.
Module 11: Tax-Exempt Organizations
Topic 1: Tax-exempt organizations
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Recall the different types of tax-exempt organizations and federal reporting
requirements.
1-2 TAX
Learning objective(s):
1. Recall the different types of tax-exempt organizations for federal income tax purposes.
2. Recall federal reporting requirements for tax-exempt organizations (e.g., Form 990).

51 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Module 12: Technology and Digital Acumen
Topic 1: Utilizing technology and data analysis in the tax function
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain the use of technology and data analysis in the tax function beyond
the use of tax preparation software.
1.5-2.5 TAX
Learning objective(s):
1. Combining data sets leveraging technology.
2. Explain where to nd useful, relevant data (i.e., helping a large client with a retail sales tax audit, knowing what
data is relevant and where to nd it), and how to use it to provide helpful insights to the owners of the data.
Topic 2: Digital acumen
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify prevailing technological trends and applications and their impact
on tax compliance and planning.
1-2 TAX
Learning objective(s):
1. Recall how to identify prevailing technological trends and anticipate their impact on tax compliance and planning.
2. Recall existing technological trends that are impacting tax compliance and planning.
3. Identify common technological applications and their uses when delivering services relative to tax compliance
and planning.

52 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Part II: CPA Evolution Discipline
Section 1: Business Analysis and Reporting (BAR) Discipline
Module 1: Accounting Research
Topic 1: Accounting research
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain accounting research and application. 2-5 ADV
Learning objective(s):
1. Explain the importance of accounting research and appropriate techniques for conducting accounting research.
2. Identify the appropriate authoritative guidance (e.g., FASB ASC, PCC) and resources for accounting research.
3. Apply research techniques to resolve basic to intermediate accounting issues.
Module 2: For-Prot Entity Financial Statements
Topic 1: Notes to nancial statements
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Classify and interpret notes to nancial statements and use to make
informed decisions.
1-3 ADV
Learning objective(s):
1. Use the notes from an investor’s perspective to make an informed decision.
2. Identify the impact of the accounting transactions/errors on the notes to the nancial statements.
3. Interpret the interrelationship of accounting transactions/errors to the notes to the nancial statements.
Topic 2: Consolidated nancial statements
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Recall more complex consolidated concepts and terms and prepare a
set of consolidated nancial statements using appropriate technology
(e.g., spreadsheet software/application; general ledger software; ERP applications).
12-18 ADV
Learning objective(s):
1. Recall more complex consolidation concepts and terms (e.g., controlling interest, noncontrolling interest,
primary beneciary, variable interest entity).
2. Prepare consolidation adjustments for a single entity’s consolidation of both wholly- and partially-owned
subsidiaries, with basic intercompany transactions.
3. Prepare consolidated nancial statements for a single entity with one or more subsidiaries, both wholly- and
partially-owned, with basic intercompany transactions.

53 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 3: Public company reporting topics
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Dene elements and prepare required nancial statement note disclosures. 1-3 ADV; INT
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify and interpret public company disclosure requirements (i.e., S-X and S-K).
2. Prepare nancial statement note disclosures for reportable segments.
3. Describe XBRL including its usefulness and use in the U.S.
Topic 4: Emerging reporting frameworks
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Discuss emerging reporting frameworks. 1-3 ADV
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify emerging reporting frameworks including sustainability/integrated reporting.
2. Describe emerging reporting frameworks including sustainability/integrated reporting and their connection
to nancial reporting.
3. Discuss the implications of supply chain management for nancial reporting.
Module 3: Select Financial Statement Accounts
Topic 1: Goodwill and other indenite-lived intangible assets.
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify and calculate goodwill and other indenite-lived intangible assets reported
in the nancial statements and prepare entries. Use appropriate technology
(e.g., general ledger software, spreadsheet software/applications) as applicable.
1-6 ADV; INT
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify impairment indicators for goodwill and other indenite-lived intangible assets.
2. Calculate the carrying amount of goodwill and other indenite-lived intangible assets reported in the nancial
statements (includes initial measurement and impairment) and prepare journal entries.
3. Identify Private Company Council (PCC) alternative for subsequent measurement of goodwill measurement.

54 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 2: Revenue recognition
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify and calculate revenue recognized in the nancial statements using
appropriate technology.
6-9 ADV; INT
Learning objective(s):
1. Interpret agreements, contracts and/or other supporting documentation to determine the amount and timing
of revenue to be recognized in the nancial statements.
2. Calculate revenue to be recognized in the appropriate accounting period.
Topic 3: Stock compensation
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Dene and calculate compensation costs associated with share-based
payment arrangements using appropriate technology.
1-3 ADV; INT
Learning objective(s):
1. Recall concepts associated with share-based payment arrangements (grant date, vesting conditions, inputs to
valuation techniques, valuation models).
2. Calculate compensation costs to be recognized for a share-based payment arrangement classied as equity and
prepare journal entries.
3. Calculate compensation costs to be recognized for a share-based payment arrangement classied as a liability and
prepare journal entries.
Module 4: Select Transactions
Topic 1: Business combinations
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Dene concepts of and prepare journal entries to account for business
combinations using appropriate technology.
3-6 ADV
Learning objective(s):
1. Recall concepts of accounting for business combinations.
2. Prepare journal entries to record the identiable net assets acquired in a business combination that results
in the recognition of goodwill or a bargain purchase gain.
3. Prepare journal entries to record the identiable net assets acquired in a business combination that includes
a noncontrolling interest.
4. Adjust the nancial statements to properly reect changes in contingent consideration related to a
business combination.
5. Calculate the consideration transferred in a business combination.
6. Adjust the nancial statements to properly reect measurement of period adjustments related to a
business combination.

55 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 2: Derivatives and hedge accounting
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify characteristics of derivatives and hedge accounting and prepare
journal entries under hedge accounting for derivative nancial instruments
using appropriate technology.
3-6 ADV
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify the characteristics of a freestanding and/or embedded derivative nancial instrument to be recognized
in the nancial statements.
2. Identify the criteria necessary to qualify for hedge accounting.
3. Prepare journal entries under hedge accounting and for derivative nancial instruments (e.g., swaps,
options, forwards).
4. Identify Private Company Council (PCC) alternative for hedge accounting.
Topic 3: Foreign currency translation
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Dene foreign currency translation concepts and calculate gains or losses
from translation of foreign currencies using appropriate technology.
3-6 ADV
Learning objective(s):
1. Recall the basic functional currency concepts including the indicators to be considered when determining an
entity’s functional currency.
2. Adjust an entity’s nancial statements (remeasure from local currency to functional currency and/or translate
from functional currency to reporting currency) and recognize the effect on equity through net income or other
comprehensive income.
Topic 4: Leases
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Interpret contracts and determine lease accounting as recognized for lessees
and lessors. Use appropriate technology as applicable.
4.5-6 ADV; INT
Learning objective(s):
1. Determine the amount and timing of lease accounting to be recognized under a complex lease contract and
prepare journal entries for lessee.
2. Determine the amount and timing of lease accounting to be recognized under a basic or complex lease contract
and prepare journal entries for lessor.
3. Identify and demonstrate knowledge of all leasing standards for the lessor.
4. Interpret agreements, lease contracts and/or supporting documentation to determine the amount and timing of
leasing arrangement to be recognized in the nancial statements for lessee.
5. Analyze requirements of a lease contract from a lessee standpoint.

56 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 5: Research and development costs
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify and calculate research and development costs using appropriate
technology.
1-3 ADV; INT
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify research and development costs and classify the costs as an expense in the nancial statements.
2. Calculate the research and development costs to be reported as an expense in the nancial statements.
Topic 6: Software costs
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify and calculate capitalized software costs using appropriate technology. 1-3 ADV; INT
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify the criteria necessary to capitalize software costs (software for internal use or sale) in the
nancial statements.
2. Calculate capitalized software costs (software for internal use or sale) to be reported in the nancial
statements and the related amortization expense.
Module 5: Cost Accounting
Topic 1: Cost measurement concepts, methods, and techniques
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify and apply cost accounting concepts and methods. 6-9 AMA; AMDA
Learning objective(s):
1. Apply cost accounting concepts, terminology, methods, and measurement techniques within an entity.
2. Differentiate the characteristics of xed, variable, and mixed costs within an entity.
3. Compare and contrast the different costing methods such as absorption vs. variable and process vs.
job order costing.

57 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 2: Variance analysis
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Determine the appropriate variance analysis method. 3-4 ADA; AMA; AMDA
Learning objective(s):
1. Determine the appropriate variance analysis method to measure the key cost drivers by analyzing business
scenarios.
Module 6: State and Local Governments**
Topic 1: Government-wide nancial statements
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)**
Identify basics of and prepare government-wide nancial statements. 3-9 ADV; GVT/NFP
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify and recall basic concepts and principles associated with government-wide nancial statements
(e.g., required activities, nancial statements, and nancial statement components).
2. Prepare the government-wide statement of net position for a state or local government from trial balances
and supporting documentation.
3. Prepare the government-wide statement of activities for a state or local government from trial balances
and supporting documentation.
4. Recall the disclosure requirements for the notes to the basic nancial statements of state and local governments.
5. Prepare worksheets to convert the governmental fund nancial statements to the governmental activities
reported in the government-wide nancial statements.
6. Prepare the schedule to reconcile the total fund balances and the net change in fund balances reported in
the governmental fund nancial statements to the net position and change in net position reported in the
government-wide nancial statements.

58 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 2: Other types of government nancial statements
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify basics of and prepare government nancial statements, including
proprietary fund nancial statements and duciary fund nancial statements.
3-9 ADV; GVT/NFP
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify and recall basic concepts and principles associated with governmental fund nancial statements
(e.g., required funds, nancial statements, and nancial statement components).
2. Prepare the statement of revenues, expenditures, and changes in fund balances for the governmental funds
of a state or local government from trial balances and supporting documentation.
3. Prepare the balance sheet for the governmental funds of a state or local government from trial balances and
supporting documentation.
4. Identify and recall basic concepts and principles associated with proprietary fund nancial statements
(e.g., required funds, nancial statements, and nancial statement components).
5. Prepare the statement of revenues, expenses, and changes in fund net position for the proprietary funds of
a state or local government from trial balances and supporting documentation.
6. Prepare the statement of net position for the proprietary funds of a state or local government from trial
balances and supporting documentation.
7. Prepare the statement of cash ows for the proprietary funds of a state or local government.
8. Identify and recall basic concepts and principles associated with duciary fund nancial statements
(e.g., required funds, nancial statements, and nancial statement components).
9. Prepare the statement of changes in duciary net position for the duciary funds of a state or local government
from trial balances and supporting documentation.
10. Prepare the statement of net position for the duciary funds of a state or local government from trial balances
and supporting documentation.
Topic 3: Annual comprehensive nancial report elements
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain the objectives and components of an annual comprehensive
nancial report.
2-6 GVT/NFP
Learning objective(s):
1. Recall the objectives and components of management’s discussion and analysis in the comprehensive annual
nancial report for state and local governments.
2. Recall the objectives and components of budgetary comparison reporting in the comprehensive annual nancial
report for state and local governments.
3. Recall the objectives and components of required supplementary information other than management’s discussion
and analysis in the comprehensive annual nancial report for state and local governments.
59 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 4: Financial reporting entity, including blended and discrete component units
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain the criteria for classifying an entity as a component unit. 1-3 GVT/NFP
Learning objective(s):
1. Recall the criteria for classifying an entity as a component unit of a state or local government and the nancial
statement presentation requirements (discrete or blended).
Topic 5: Select governmental concepts
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Calculate and prepare journal entries for net position balances, fund balances,
capital assets, general and propriety long-term liabilities, interfund activity, the
amount of nonexchange revenue and expenditures using both modied accrual
and accrual basis of accounting, and to record budgets and encumbrances.
12-15 GVT/NFP
Learning objective(s):
1. Calculate the net position balances (unrestricted, restricted, and net investment in capital assets) for state and
local governments and prepare journal entries.
2. Calculate the fund balances (assigned, unassigned, nonspendable, committed, and restricted) for state and local
governments and prepare journal entries.
3. Identify capital assets reported in the government-wide nancial statements of state and local governments.
4. Calculate the net general capital assets balance for state and local governments and prepare journal entries
(initial measurement and subsequent depreciation and amortization).
5. Identify general and proprietary long-term liabilities reported in the government-wide nancial statements of state
and local governments.
6. Calculate the total indebtedness to be reported in the government-wide nancial statements of a state or local
government.
7. Calculate the net general long-term debt balance for state and local governments and prepare journal entries
(debt issuance, interest payments, issue premiums or issue discounts).
8. Prepare eliminations of interfund activity in the government-wide nancial statements of state and local governments.
9. Prepare journal entries to recognize interfund activity within state and local governments.
10. Calculate the amount of nonexchange revenue to be recognized by state and local governments using the
modied accrual basis of accounting and prepare journal entries.
11. Calculate the amount of nonexchange revenue to be recognized by state and local governments using the
accrual basis of accounting and prepare journal entries.
12. Calculate expenditures to be recognized under the modied accrual basis of accounting (paid from available
fund nancial resources) for state and local governments and prepare journal entries.
13. Calculate expenses to be recognized under the accrual basis of accounting for state and local governments
and prepare journal entries.
14. Recall and explain the types of budgets used by state and local governments.
15. Prepare journal entries to record budgets (original and nal) of state and local governments.
16. Prepare journal entries to record encumbrances of state and local governments.
** For programs with a dedicated GVT/NFP or similar course, these topics would likely be taught in this course. For programs without the GVT/NFP course,
depending on the programs’ objectives, they could elect to add some level of this topic into ADV or could decide that this topic could be developed in an internship
or other post-graduation studies/experiences.

60 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Module 7: Employee Benet Plan Accounting
Topic 1: Financial statements of employee benet plans
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify and prepare statements for dened contribution employee benet plans. 1-3 ADV
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify the required nancial statements for a dened contribution pension plan.
2. Prepare a statement of changes in net assets available for a dened contribution pension plan.
3. Prepare a statement of net assets available for a dened contribution pension plan.
Module 8: Planning Techniques
Topic 1: Forecasting and projection
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Describe and apply techniques used for forecasting and projection. 3-6 ADA; AMA; AMDA
Learning objective(s):
1. Use forecasting and projection techniques to model revenue growth, cost and expense characteristics,
protability, etc.
2. Prepare and calculate metrics to be utilized in the planning process, such as cost benet analysis, sensitivity
analysis, breakeven analysis, economic order quantity, etc.
3. Analyze results of forecasts and projections using ratio analysis and explanations of correlations to, or variations
from, key nancial indices.
4. Compare and contrast alternative approaches (such as system replacement, make vs. buy and cost/benet)
proposed to address business challenges or opportunities for a given entity.
5. Entity strategies and impact on nancial reporting (i.e., sensitivity analysis, impact of transactions on debt
covenants, etc.).

61 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 2: Financial valuation methods and decision models
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify and dene nancial valuation methods and decision models. 1-6 ADA; AMA; AMDA
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify and dene the different nancial valuation methods and their assumptions, including but not limited to fair
value, Black-Scholes, Capital Asset Pricing Model, and Dividend Discount Model.
2. Identify and dene the different nancial decision models and assumptions involved in making decisions relating to
asset and investment management, debt, equity, and leasing.
3. Identify the sources of data and factors that management considers in forming the assumptions used to prepare
an accounting estimate.
4. Describe the process and framework within which management exercises its responsibilities over the review and
approval of accounting estimates.
5. Calculate the value of an asset using commonly accepted nancial valuation methods.
6. Compare investment alternatives using calculations of nancial metrics (e.g., payback period, net-present value,
economic value added, cash ow analysis, and internal rate of return), nancial modeling, forecasting, projection,
and analysis techniques.
7. Compare options in a lease vs. buy decision scenario.
Module 9: Financial Statement Analysis
Topic 1: Financial statement analysis
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Perform nancial statement analysis to identify and analyze errors. 3-5 ADA; AMA; AMDA
Learning objective(s):
1. Perform nancial statement analysis to interpret and assess the liquidity, solvency, and protability of an entity
over time and in comparison to another entity or peer group.
2. Identify and analyze errors, missing or incomplete information in nancial statements and notes.
3. Describe and analyze the articulation (interrelationship) of the nancial statements and note disclosures.
Topic 2: Financial risk management
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Quantify and mitigate nancial risks in a business entity. 3-6 ADA; AMA; AMDA
Learning objective(s):
1. Calculate and use ratios and measures to quantify risks associated with interest rates, currency exchange,
liquidity, prices, etc., in a business entity.
2. Identify strategies to mitigate nancial risks (e.g., market, interest rate, currency, and liquidity) and quantify their
impact on a business entity.

62 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 3: Working capital
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Describe and analyze working capital components. 1-3 ADA; AMA; AMDA
Learning objective(s):
1. Detect signicant uctuations or variances in the working capital cycle using working capital ratio analyses.
2. Examine an effect of a proposed or past transaction on a metric.
3. Compare inventory management processes, including pricing and valuation methods, to determine the effects on
the working capital of a given entity.
4. Compare accounts payable management techniques, including usage of discounts, factors affecting discount
policy, uses of electronic funds transfer as a payment method, and determination of an optimal vendor payment
schedule in order to determine the effects on the working capital of a given entity.
5. Distinguish between corporate banking arrangements, including establishment of lines of credit, borrowing
capacity, and monitoring of compliance with debt covenants in order to determine the effects on the working
capital of a given entity.
6. Interpret the differences between the business risks and the opportunities in an entity’s credit management
policies to determine the effects on the working capital of a given entity.
7. Analyze the effects on working capital caused by nancing using long-term debt and/or short-term debt.
Module 10: Advanced Data Analytics
Topic 1: Advanced critical thinking
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Evaluate stakeholders’ interests and recommend a course of action by developing
relevant questions, examining bias, calculating probabilities and weightings, and
comparing and engaging alternative and iterative analyses.
2-4 ADA; AMA; AMDA
Learning objective(s):
1. Evaluate various stakeholders’ interests.
2. Recommend a course of action, given a situation.
3. Develop relevant questions.
4. Apply relevant knowledge to question generation.
5. Examine the specic type of bias (i.e., conrmation bias, anchoring).
6. Calculate and analyze outcome probabilities and weightings.
7. Compare alternative analyses.
8. Engage in iterative analyses.
9. Contrast signal and noise.

63 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 2: Advanced logical thinking
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Demonstrate ability to apply logical thinking to interpret and create conditional
statements and apply relational concepts.
4-7 ADA; AMDA
Learning objective(s):
1. Apply relational logic concepts to answer questions.
2. Interpret conditional logic statements.
3. Create a condition statement.
4. Understand alternative accounting information system models, such as the resources, events, and agents (REA)
model, and create the appropriate model.
5. Apply relational concepts.
6. Create program code using proper syntax.
Topic 3: Advanced data concepts
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Demonstrate ability to extract, transform, and load data. 3-5 ADA; AMDA
Learning objective(s):
1. Apply appropriate joins to analyze data.
2. Explain and apply principles of Extract, Transform, and Load (ETL).
3. Design and implement controls used to ensure completeness, accuracy, and validity of data.
4. Extract data from a raw data le.
5. Construct a data set.
6. Apply data cleaning techniques.
7. Apply data transformation techniques.
8. Describe and evaluate relational, dimensional, and big data models.
9. Explain and implement data loading processes.
10. Identify the capabilities needed in tools that support data modeling and analysis.
Topic 4: Advanced data mining
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Apply data mining techniques. 0.5-1 ADA; AMDA
Learning objective(s):
1. Apply data mining techniques to a data set.

64 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 5: Advanced data analysis
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Determine and interpret appropriate predictive and prescriptive analysis. 3-5 ADA; AMDA
Learning objective(s):
1. Determine/interpret appropriate predictive analysis, (e.g., regression, time series, forecasting).
2. Determine/interpret appropriate prescriptive, (e.g., optimization modeling, Monte Carlo simulation).
Topic 6: Advanced data visualization
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain and apply data visualization methods. 4-7 ADA; AMDA
Learning objective(s):
1. Compare and contrast data visualization methods.
2. Apply data visualization methods to specic data sets and circumstances.
3. Create appropriate dashboards and scorecards.
Topic 7: Communicating results on advanced data analytics
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Design and interpret the results of a Key Performance Indicators (KPI) dashboard;
apply what-if analysis to assumptions.
1-3 ADA; AMDA
Learning objective(s):
1. Design a KPI dashboard based on business user roles.
2. Interpret the results of a KPI and provide recommended response.
3. Apply what-if analysis to assumptions.
4. Design analytic with built in controls for completeness, accuracy, and validity.

65 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 8: Advanced data ethics
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify misleading visuals and evaluate data models for appropriate checks
and balances.
1-3 ADA; AMDA
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify and critique a misleading visual.
2. Identify common design principles to avoid misleading visuals.
3. Evaluate data models for appropriate checks and balances.
4. Evaluate the impact of Articial Intelligence (AI) on data analysis and processing.
Topic 9: Advanced data management and relationships
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify considerations associated with loading data into a nal target
database; dene attributes of a data repository; and determine methods
to transform raw data.
1-3 ADA; AMDA
Learning objective(s):
1. Describe considerations associated with loading data into the nal target database (e.g., operational data store,
data warehouse or data lake) including the constraints that apply (e.g., uniqueness, referential integrity, mandatory
elds), the types of loading (initial, incremental, full refresh) and load verication.
2. Dene the attributes of a data repository such as its relevance, elements to be included or excluded, relationships
between those elements and characteristics used to determine its validity, completeness, and accuracy.
3. Determine methods to transform raw data (structured and unstructured) to make it useful for decision-making
by correcting or removing data in the data set that is incorrect, inaccurate, incomplete, improperly formatted or
duplicated and to convert, aggregate, merge, replace, validate, format, and split data.

66 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Part II: CPA Evolution Discipline
Section 2: Information Systems and Controls (ISC) Discipline
Module 1: IT Governance and Risk Assessment
Topic 1: IT governance, strategy and standards
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain information technology (IT) governance and strategy, and awareness of IT
standards.
3-7 ISAA
Learning objective(s):
1. Summarize relevant IT standards.
2. Dene the basics of hardware, software, databases, networks, mobile technology, etc. used by an entity internally,
externally, and through outsourcing arrangements (e.g., application service providers and cloud computing).
3. Summarize relevant IT standards.
Topic 2: Assurance-related research
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain basics of assurance-related research and techniques. 2-3 ISAA
Learning objective(s):
1. Explain the importance of assurance-related research and appropriate techniques for conducting it.
2. Apply research techniques to resolve basic to intermediate assurance-related issues.
Topic 3: Business processes and the design of IT internal controls
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain IT systems, controls, and resources; identify risks to information systems
and the organizational risk appetite.
15-20 ISAA
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify IT systems that are, directly or indirectly, the source of nancial and operational transactions or the data
used for the processes/systems in scope of the engagement (e.g., how the entity uses IT systems to capture, store,
and process information).
2. Identify and document an entity’s relevant IT automated and manual internal controls for applications and data,
within the ow of an entity’s transactions for a signicant business process and consider the effect of these
controls on the completeness, accuracy, and reliability of an entity’s data.
3. Evaluate whether relevant internal controls (automated and manual for applications and data) are effectively
designed and placed in operation.
4. Identify the controls associated with availability.
5. Explain the role and appropriate usage of various IT resources: applications, data, infrastructure, and people.
6. Recall risks inherent to information systems and the organizational risk appetite.

67 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 4: IT risk identication and assessment
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Demonstrate awareness of IT risks and their related business impact. 1-2 ISAA
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify IT-related risks at the entity, application and IT general control level and related business impact
on the layers of security (data/database, application, server/operating system, network/infrastructure).
Topic 5: IT control frameworks
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify IT control frameworks. 2-4 ISAA
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify major IT control frameworks (e.g., Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology (COBIT),
ISO/IEC 17799: Code of Practice for Information Security Management, and Information Technology Infrastructure
Library (ITIL)).
Topic 6: IT general controls (ITGC)
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify IT control activities. 1-2 ISAA
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify effective IT control activities, including manual, IT dependent, and automated controls, as well
as preventive, detective, and corrective controls.
Topic 7: Application controls
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify and evaluate appropriate application controls. 1-2 ISAA
Learning objective(s):
1. Choose appropriate, identify, and make use of specic application controls (e.g., authorization, access, separation
of duties) for a given set of circumstances.
2. Evaluate the results of the appropriate tests of application controls (manual, automated, IT dependent) related to
business processes.
3. Apply special consideration when controls have design or operating effectiveness deciencies or exceptions.

68 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 8: IT change management
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain IT change management risks and processes. 1-2 ISAA
Learning objective(s):
1. Explain the risks associated with an inadequate change control and change management process for an entity’s
information systems and processes, including acquisition, integration, and outsourcing.
2. Identify the design of the appropriate tests of change management controls.
Topic 9: Cybersecurity risk management
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Recognize the basics of cybersecurity and risk management. 6-9 ISAA
Learning objective(s):
1. Recognize key cybersecurity concepts and terms.
2. Recognize common cybersecurity frameworks and standards (e.g., NIST, AICPA Trust Services Criteria).
3. Recall types of tests of cybersecurity testing approaches.
4. Identify threats and risks related to information condentiality and privacy.
Topic 10: System interfaces/ow of data
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Analyze and evaluate the ow of transactions in a system interface diagram
to identify risks.
1-4 ISAA
Learning objective(s):
1. Analyze and evaluate the ow of transactions represented in a narrative, owchart, data diagram, and system
interface diagram to identify the risks in key business processes related to the completeness, accuracy, and
continued processing integrity in input, storage, processing, and output processes.

69 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Module 2: Performing Procedures, Tests of Internal Controls
Topic 1: Logical access controls
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Determine logical access controls and prepare results of appropriate
tests of security.
1-2 ISAA
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify logical and physical access and segregation of duties risks.
2. Explain the design of the appropriate test to evaluate security, logical, and physical access in support of data,
application, operating system, network, and infrastructure.
3. Prepare results of the appropriate tests of security, logical, and physical access in support of data, application,
operating system, network, and infrastructure.
Topic 2: IT change management
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Perform tests and report on the results of change management controls. 0.25-0.5 ISAA
Learning objective(s):
1. Perform tests of the design and operating effectiveness of relevant internal controls (automated and manual
for applications and data).
2. Prepare the results of the appropriate tests of change management controls.
Topic 3: Tests of internal controls related to business processes
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Design appropriate tests of the application controls related to business processes. 4-5 ISAA
Learning objective(s):
1. Design of the appropriate tests of the application controls (manual, automated, IT dependent) related
to business processes.
Topic 4: Sucient appropriate evidence: specic matters that require special consideration
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify additional procedures needed to obtain sucient appropriate evidence
due to data analytic procedures.
3-4 ISAA
Learning objective(s):
1. Interpret results and determine additional procedures to be performed as a result of data analytic procedures
using outputs (e.g., reports and visualizations) from audit data analytic techniques to determine relationships
among variables.

70 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Module 3: SOC Engagements
Topic 1: Basic concepts
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Recognize the basics of SOC engagements and SOC reports. 3-4 ISAA; EA
Learning objective(s):
1. List the types of SOC engagements across industries and types of organizations.
2. Describe intended use and users of SOC reports based on the type of SOC.
3. Recognize applicable attestation standards, guidance (i.e., audit guides and description criteria and trust services
criteria) and associated requirements for SOC.
4. Recall control objectives, trust services criteria, and control activities.
5. Describe management and auditor roles in a SOC engagement.
6. Explain the importance of exercising professional skepticism and professional judgment in the conduct
of a SOC engagement.
7. Recall independence requirements, risk assessment timing, and testing and sampling approach.
Topic 2: SOC engagement: planning
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify scope considerations for the SOC engagement and
complementary controls.
1-2 ISAA; EA
Learning objective(s):
1. Explain scope considerations for the SOC engagement.
2. Describe complementary subservice organization controls and complementary user entity controls.
Topic 3: SOC engagement: performing procedures
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Perform SOC engagement procedures. 2-4 ISAA; EA
Learning objective(s):
1. Perform and evaluate test of control design and operating effectiveness.
2. Document results of tests of control operating effectiveness, and related exceptions.
3. Document completeness and accuracy of populations, samples, and supporting evidence (information provided
by entity).

71 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 4: SOC engagement: reporting
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain SOC reports, considerations, exceptions, and distribution. 2-4 ISAA; EA
Learning objective(s):
1. Compare and contrast the components and types of the SOC reports and management, and service
auditor responsibilities.
2. Recall the service auditor opinions considerations.
3. Communicate effects of exceptions or deviations.
4. Explain the distribution of the nal SOC report.
Module 4: Use and Management of Data
Topic 1: Data governance
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Recognize the basics of a data governance program. 3-5 ISAA; ADA
Learning objective(s):
1. Recognize the legal, ethical, business intellectual property and customer sensitivity considerations that should be
included in a data governance program that covers what data is needed, the necessary practices throughout the
data life cycle, and assignment of responsibility for the governance program.
Topic 2: Data preparation/manipulation
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify basics of data extraction, preparation, and manipulation. 8-12 ISAA; ADA
Learning objective(s):
1. Recall the capabilities needed in data extraction tools and the important considerations in making a data extraction
request such as the data source, format, and integrity of the data.
2. Describe key characteristics of a relational database (e.g., data dictionary, data types, tables, records, elds,
relationships, keys, views, queries, and reports).
3. Explain considerations associated with loading data into the nal target database (e.g., operational data store, data
warehouse or data lake) including the constraints that apply (e.g., uniqueness, referential integrity, mandatory elds),
the types of loading (initial, incremental, full refresh) and load verication.
4. Dene the attributes of a data repository such as its relevance, elements to be included or excluded, relationships
between those elements, and characteristics used to determine its validity, completeness, and accuracy.
5. Determine methods to transform raw data (structured and unstructured) to make it useful for decision-making
by correcting or removing data in the data set that is incorrect, inaccurate, incomplete, improperly formatted, or
duplicated and to convert, aggregate, merge, replace, validate, format, and split data.

72 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Module 5: Information Security and Protection of Information Assets
Topic 1: Information security and privacy frameworks, and standards
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Identify and dene information security and privacy frameworks and their
associated risks.
9-15 ISAA; INFOSEC
Learning objective(s):
1. Recognize sources of common privacy frameworks and guidelines.
2. Recall denitions of the layers of security (data, database, application, server, operating system, network, and/or
infrastructure).
3. Identify the layers of security risks (data, database, application server, operating system network, infrastructure)
associated with protecting sensitive and critical information (e.g., proprietary and personal information)
within information systems (including processing, storing, and transmitting information internally and with
external parties).
4. Identify threats and risks related to availability.
5. Identify the controls associated with protecting sensitive and critical information (e.g., proprietary, and personal;
condentiality and privacy).
6. Determine responses to condentiality, privacy, and availability risks (e.g., incident response plan).
Topic 2: Business resiliency
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Recognize the basics of business resiliency. 0.5-1.25 ISAA; INFOSEC
Learning objective(s):
1. Explain the importance of business resiliency for an entity and the key strategies, resources, business functions,
employees, and steps involved in planning for it.
Topic 3: Business continuity
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Recognize the basics of business continuity. 0.25-1.25 ISAA; INFOSEC
Learning objective(s):
1. Recognize the importance of business continuity and disaster recovery for an entity and the key strategies,
resources, business functions, employees, and steps involved in planning for it.

73 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Part II: CPA Evolution Discipline
Section 3: Tax Compliance and Planning (TCP) Discipline
Module 1: Individual Tax Fundamentals and Tax Planning
Topic 1: Tax planning consideration for gross income, inclusions, and exclusions
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain tax planning consideration for gross income, inclusions, and exclusions. 3-6 ICP
Learning objective(s):
1. Demonstrate knowledge of tax planning as it relates to gross income recognized and reported on an individual’s
Form 1040. Examples of knowledge include a) determine if election to include child’s unearned income on
parent’s return is allowed; b) reporting of distribution from qualied plans; c) after-tax return on investments;
d) timing strategies.
Topic 2: Adjustments and deductions to arrive at adjusted gross income and taxable income
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Tax planning consideration for gross income, inclusions, and exclusions. 3-4.5 ICP
Learning objective(s):
1. Demonstrate knowledge of tax planning as it relates to taxable income. Examples of knowledge include
a) charitable giving consideration when donating property; b) calculation of taxable income using the higher
of itemized deductions or standard deductions; c) timing strategies.
2. Calculate the qualied business income (QBI) deduction for federal income tax purposes.
3. Explain the basics of interest tracing rules and signicance of each categorization of interest and
corresponding limitations.
Topic 3: Passive activity and at-risk loss limitations
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Demonstrate knowledge of passive activity and at-risk loss limitations. 1-3 ICP
Learning objective(s):
1. Demonstrate knowledge of passive activity and at-risk loss limitations. Examples of knowledge include a) passive
activity losses; b) at-risk limitations of both passive and nonpassive activities; c) rental activity losses allowed.
2. Recall passive activities for federal income tax purposes.
3. Calculate net passive activity gains and losses for federal income tax purposes.
4. Prepare a loss carryforward schedule for passive activities for federal income tax purposes.
5. Calculate utilization of suspended losses on the disposition of a passive activity for federal income tax purposes.

74 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 4: Loss limitations
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Calculate and analyze loss limitations. 1-3 ICP
Learning objective(s):
1. Calculate loss limitations for federal income tax purposes for an individual taxpayer.
2. Analyze projections to effectively minimize loss limitations for federal income tax purposes for an
individual taxpayer.
3. Determine the basis and the potential application of at-risk rules that can apply to activities for federal income
tax purposes.
Topic 5: Tax attributes
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain relevance, tracking, and expiration of tax attributes. 1-2 ICP
Learning objective(s):
1. Explain the relevance of tax attributes (i.e., why they matter).
2. Explain tracking and expirations of tax attributes.
Topic 6: Tax planning consideration for computation of tax, estimated taxes, and tax credits
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain tax planning consideration for computation of tax, estimated taxes,
and tax credits.
1-2 ICP
Learning objective(s):
1. Demonstrate knowledge as it relates to the computation of income tax, self-employment tax, estimated tax, and
tax credit for tax planning purposes. Examples of knowledge include nonroutine tasks, such as: a) calculation of
required calculated tax payments for an individual based on projected income; and b) understanding of estimated
tax requirements.

75 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Module 2: Acquisition, Use, and Disposition of Assets
Topic 1: Nontaxable dispositions
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Analyze sale and exchange property transactions and calculate gain for
federal tax purposes.
3-6 ECP
Learning objective(s):
1. Calculate the realized gain, recognized gain, and deferred gain on like-kind property exchange transactions
for federal income tax purposes.
2. Analyze asset sale and exchange transactions to determine whether they are taxable or nontaxable.
3. Identify personal and business property disposition in which there is no recognized gain for tax purposes
(e.g., nonroutine transactions, such as Sec. 1031 like-kind exchanges, exchanges not qualifying under Sec. 1031,
Sec. 1033 involuntary conversions, Sec. 1041 transfer of property from divorce agreement).
Topic 2: Depreciation and amortization
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain concepts related to depreciation and amortization. 1.5-3 ECP
Learning objective(s):
1. Explain how depreciation can affect the tax gain on disposition of depreciable property (Sec. 1245 recapture)
including a building disposed of by a C corporation (Sec. 291 recapture).
2. Explain how intangible assets are amortized (including Sec. 195 start-up expenses and Sec. 248/709 costs).
Topic 3: Amount and character of gains and losses, and netting process
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Calculate the amount of ordinary income, loss, and gain. 1-3 ECP
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify capital assets and Sec. 1231 assets.
2. Calculate the amount of ordinary income and loss for federal income tax purposes.
3. Calculate the amount of gain for federal income tax purposes related to installment sales, Sec. 1231 gains,
Sec. 1244 sale of small business stock, Sec. 1245 recapture, Sec. 1250 unrecaptured gain.
4. Review asset transactions to determine the character (capital vs. ordinary) of the gain or loss for federal
income tax purposes.
5. Analyze an agreement of sale of an asset to determine whether it qualies for installment sale treatment for
federal income tax purposes.

76 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 4: Related party transactions (including imputed interest)
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Describe and calculate tax consequences of related party transactions. 1-3 ICP; ECP
Learning objective(s):
1. Explain the denition of a related party and meaning of direct and indirect ownership.
2. Recall the impact of related party ownership percentages on acquisition and disposition transactions of property
for federal income tax purposes.
3. Compute basis of property purchased from a related party.
4. Determine holding period of property purchased from a related party (as it relates to the sale of the property).
5. Calculate the direct and indirect ownership percentages of corporation stock or partnership interests to determine
whether there are related parties for federal income tax purposes.
6. Calculate a taxpayer’s basis in an asset that was disposed of at a loss to the taxpayer by a related party.
7. Calculate a taxpayer’s gain or loss on a subsequent disposition of an asset to an unrelated third party that was
previously disposed of at a loss to the taxpayer by a related party.
8. Calculate the impact of imputed interest on related party transactions for federal income tax purposes.
Module 3: Tax Accounting Methods
Topic 1: Tax accounting methods
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Describe and evaluate tax accounting methods for different business entities. 1-2 ECP
Learning objective(s):
1. Compute a simple Sec. 481(a) adjustment for an accounting method change.
2. Explain relevance of Sec. 448 and tax shelter status to availability of accounting methods.
3. Identify available inventory methods for small vs. large businesses.
4. Identify tax accounting methods for long-term contracts.

77 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Module 4: Federal Taxation of Entities
Topic 1: Tax planning strategies
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Describe and evaluate tax planning strategies for entities. 1-3 ECP
Learning objective(s):
1. Explain tax considerations in choice of entity for starting or acquiring a business.
2. Evaluate and model tax elections or options under varying fact patterns.
3. Evaluate after-tax investment returns.
Topic 2: Basics of mergers, acquisitions, and divestitures tax planning and structuring
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain basics of mergers, acquisitions, and divestitures tax planning
and structuring.
3-6 ECP
Learning objective(s):
1. Differentiate between taxable and nontaxable acquisitions.
2. Explain the basic tax planning considerations of asset versus stock acquisitions.
3. Explain the basic tax treatment of a spinoff, partial liquidation, and subsidiary liquidation.
Topic 3: Employee and business-owner planning
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Describe the different forms of equity compensation. 1-2 ECP
Learning objective(s):
1. Describe the different forms of equity compensation (basics of Sec. 83 and stock compensation).
Topic 4: Qualied joint venture
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain the tax classication of a qualied joint venture. 1-2 ECP
Learning objective(s):
1. Explain a qualied joint venture and when and why eligible business owner would use this tax classication.

78 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Module 5: C Corporations
Topic 1: Net operating losses (NOL)
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Demonstrate knowledge of NOLs and loss limitations when preparing a tax return. 1-2 ECP
Learning objective(s):
1. Demonstrate knowledge of NOLs and loss limitations when preparing a tax return. Examples include nonroutine
transactions, such as a) prepare a NOL carryforward schedule for a C corporation, b) utilization of an NOL in
a given year.
2. Calculate the maximum allowable charitable contribution deduction and the treatment of excess
charitable contributions.
3. Explain the special charitable contribution rule for accrual basis corporations.
4. Describe the potential Sec. 382 limitation of a corporation’s net operating loss carryover usage due to
ownership changes.
Topic 2: Transactions between a shareholder and the corporation
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Analyze transactions between a shareholder and the corporation, calculate
resulting gains and losses.
3-6 ECP
Learning objective(s):
1. Compute shareholder’s gain on transfer of property (Sec. 351).
2. Distinguish between distribution vs. dividend.
3. Analyze loans from shareholder to corporation or vice versa.
4. Calculate the tax gain (loss) realized and recognized by both the shareholders and the corporation on a contribution
or on a distribution in complete liquidation of a C corporation for federal income tax purposes.
5. Calculate the tax gain (loss) realized and recognized on a nonliquidating distribution by both a C corporation
and its shareholders for federal income tax purposes.
6. Calculate the amount of the cash distributions to shareholders of a C corporation that represents a dividend,
return of capital or capital gain for federal income tax purposes.
7. Dene and measure earnings and prots (E&P).
8. Explain tax complications for not issuing a dividend (i.e., accumulated earnings tax and personal holding
company tax).
9. Explain constructive dividend and the tax implications.

79 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 3: Consolidated tax returns
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Demonstrate knowledge of consolidated return concepts. 3-6 ECP
Learning objective(s):
1. Demonstrate knowledge of consolidated return concepts, such as a) elimination of intercompany transactions,
b) advantages/disadvantages of consolidated returns, c) determine eligibility to le a consolidated return,
and d) limitation rules for consolidated returns (e.g., charitable contributions, capital loss).
2. Explain the basics of what entities can be in a consolidated group and separate return limitation year (SRLY) related
to federal Form 1120 — U.S. Corporation Income Tax Return.
3. Calculate federal taxable income for a consolidated federal Form 1120 — U.S. Corporation Income Tax Return.
Module 6: S Corporations
Topic 1: Basis of shareholder’s interest
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Calculate basis of shareholder’s interest. 1-2 ECP
Learning objective(s):
1. Demonstrate knowledge of shareholder basis for all transactions that fall outside of what would be considered
business operations.
2. Calculate increase to shareholder basis resulting from shareholder contributions (cash or property).
3. Calculate decrease to shareholder basis resulting from distributions to shareholder (cash or property) and
distribution ordering rules.
4. Calculate increase/decrease to shareholder basis resulting from new loans from shareholder to the S corporation.
5. Calculate S corporation’s basis in assets contributed (i.e., carryover of shareholder basis and holding period).
6. Calculate loss limited to shareholder stock and debt basis.
7. Calculate the shareholder’s basis in S corporation stock for federal income tax purposes.
8. Analyze shareholder transactions with an S corporation to determine the impact on the shareholder’s basis for
federal income tax purposes.
9. Calculate corporation’s basis in contributed property.

80 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 2: Entity/owner transactions
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Analyze entity/owner transactions and calculate their tax impact. 1-3 ICP
Learning objective(s):
1. Calculate the allocation of S corporation income (loss) after the sale of a shareholder’s share in the S corporation
for federal income tax purposes.
2. Calculate the realized and recognized gain or loss to the shareholder of property contribution to an S corporation.
3. Analyze the shareholder’s impact of an S corporation’s loss in excess of the shareholder’s basis for federal income
tax purposes.
4. Analyze the federal income tax implication to the shareholders and the S corporation resulting from shareholder
contributions and loans as well as S corporation liquidating and nonliquidating distributions and loans to and
from shareholders.
5. Analyze components of S corporation income/deductions to determine classication as ordinary business income
(loss) or separately stated items on federal Form 1120-S — U.S. Return for an S corporation.
Module 7: Partnerships
Topic 1: Basis of partner’s interest
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Calculate basis of partner’s interest. 1-2 ICP
Learning objective(s):
1. Demonstrate knowledge of partner basis for all transactions that fall outside of what would be considered
business operations.
2. Calculate increase to partner basis resulting from partner contributions (cash or property).
3. Calculate decrease to partner basis resulting from distributions to partner (cash or property).
4. Calculate increase/decrease to partner basis resulting from new loans from partner to the partnership.
5. Distinguish between recourse vs. nonrecourse loans and liabilities.
6. Calculate loss limited to partner stock and debt basis.
7. Calculate the partner’s basis in the partnership for federal income tax purposes.
8. Calculate the partnership’s basis in assets contributed by the partner for federal income tax purposes.
9. Analyze partner contributions to the partnership to determine the impact on the partner’s basis for federal income
tax purposes.

81 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 2: Partnership and partner elections
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Demonstrate basic knowledge of various partnership elections. 1-2 ICP
Learning objective(s):
1. Explain the basics of the special audit rules applicable to partnerships.
2. Demonstrate basic knowledge of various partnership elections (election year, election for adjustment to basis in
partnership property, Sec. 179 deduction election, inventory method election, organizational/start-up cost elections)
and partner elections (discharge of indebtedness election, foreign tax election) and their impact.
Topic 3: Transactions between a partner and the partnership
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Analyze transactions between a partner and the partnership and calculate
their tax impact.
1-5 ICP
Learning objective(s):
1. Demonstrate knowledge of nonroutine transactions between a partner and partnership.
2. Calculate guaranteed payments to partner.
3. Analyze contribution of property (including property with liability assumed by partnership).
4. Calculate nonliquidating distributions of property to partner.
5. Calculate liquidating distributions of property to partner.
6. Calculate gain/loss realized and recognized by partnership on distribution of property.
7. Calculate partner’s basis of property received in a nonliquidating and liquidating distribution.
8. Analyze loans from partner to partnership.
9. Calculate the tax implications of certain transactions between a partner and partnership (such as services
performed by a partner or loans) for federal income tax purposes.
10. Analyze the tax implications of a partner transaction with the partnership (such as services performed
by a partner or loans) to determine the impact on the partner’s tax basis for federal income tax purposes,
treatment of guaranteed payments.
Topic 4: Impact of partnership liabilities on a partner’s interest in a partnership
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain impact of partnership liabilities on a partner’s interest in a partnership. 0.5-3 ICP
Learning objective(s):
1. Recall that general partners have unlimited liability and limited partners can only lose their investment.
2. Calculate the impact of increases and decreases of partnership liabilities on a partner’s basis for federal income
tax purposes.
3. Analyze the impact of partnership liabilities as they relate to the general partners and limited partners for federal
income tax purposes.

82 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 5: Distribution of partnership assets
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Make necessary calculations in distribution of partnership assets. 0.5-2 ICP
Learning objective(s):
1. Calculate the realized and recognized gains (losses) by the partnership and partners of liquidating distributions
from the partnership for federal income tax purposes.
2. Calculate the realized and recognized gains (losses) by the partnership and partners of nonliquidating distributions
from the partnership for federal income tax purposes.
3. Calculate the partner’s basis of partnership assets received in a liquidating distribution for federal income
tax purposes (including basics of hot assets).
4. Calculate the partner’s basis of partnership assets received in a nonliquidating distribution for federal income
tax purposes.
Topic 6: Ownership changes
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Demonstrate knowledge about changes in ownership, termination of partnership,
and prepare relevant calculations.
0.5-2 ICP; ECP
Learning objective(s):
1. Demonstrate knowledge about changes in ownership and termination of partnership.
2. Compute amounts related to a purchase by an individual of a partnership interest from another individual.
3. Calculate allocation of partnership income (loss) in year of ownership transfer.
4. Calculate gain/loss recognized by partner on sale of partnership interest.
5. Recall the situations in which a partnership would be terminated for federal income tax purposes.
6. Calculate the allocation of partnership income (loss) after the sale of a partner’s share in the partnership for
federal income tax purposes.
7. Calculate the revised basis of partnership assets due to a transfer of a partnership interest for federal income
tax purposes.

83 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Module 8: Tax Planning for Entities
Topic 1: Tax treatment of formation and liquidation of business entities
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Describe tax treatment of formation and liquidation of business entities. 3-6 ECP
Learning objective(s):
1. Analyze the tax advantages and disadvantages in the formation of a new business entity (LLCs, all forms of
partnerships, all forms of corporations, and sole proprietorships).
2. Calculate the realized and recognized gain for the owner and entity upon the formation of business entities
for federal income tax purposes.
3. Compare the tax implications of liquidating distributions from different business entities.
4. Calculate the realized and recognized gain for the owner and entity upon the liquidation of business entities
for federal income tax purposes.
5. Analyze tax characteristics to be considered when selecting an entity type.
Topic 2: Tax planning for C corporations
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Describe concepts related to tax planning for a C corporation. 1-3 ICP; ECP
Learning objective(s):
1. Explain planning considerations for contributions of cash versus property in exchange for corporate stock.
2. Analyze tax credit expiration dates in planning.
3. Explain impact of audit ndings.
4. Analyze capital loss carryforward expiration dates in planning.
5. Analyze changes in method of accounting, tax accounting for inventory (Sec. 263A).
6. Explain succession planning.
7. Examine employee/shareholder planning.
Topic 3: Tax planning for S corporations
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Describe concepts related to tax planning for an S corporation. 1-3 ECP
Learning objective(s):
1. Assess planning consideration for distributions and shareholder/employee compensation.
2. Explain succession planning.
3. Examine employee/shareholder planning.
84 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 4: Tax planning for partnerships
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Describe concepts related to tax planning for partnerships. 1-3 ECP
Learning objective(s):
1. Explain guaranteed payment vs. distribution to a partner and the differing tax treatments.
2. Explain planning for use of debt.
3. Explain succession planning.
4. Examine employee/partner planning.
Topic 5: Higher order tasks related to consolidated C corporation returns and income tax provision
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain how tax compliance lings impact nancial statement reporting. 3-6 ECP
Learning objective(s):
1. Explain how tax compliance lings impact nancial statement reporting.
Topic 6: Credits and incentives
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain basic parameters of credits and incentives. 1-2 ECP
Learning objective(s):
1. Explain basic parameters of claiming credits including deadlines, clawbacks, and expiration dates.
Module 9: Trusts
Topic 1: Trusts
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain major tax considerations related to trusts. 1-2 ICP
Learning objective(s):
1. Recall and explain the differences between various types of trusts (simple vs. complex, revocable vs. irrevocable)
for federal income tax purposes.
2. Determine allocation to corpus vs. distribution of the trust income and expenses.
3. Describe the ling requirements.

85 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Module 10: Tax-Exempt Organizations
Topic 1: Tax-exempt organizations
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Describe tax-exempt status and unrelated business income (UBI) concepts. 2-6 ECP
Learning objective(s):
1. Explain when an organization obtains tax-exempt status and how it maintains it.
2. Demonstrate knowledge of factors causing an entity to lose its tax-exempt status.
3. Identify and calculate UBI.
4. Recall UBI reporting requirements.
5. Recognize the difference between Sec. 501(c)(3), (c)(4) and (c)(6) organizations.
6. Recognize the need for public disclosure required for some tax-exempt organizations.
Module 11: Multijurisdictional Tax Basics
Topic 1: Multijurisdictional tax basics
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain basic multijurisdictional tax issues, including consideration of local,
state, and international issues.
3-6 ICP; ECP
Learning objective(s):
1. Dene the general concept and rationale of nexus with respect to multijurisdictional transactions.
2. Dene the general concept and rationale of apportionment and allocation with respect to state and local taxation.
3. Explain the difference between a foreign branch and foreign subsidiary with respect to federal income taxation
to a U.S. company.
4. Explain how different types of foreign income are sourced in calculating the foreign tax credit for federal income
tax purposes.
5. Identify U.S.-sources income for nonresident alien.
6. Recall the basics of Global Intangible Low-Taxed Income (GILTI).
7. Identify situations that would create nexus for multijurisdictional transactions.
8. Explain that taxpayers may have tax obligations in more than one jurisdiction and describe the factors that
play into the tax determination.
9. Recall the apportionment factors (sales, property, and payroll).
10. Calculate the apportionment percentage used in determining state taxable income.
11. Recall mechanisms used to determine where and how income is to be taxed (i.e., tax treaties, nexus,
permanent establishment, withholding regimes).
12. Recall that business presence in various states and multiple jurisdictions can cause income tax and indirect
tax consequences.
13. Explain when Forms 5471, 5472, and 8858s are required.
14. Recall the use of Form 8938 for income tax reporting of special foreign assets.
15. Recall when a taxpayer is required to le Report of Foreign Bank and Financial Accounts (FBAR) with FinCEN of
the Treasury Department and the relationship to the foreign nancial interest question on Form 1040, Schedule B.

86 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Module 12: Technology
Topic 1: Analytical review leveraging data and technology
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain analytical review leveraging data and regulations regarding use
of technology.
0.5-1 ICP; ECP
Learning objective(s):
1. Describe how data analytics can be utilized in tax compliance and planning.
2. Explain the basic requirements under the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) safeguards rule applicable
to tax preparers and basic data security for tax information.
Module 13: Tax Research
Topic 1: Tax research
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain and apply tax research techniques. 2-3 ICP; ECP; TR
Learning objective(s):
1. Explain the importance of tax research and appropriate techniques for conducting it.
2. Apply research techniques to resolve basic to intermediate tax compliance issues.
3. Distinguish primary versus secondary authority in the tax areas and provide examples of each.
4. Explain the hierarchy of federal tax guidance.

87 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Module 14: Personal Financial Advisory Services
Topic 1: Individual tax planning
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Discuss individual tax planning, including tax reduction/management
techniques, timing of income and expenses, tax consequences of various
charitable/philanthropic giving options, and professional standards.
4-6 ICP; PFAS
Learning objective(s):
1. Identify data used to help clients establish their nancial and tax goals.
2. Discuss practices and techniques that will help clients to minimize their tax liability based on various factors,
including the tax return and the potential transactions.
3. Recognize that developing a holistic nancial plan must include the clients full personal and business picture
and their personal goals, including all elements (retirement, investments, business succession, charitable giving,
wealth transfer, education, etc.).
4. Explain the various education plans available for tax planning.
5. Recall that professional standards related to these planning topics are covered in the AICPA Statement on
Standards in Personal Financial Planning Services.
Topic 2: Estate, gift, and trust taxation, compliance, and planning
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Explain concepts related to gift taxation, compliance, and planning. 4-6 ICP; PFAS
Learning objective(s):
1. Recall allowable gift tax deductions and exclusions for federal gift tax purposes (identication of property
transfers subject to gift tax, payments exempt from gift tax).
2. Calculate the amount subject to gift tax and the basis of an asset received as a gift.
3. Identify the basics and signicance of the adequate disclosure requirements.
4. Explain the basics of valuation principles and concept of valuation discounts.
5. Identify key tax credits and what actions are needed to qualify for the credit.
6. Explain basic limitations on using tax credits.
7. Explain basics of how to reduce estate and gift taxes.
8. Identify the inclusion of assets at fair market value in a decedent’s estate tax return.
9. Explain deductions allowed in an estate tax return.
10. Explain the concept of a unied credit for estate and gift tax purposes.
11. Determine a taxpayer’s basis and holding period of an asset received through an inheritance.

88 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Topic 3: Retirement planning
Summary Estimated
Hours
Suggested
course(s)
Describe concepts related to retirement planning. 4-6 ICP; PFAS
Learning objective(s):
1. Describe various retirement vehicles available and how they t into nancial planning.
2. Review limits on and tax consequences of contributions to or distributions from retirement plans.
3. Determine cash requirements to realize retirement goals.
4. Describe planning for post-retirement succession of a closely held business.

89 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Appendix
Illustrative Accounting Program Structures for Future CPAs
In response to requests from members of the accounting academic community, the AICPA and NASBA have developed
three illustrative examples of how an accounting program might be structured to prepare future CPAs.
These examples are meant to aid faculty and administrators seeking to prepare their students for the CPA profession.
Consistent with the rest of the CPA Evolution Model Curriculum, the program structures were developed under the
presumption that students will rst complete certain foundational courses, including a core business curriculum,
principles of nancial accounting, and principles of managerial accounting.
Adoption of one of these illustrative program structures is not a requirement for CPA licensure. When considering
changes to course offerings, faculty and administrators should rst review the objectives of their program and the
educational requirements of their state board of accountancy. Please visit thiswaytocpa.com where additional illustrative
accounting program structures for future CPAs will be added by end of 2021.
Example 1
This illustrative program structure would require each accounting student to complete 18 credit hours of core courses
in addition to a learning track tied to one of three disciplines. With few exceptions, each of the topics throughout
the CPA Evolution Model Curriculum are linked to one of the courses in this illustrative program structure. Schools
adopting this structure may elect to offer one, two or all three learning tracks.
Core
18 credit hours
Disciplines (students choose one track)
Business Analysis
and Reporting
6 credit hours
Information Systems
and Controls
6 credit hours
Tax Compliance
and Planning
6 credit hours
Intermediate Managerial
Accounting/Data
Analytics (IMDA)
Advanced Accounting
(ADV)
Information Systems
Assurance and
Advisory 1 (ISAA)
Individual Compliance
and Planning (ICP)
Intermediate
Accounting 1 (INT)
Advanced Managerial
Accounting/ Data
Analytics (AMDA)
Information Systems
Assurance and
Advisory 2 (ISAA)
Entity Compliance
and Planning (ECP)
Intermediate
Accounting 2 (INT)
Accounting Information
Systems (AIS)
Auditing Principles (AUD)
Introduction to Tax (TAX)

90 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Example 2
Accounting programs with more expansive course offerings (for example, those that offer Master’s of Accountancy
degrees) may elect to require students to complete additional courses relative to their discipline learning track.
Examples of courses those programs may choose to offer appear in this illustrative program structure.
Core
18 credit hours
Disciplines (students choose one track)
Business Analysis
and Reporting
12 credit hours
Information Systems
and Controls
12 credit hours
Tax Compliance
and Planning
12 credit hours
Intermediate Managerial
Accounting/Data
Analytics (IMDA)
Advanced Accounting
(ADV)
Information Systems
Assurance and Advisory
1 (ISAA)
Individual Compliance
and Planning (ICP)
Intermediate
Accounting 1 (INT)
Advanced Data
Analytics (ADA)
Information Systems
Assurance and Advisory
2 (ISAA)
Entity Compliance
and Planning (ECP)
Intermediate
Accounting 2 (INT)
Advanced Managerial
Accounting (AMA)
Emerging Attestation (EA) Personal Financial
Advisory Services (PFAS)
Accounting Information
Systems (AIS)
Governmental and
Not-For-Prot
Accounting (GVT/NFP)
Information Security
and Forensics (INFOSEC)
Tax Research (TR)
Auditing Principles (AUD)
Introduction to Tax (TAX)
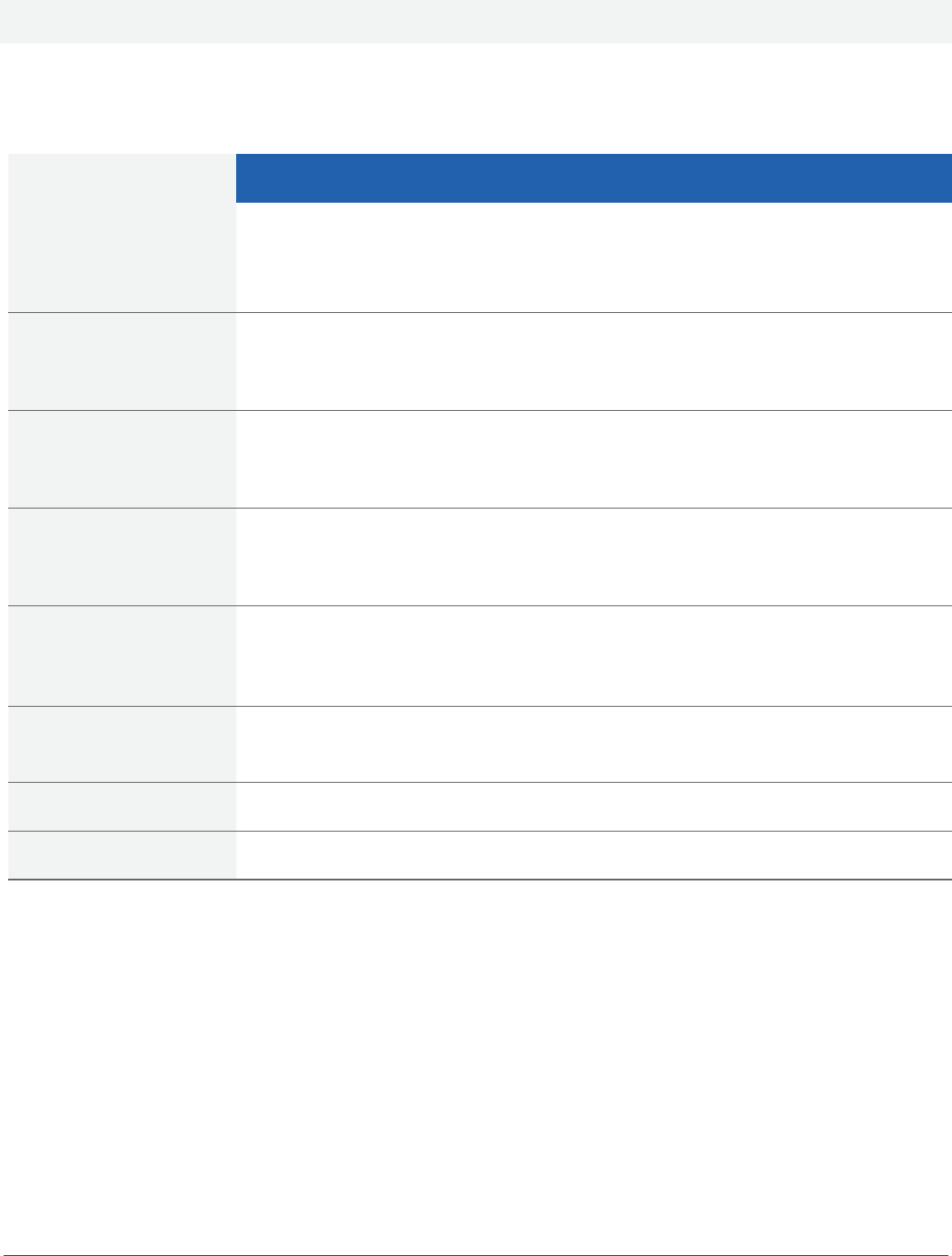
91 CPA Evolution Model Curriculum
Example 3
Accounting programs may choose to offer 21 credit hours of Core coursework and could offer both Intermediate
Managerial Accounting/Data Analytics (IMDA) and a standalone Data Analytics in Accounting (DAA) course. This
example illustrates how a program taking such an approach might be structured.
Core
21 credit hours
Disciplines (students choose one track)
Business Analysis
and Reporting
9 credit hours
Information Systems
and Controls
9 credit hours
Tax Compliance
and Planning
9 credit hours
Data Analytics in
Accounting (DAA)
Advanced Accounting
(ADV)
Information Systems
Assurance and
Advisory 1 (ISAA)
Individual Compliance
and Planning (ICP)
Intermediate Accounting
1 (INT)
Advanced Managerial
Accounting/Data
Analytics (AMDA)
Information Systems
Assurance and
Advisory 2 (ISAA)
Entity Compliance
and Planning (ECP)
Intermediate Accounting
2 (INT)
Governmental and
Not-For-Prot
Accounting (GVT/NFP)
Emerging Attestation (EA) Personal Financial
Advisory Services
(PFAS)
Intermediate Managerial
Accounting/Data
Analytics (IMDA)
Accounting Information
Systems (AIS)
Auditing Principles (AUD)
Introduction to Tax (TAX)

aicpa.org | aicpa.org/academics | nasba.org
Founded by AICPA and CIMA, the Association of International Certied Professional Accountants powers leaders in accounting and nance around the globe.
© 2021 Association of International Certied Professional Accountants. All rights reserved. AICPA and American Institute of CPAs are trademarks of the American Institute of Certied Public Accountants
and are registered in the US, the EU and other countries. The Globe Design is a trademark of the Association of International Certied Professional Accountants and licensed to the AICPA. 2103-57395
Copyright © 2006 – 2021 National Association of State Boards of Accountancy, Inc. All rights reserved.
For information about obtaining permission to use this material other than for personal use, please email mary.walter@aicpa-cima.com.
All other rights are hereby expressly reserved. The information provided in this publication is general and may not apply in a specic
situation. Legal advice should always be sought before taking any legal action based on the information provided. Although the
information provided is believed to be correct as of the publication date, be advised that this is a developing area. The Association,
AICPA, and CIMA cannot accept responsibility for the consequences of its use for other purposes or other contexts.
The information and any opinions expressed in this material do not represent ocial pronouncements of or on behalf of the AICPA,
CIMA, or the Association of International Certied Professional Accountants. This material is offered with the understanding that it
does not constitute legal, accounting, or other professional services or advice. If legal advice or other expert assistance is required, the
services of a competent professional should be sought.
The information contained herein is provided to assist the reader in developing a general understanding of the topics discussed but no
attempt has been made to cover the subjects or issues exhaustively. While every attempt to verify the timeliness and accuracy of
the information herein as of the date of issuance has been made, no guarantee is or can be given regarding the applicability of the
information found within any given set of facts and circumstances.
